132. And February 4 was day 400 (= 370 + 30 ↔ 364 + 36 ↔ 360 + 40 ↔ 354 + 46 ↔ 348 + 52 ↔ 336 + 64 etc): ... In the arabesque of interlaced motifs, one can mark those where the theme of 'pulling down the structure' is in evidence. The powerful Maori hero Whakatau, bent on vengeance, laid hold of the end of the rope which had passed round the posts of the house, and, rushing out, pulled it with all his strength, and straightaway the house fell down, crushing all within it, so that the whole tribe perished, and Whakatau set it on fire. This is familiar. At least one such event comes down dimly from history. It happened to the earliest meetinghouse of the Pythagorean sect, and it is set down as a sober account of the outcome of a political conflict, but the legend of Pythagoras was so artfully constructed in early times out of prefabricated materials that doubt is allowable. The essence of true myth is to masquerade behind seemingly objective and everyday details borrowed from known circumstances. However that may be, in many other stories the destruction of the building is linked with a net. Saxo's Amlethus does not pull down pillars; he reappears at the banquet set by the king for his own supposed funeral, like Great-Land-Master himself. He throws the knotted carpet net prepared by his mother over the drunken crowd and burns down the hall. In Japan the parallel does not go farther than that but it has its own relevance nevertheless. It suggests the fall of the House of Atreus. The net thrown by Clytemnestra over the king struggling in his bath cannot have come in by chance. But this is an uncertain lead as yet. The Sacred Book of the ancient Maya Quiche, the famous Popol Vuh (the Book of Counsel) tells of Zipacna, son of Vucub-Caquix (= Seven Arata). He sees 400 youths dragging a huge log that they want as a ridgepole for their house. Zipacna alone carries the tree without effort to the spot where a hole has been dug for the post to support the ridgepole. The youths, jealous and afraid, try to kill Zipacna by crushing him in the hole, but he escapes and brings down the house on their heads. They are removed to the sky, in a 'group', and the Pleiades are called after them. Then there is a true avanger-of-his-father, the Tuamotuan Tahaki, who, after long travels, arrive in the dark at the house of the goblin band who tortured his father. He conjures upon them 'the immense cold of Havaiki' (the other world) which puts them to sleep. Then Tahaki gathered up the net given to him by Kuhi, and carried it to the door of the long house. He set fire to the house. When the goblin myriads shouted out together 'Where is the door?' Tahaki called out: 'Here is it.' They thought it was one of their own band who had called out, and so they rushed headlong into the net, and Tahaki burned them up in the fire. What the net could be is known from the story of Kaulu. This adventurous hero, wanting to destroy a she-cannibal, first flew up to Makalii the great god, and asked for his nets, the Pleiades and the Hyades, into which he entangled the evil one before he burned down her house. It is clear who was the owner of the nets up there. The Pleiades are in the right hand of Orion on the Farnese Globe, and they used to be called the 'lagobolion' (hare net). The Hyades were for big game ...
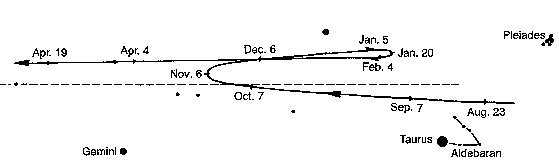
The distance from January 20 to February 4 was 11 + 4 = 15 days, which suggests a structure with half-months. 24h for a full cycle could be perceived as 360 days (º) = 12 times 30, and 24 * 15 = 360.
