6-3. The looking back figure (with no future ahead) at Ea6-5 has lost his right arm, corresponding to that place where the Sun reached day 500:
|
May 12 (32 + 100) |
13 (315 - 182) |
14 |
15 (500) |
|
Nov 10 (314
→
π) |
11 |
12
(*236 →
8 * 29½) |
13 (500 - 183) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ea6-2
(180) |
Ea6-3 |
Ea6-4
(182) |
Ea6-5 |
|
vaha mea |
koia |
kua
vaha |
kiore |
|
Vaha.
Hollow; opening; space between the fingers (vaha
rima); door cracks (vaha papare). Vahavaha,
to fight, to wrangle, to argue with abusive words.
Vanaga. 1. Space, before T; vaha takitua,
perineum. PS Mgv.: vaha, a space, an open place.
Mq.: vaha, separated, not joined. Ta.: vaha,
an opening. Sa.: vasa, space, interval. To.:
vaha, vahaa, id. Fu.: vasa, vāsaà,
id. Niuē: vahā.
2. Muscle, tendon; vahavaha,
id. Vahahora
(vaha 1 -
hora 2),
spring. Vahatoga
(vaha 1 -
toga 1),
autumn. 3. Ta.: vahavaha,
to disdain, to dislike. Ha.: wahawaha,
to hate, to dislike. Churchill.
Mea.
1. Tonsil, gill (of fish). 2. Red (probably
because it is the colour of gills); light red, rose;
also meamea. 3. To grow or to exist in abundance
in a place or around a place: ku-mea-á te maîka,
bananas grow in abundance (in this place); ku-mea-á
te ka, there is plenty of fish (in a stretch of the
coast or the sea); ku-mea-á te tai, the tide is
low and the sea completely calm (good for fishing);
mau mea, abundance. Vanaga. 1. Red;
ata mea, the
dawn. Meamea,
red, ruddy, rubricund, scarlet, vermilion, yellow;
ariga meamea,
florid; kahu meamea
purple; moni meamea,
gold; hanuanua meamea,
rainbow; pua ei meamea,
to make yellow.
Hakameamea, to redden, to make yellow. PS
Ta.: mea,
red. Sa.: memea,
yellowish brown, sere. To.:
memea, drab. Fu.:
mea, blond,
yellowish, red, chestnut. 2. A thing, an object,
elements (mee);
e mea,
circumstance; mea ke,
differently, excepted, save, but;
ra mea, to
belong; mea rakerake,
assault; ko mea,
such a one; a mea nei,
this; a mea ka,
during; a mea,
then; no te mea,
because, since, seeing that;
na te mea,
since; a mea era,
that; ko mea tera,
however, but. Hakamea,
to prepare, to make ready. P Pau., Mgv., Mq., Ta.:
mea, a thing.
3. In order that, for. Mgv.:
mea, because,
on account of, seeing that, since. Mq.:
mea, for. 4.
An individual; tagata
mea, tagata
mee, an individual. Mgv.:
mea, an
individual, such a one. Mq., Ta.:
mea, such a
one. 5. Necessary, urgent;
e mea ka, must
needs be, necessary; e
mea, urgent. 6. Manners, customs. 7. Mgv.:
ako-mea, a
red fish. 8. Ta.: mea,
to do. Mq.: mea,
id. Sa.: mea,
id. Mao.: mea,
id. Churchill.
MARCH 25 (84)
→ 84 + 64 = 148 (May
28) → 132 (May 12) where Nusakan should be at
the Full Moon + 16 (change from waiting to return to
visibility to true heliacal dates).
|
|
No star listed (52) |
ψ
Persei (53.1)
ACRUX (α
CRUCIS) |
δ
Persei (54.7) |
Al Thurayya-27 (Many Little
Ones) /
Krittikā-3 (Nurses of Kārttikeya)
/
TAU-ONO (Six Stones)
ATIKS =
ο
Persei,
RANA (Frog) =
δ
Eridani
(55.1),
CELAENO (16 Tauri), ELECTRA (17), TAYGETA (19),
ν
Persei (55.3), MAIA (20), ASTEROPE (21), MEROPE (23)
(55.6) |
|
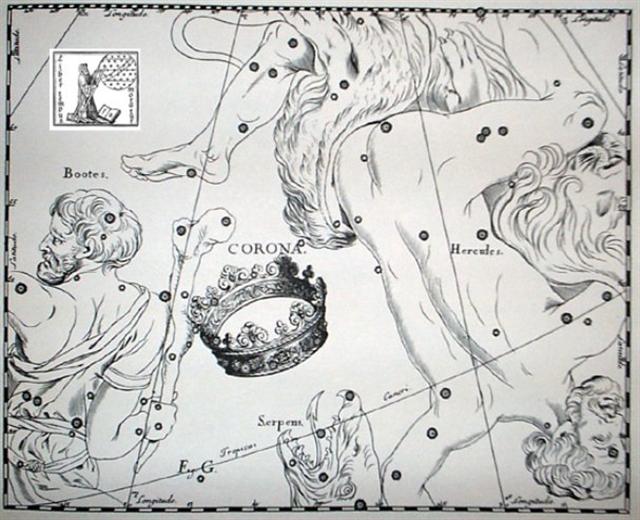
NUSAKAN (Pauper's Bowl) = β Cor. Bor.
(234.0), κ¹ Apodis (234.3), ν Bootis (234.7), ζ Librae
(234.9) |
θ Cor. Borealis (235.3), γ Lupi (235.6),
GEMMA = α
Cor. Bor.,
ZUBEN ELAKRAB = γ Librae, QIN = δ Serpentis, ε Tr.
Austr.