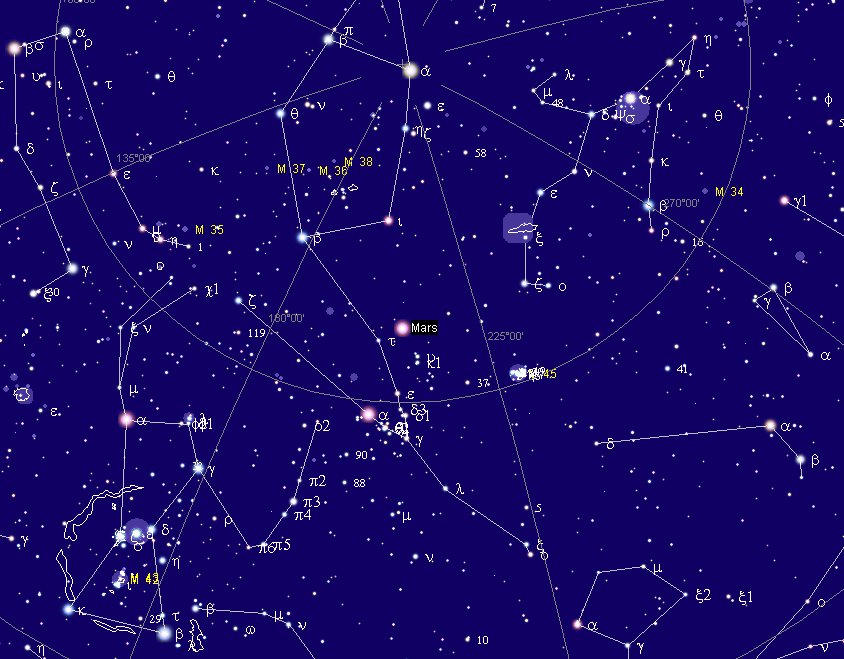
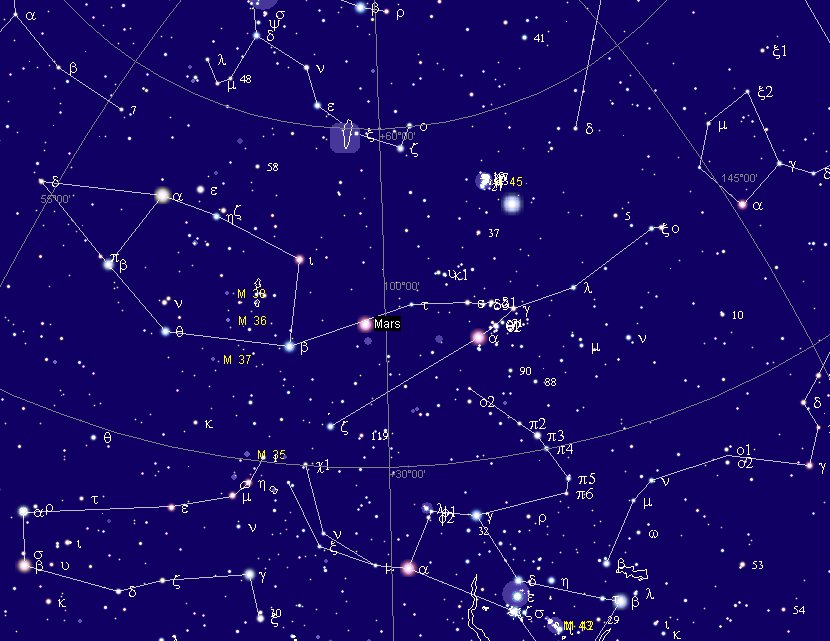
Mars visible in the night of February 4 (400) AD 2023 was at *68 → Aldebaran. And 60 nights earlier - in December 6 - Mars had been at the right ascension line for 5h (*76).
In my old astronomy book it is said that 'Orion was a hunter, loved by Eos':
Dawn (Eos) was evidently at 5h:
Here was the Line of Fire, around (76 + 16) / 365.25 * 26000 = 6549 years ago. AD 1842 + 4707 BC = 6549. ... It should be stated right now that 'fire' is actually a great circle reaching from the North Pole of the celestial sphere to its South Pole ...
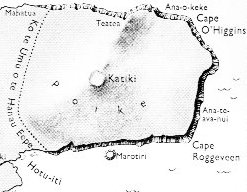
... 'Watch my house. Watch it for the sign that I shall give. On the day after tomorrow the Long-ears are to light the oven for your corpses. Form yourselves into a line, make everybody join in, come there, make a circle round the Long-ears, round their land of Poike. Start killing them. Throw them into the pit, change that oven to your own and cook the Long-ears for yourselves.' Before the dawn that woman went back to her house at Potu te rangi. She said to her people, 'Be quick and do.' Then she went to her house and stayed there, plaiting a basket in the doorway. She was plaiting a basket with her eyes on the Long-ear men. They were filling their oven with firewood. When it was sunset the Short-ears gathered. It was already dark; they gathered, they came; the first men hid in the house of the woman who was plaiting the basket. The rest concealed themselves behind, they formed a line, they waited. The woman who was plaiting told them where the Long-ears were. They were in their houses. Therefore the Short-ears went around Kikiriroa and Mount Teatea. They drew up all in order, they marched in the night, they came down to the point of Mahatua. They remained there, they slept, they hid themselves. And at the first light all those Short-ears rose up, they rushed out with their spears and surprised the Long-ear people, they were all still resting in their houses. They rushed and chased, those Short-ear men, they chased the Long-ears out. They made them all run to the ditch which they had dug themselves. They lit the fires. ... The woman was plaiting a basket, while she was in waiting. Branches from a Weeping Willow (5) serves well for plaiting.
Hiri. 1. To braid, plait, tress (hair, threads). 2. To rise in coils (of smoke). 3. To hover (of birds). Vanaga. 1. To elevate, to mount. Hiriga, to elevate; elevation, mounted, ascension, assumption, declivity; hiriga mouga, hillside. Hirihiri, a swing, seesaw. P. Pau.: iri, to be put up in a place, to lodge. Mgv.: iri, placed in a higher position than the observer, as a box on a high shelf. Ta.: iri, to lodge or stick up in a place. The germ signification is 'above, higher'. In Samoa it is used most commonly in a tropical sense, but the primal sense is sufficiently retained in the signification to lodge, to stick in, to show general concord with Rapanui and particular harmony with the other languages of Southeast Polynesia. 2. To make a bag; taura hiri, to make a cord; rauoho hiri, plaited hair; hirihiri, frizzed; rauoho hirihiri, lock of hair. P Mgv.: hiri, to weave, to plait; akahiri, to make a mat. Mq.: hii, large plait of coconut fiber. Ta.: firi, to plait, to braid. When we interpret in the sense of local conditions Père Roussel's definition 'to make a bag' the concord is perfect, for bags are woven. The germ sense is plainly the act of twining in and out, over and under, which, with specific differences due to manner and material, may result in plaiting or weaving; see hiro. 3. To go, to walk, to voyage, to arrive, to appear; hiri tê reka, to go without noise; hiri koroiti, to go softly; hiri tahaga no mai, to go without a halt. Hiriga, voyage, journey; hiriga hakapa, to go by twos; hiriga hipa, to go obliquely; hiriga kokekoke, to go by sudden steps; hiriga okorua, to go by twos; hiriga tahataha to go across; hiriga tekiteki, to go on hopping; hiriga tê mataku, to go on fearlessly; hiriga totoro, to go on all fours; hiriga varikapau; to go in a ring; hiriga veveveve, to go boldly. Churchill. Pau.: Hirinaki. 1. To incline, to slope. Ta.: hirinai, to rest upon. Ma.: irinaki, to rest upon. 2. To be apprehensive. Ta.: hirinai, to apprehend. Churchill. Mgv.: Aka-hiria, to enquire after. Sa.: sili, to ask, to demand. Hirihiri, to fish for turtle. Mq.: fiifiii, a small net for taking turtle. Churchill. Hiro. 1. A deity invoked when praying for rain (meaning uncertain). 2. To twine tree fibres (hauhau, mahute) into strings or ropes. Ohirohiro, waterspout (more exactly pú ohirohiro), a column of water which rises spinning on itself. Vanaga. To spin, to twist. P Mgv.: hiro, iro, to make a cord or line in the native manner by twisting on the thigh. Mq.: fió, hió, to spin, to twist, to twine. Ta.: hiro, to twist. This differs essentially from the in-and-out movement involved in hiri 2, for here the movement is that of rolling on the axis of length, the result is that of spinning. Starting with the coir fiber, the first operation is to roll (hiro) by the palm of the hand upon the thigh, which lies coveniently exposed in the crosslegged sedentary posture, two or three threads into a cord; next to plait (hiri) three or other odd number of such cords into sennit. Hirohiro, to mix, to blend, to dissolve, to infuse, to inject, to season, to streak with several colors; hirohiro ei paatai, to salt. Hirohiroa, to mingle; hirohiroa ei vai, diluted with water. Churchill. Ta.: Hiro, to exaggerate. Ha.: hilohilo, to lengthen a speech by mentioning little circumstances, to make nice oratorial language. Churchill. Whiro 'Steals-off-and-hides'; also [in addition to the name of Mercury] the universal name for the 'dark of the Moon' or the first day of the lunar month; also the deity of sneak thieves and rascals. Makemson.