(235.7), μ Cor. Borealis (235.8), υ Librae (235.9)
CAPH
(β Cassiopeiae)
SIRRAH (α Andromedae) |
φ Bootis (236.2), ω Lupi, τ Librae (236.3), ψ¹ Lupi
(236.7), ζ Cor. Borealis (236.9) |
κ
Librae (237.2),
ι
Serpentis (237.4),
ψ²
Lupi,
ρ
Oct.
(237.5), γ Cor. Borealis, η Librae (237.7), COR
SERPENTIS = α Serpentis
(237.9)
*196.0 = *237.4 - *41.4 |
|
... In other words,
the ancient Druidic religion based on the oak-cult will
be swept away by Christianity and the door - the god
Llyr - will languish forgotten in the Castle of
Arianrhod, the Corona Borealis. This helps us to
understand the relationship at Rome of Janus and the
White Goddess Cardea who is ... the Goddess of Hinges
who came to Rome from Alba Longa. She was the hinge on
which the year swung - the ancient Latin, not the
Etruscan year - and her importance as such is recorded
in the Latin adjective cardinalis - as we say in
English 'of cardinal importance - which was also applied
to the four main winds; for winds were considered as
under the sole direction of the Great Goddess until
Classical times ... Notably the Full Moon would ideally be at
the right ascension line of Nusakan
(*234.0) in Corona Borealis in the night
before Sirrah (*0.5) culminated at
21h. My list of star culminations contains
only a selected few of all the stars in my
star list, but we can assume the culmination
(at 21h) of Caph (*0.5) also occurred
in November 11.
 |
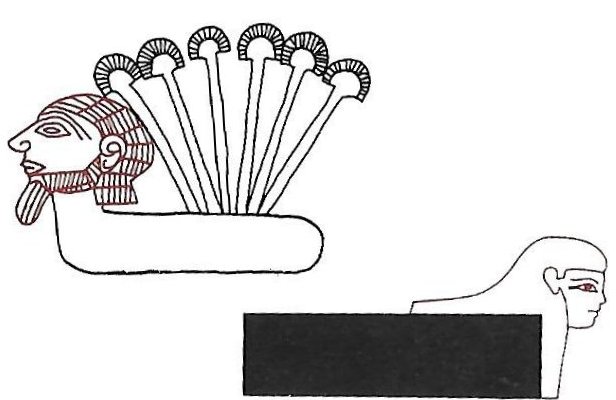
The domain of the Winds was the Air → Shu
/ Shut:
... Hercules first appears in legend as a
pastoral sacred king and, perhaps because shepherds welcome the
birth of twin lambs, is a twin himself.
His characteristics and history can be
deduced from a mass of legends, folk-customs and megalithic
monuments. He is the rain-maker of his tribe and a sort of human
thunder-storm. Legends connect him with Libya and the Atlas
Mountains; he may well have originated thereabouts in
Palaeolithic times. The priests of Egyptian Thebes, who called
him Shu, dated his origin as '17,000 years before the
reign of King Amasis'. He carries an oak-club, because the oak
provides his beasts and his people with mast and because it
attracts lightning more than any other tree. His symbols are the
acorn; the rock-dove, which nests in oaks as well as in clefts
of rocks; the mistletoe, or Loranthus; and the serpent.
All these are sexual emblems. The dove was sacred to the
Love-goddess of Greece and Syria; the serpent was the most
ancient of phallic totem-beasts; the cupped acorn stood for the
glans penis in both Greek and Latin; the mistletoe was an
all-heal and its names viscus (Latin) and ixias
(Greek) are connected with vis and ischus
(strength) - probably because of the spermal viscosity of its
berries, sperm being the vehicle of life.
Birds and flies (kuhane) inhabit the Air.
... From a religious point of view, the high
regard for flies, whose increase or reduction causes a similar
increase or reduction in the size of the human population, is
interesting, even more so because swarms of flies are often a
real nuisance on Easter Island, something most visitors have
commented on in vivid language. The explanation seems to be that
there is a parallel relationship between flies and human souls,
in this case, the souls of the unborn. There is a widespread
belief throughout Polynesia that insects are the embodiment of
numinous beings, such as gods or the spirits of the dead, and
this concept extends into Southeast Asia, where insects are seen
as the embodiment of the soul ...
In Manuscript E number 500 [E:74]
was contrasted with 600 [E:54].
Possibly because →
500 + 84 = 584 (synodic cycle of Venus) +
16 (change from waiting to return to visibility to true heliacal
dates) =
600:
... During the reign of Matua, the Hanau Eepe
came [he ea]. They stole [he toke] one side
(etahi painga) of the land of the king of Hanau Momoko
and moved [he hakaneke] the border [te tita'a koîa]
from their side toward the side of the Hanau Momoko. Five
hundred [erima te rau] Hanau Eepe stole the land of the
king of the Hanau Momoko. [E:53]
... The king assigned [he vavae] six
hundred [eono te rau] men ...The king reproached [he
kakai] the Hanau Eepe severely, 'Who sent you out to steal
the land?' The Hanau Eepe answered, 'We ourselves did!' [O
matou ana.he ki.]
... 'Oh, you, why [mo-te-aha] have you
violated [toke] the borders of my [tooku] land?'
The Hanau Eepe answered, 'There is not enough land [he kainga
kore] to live on!' Thereupon the king called out [he
rangi] to the Hanau Eepe, 'Here I stand, and I tell all of
you: I am taking [he too au] you prisoners [he
puru] and I am locking you up in the house of prisoners (hare
kopu) for fifty [50, erima te kauatu] years!' Then
the king called out [he rangi] to his men, 'Seize [ka
too] all of them, and lock up all of the Hanau Eepe!
Lock them up [ka puru] for good!' [E:55]



|