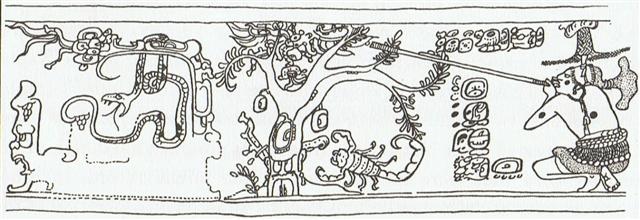
Adding 5 intercalated days for Nut → February 4 (40) + 5 = 45 (February 9): ... On February 9 the Chorti Ah K'in, 'diviners', begin the agricultural year. Both the 260-day cycle and the solar year are used in setting dates for religious and agricultural ceremonies, especially when those rituals fall at the same time in both calendars. The ceremony begins when the diviners go to a sacred spring where they choose five stones with the proper shape and color. These stones will mark the five positions of the sacred cosmogram created by the ritual. When the stones are brought back to the ceremonial house, two diviners start the ritual by placing the stones on a table in a careful pattern that reproduces the schematic of the universe. At the same time, helpers under the table replace last year's diagram with the new one. They believe that by placing the cosmic diagram under the base of God at the center of the world they demonstrate that God dominates the universe. The priests place the stones in a very particular order. First the stone that corresponds to the sun in the eastern, sunrise position of summer solstice is set down; then the stone corresponding to the western, sunset position of the same solstice. This is followed by stones representing the western, sunset position of the winter solstice, then its eastern, sunrise position. Together these four stones form a square. They sit at the four corners of the square just as we saw in the Creation story from the Classic period and in the Popol Vuh. Finally, the center stone is placed to form the ancient five-point sign modern researchers called the quincunx ...
... What happens after (or happened, or will happen sometime, for this myth is written in the future tense), is told in the Völuspa, but it is also amplified in Snorri's Gylfaginning (53), a tale of a strange encounter of King Gylfi with the Aesir themselves, disguised as men, who do not reveal their identity but are willing to answer questions: 'What happens when the whole world has burned up, the gods are dead, and all of mankind is gone? You have said earlier, that each human being would go on living in this or that world.' So it is, goes the answer, there are several worlds for the good and the bad. Then Gylfi asks: 'Shall any gods be alive, and shall there be something of earth and heaven?' And the answer is: 'The earth rises up from the sea again, and is green and beautiful and things grow without sowing. Vidar and Vali are alive, for neither the sea nor the flames of Surt have hurt them and they dwell on the Eddyfield, where once stood Asgard. There come also the sons of Thor, Modi and Magni, and bring along his hammer. There come also Balder and Hoder from the other world. All sit down and converse together. They rehearse their runes and talk of events of old days. Then they find in the grass the golden tablets that the Aesir once played with ...
I notice that my ΣΣ chapter numbered 53 as if by coincidence is like 53 in Snorri's Gylfaginning. And we will remember the Chorti diviners would later on by using sympathetic magic ... While religious systems differ not only in different countries, but in the same country in different ages, the system of sympathetic magic remains everywhere and at all times substantially alike in its principles and practice ... raise high the sky dome of the new cosmos: ... Later on in this series of rituals, the Chorti go through a ceremony they call raising the sky. This ritual takes place at midnight on the twenty-fifth of April and continues each night until the rains arrive. In this ceremony two diviners and their wives sit on benches so that they occupy the corner positions of the cosmic square. They take their seats in the same order as the stones were placed, with the men on the eastern side and the women on the west. The ritual actions of sitting down and lifting upward are done with great precision and care, because they are directly related to the actions done by the gods at Creation. The people represent the gods of the four corners and the clouds that cover the earth. As they rise from their seats, they metaphorically lift the sky. If their lifting motion is uneven, the rains will be irregular and harmful ...
Perhaps the ancient cosmogram with a 5th stone in the center (the quincunx) was abandoned in favour of a cosmogram with only 4 stones - because Sirius moved with the Sun, i.e. was a rolling (living) stone, and could not be fixed in the star cosmogram.
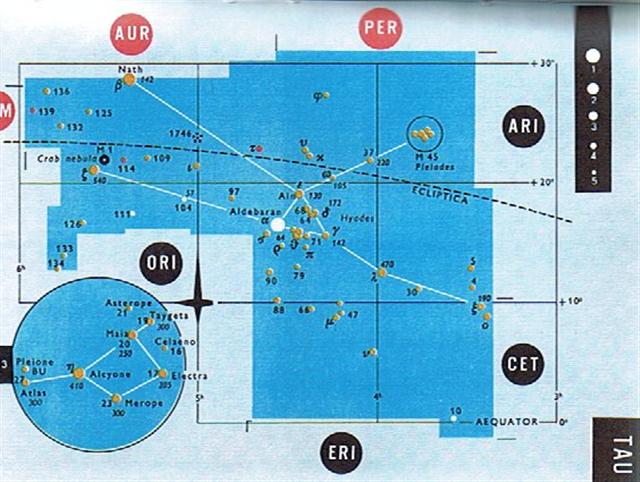
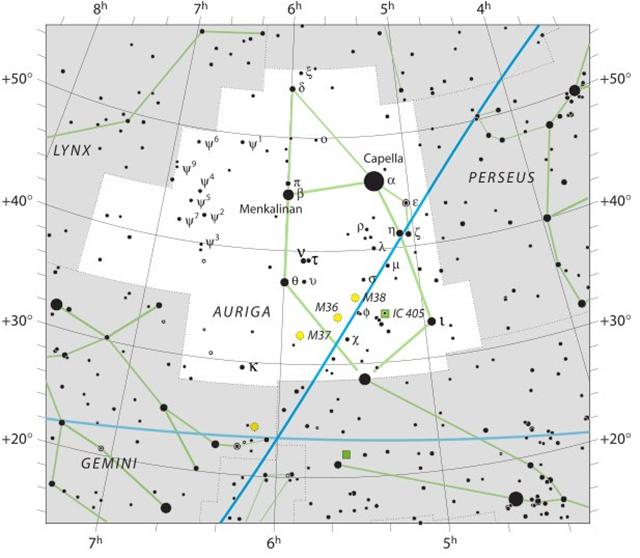
... To a casual glance, the Pleiades cluster appears as a fuzzy patch like a swarm of flies over the back of the bull ... According to mythology, Alcyone and Celaeno were both seduced by Poseidon. Maia, the eldest and most beautiful of the sisters, was seduced by Zeus and gave birth to Hermes; she later became foster-mother to Arcas, son of Zeus and Callisto. Zeus also seduced two others of the Pleiades: Electra, who gave birth to Dardanus, the founder of Troy; and Taygete, who gave birth to Lacedaemon, founder of Sparta. Asterope was ravished by Ares and became mother of Oenomaus, king of Pisa, near Olympia, who features in the legend of Auriga. Hence six Pleiades became paramours of the gods. Only Merope married a mortal, Sisyphus, a notorious trickster who was subsequently condemned to roll a stone eternally up a hill ...
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

.jpg)

























.jpg)