|
TAHUA
4. The beginning of line Cb1 seems to have been designed to look similar to the beginning of line Cb2 - possibly in order to pull on our attention:
As I remember it the earliest 'mill' was a pair of suitable stones, grinding tools for crushing the cereals by moving the upper body (of the kneeling woman) strongly forward and then back again repeatedly until the intended results had been achieved. Then would come the winnowing.
Thus the precession of the cardinal points of the Sun could have been imagined to be not cyclical but swinging to and fro, like the tidal waters moving quickly in and then out again.
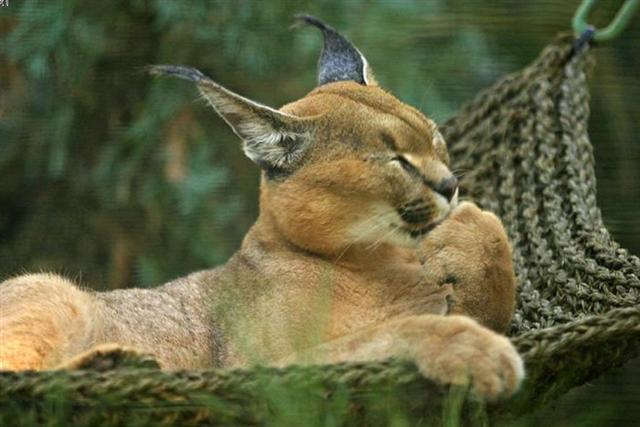
The amplitude of such an ideal swing might have been determined by the position of the Caracal (Alamak, γ Andromedae), when lazily resting in his woven Cradle.
The Rainy Pleiades were evidently located early in line Cb2:
After rain there should be sunshine
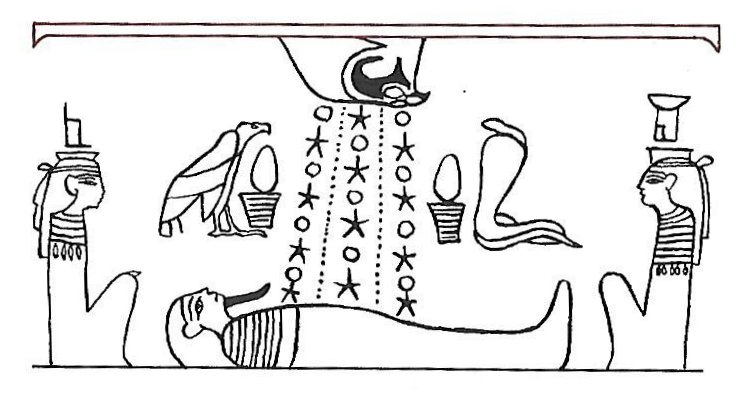
and inky pinky spider would climb up again. ... We can perceive the gap in Cb2-6 as an illustration of the gap here forced upon between the upside down sky bowl (right) and the world below - receiving the benefits of rain and beams from the Sun. South of the equator November was a spring month corresponding to May in the north.
... In essence the central element in Cb2-6 is a tapa mea (red light cloth) type of glyph with 8 'Tree Feathers', 4 of them p.m. ('males') and 4 of them a.m. ('females'):
If we should count according to an ideally swinging movement:
we could find for instance: ... All the natives of the South Sea islands are great swimmers. Both men, women and children could almost be called amphibians, because they spend a good portion of their day swimming, diving, bathing and doing all those and similar sports in the midst of the breakers and the surging sea rolling in over the coral banks. The more the sea is heaving, the more the islander feels at home in this his right element. These islanders seem to be very fond of children, especially their neighbours, which they until quite recently did not hesitate to eat. That in addition to the repulsive murder of their own children, especially as regards girls, results in a quite considerable reduction in the number of the children. But otherwise the children are as merry and free from sorrow as their parents. They learn to swim almost as soon as they begin to walk. The children are very amused by swinging and by sending up paper kites. They also have a rather peculiar game, which consists of keeping their eyes wide open with the help of a stiff straw of grass pushing the eye-lids apart ...
... In reference to your question, 'How do the natives of Easter Island obtain fire?' I [Mr. Croft] have to answer that they cannot tell. Their forefathers, like the ancient Romans, had their 'vestal' fires, preserved from ancient times; but the 'Vestal Virgins' of Easter Island were gray-headed and gray-bearded old heathen priests. It was a part of their duty, sacredly attended to, to guard the eternal fire, which was neutral, together with its guardians, in all wars. From this sacred fire the whole community - at one time a large one - could obtain that useful 'element' from time to time, as they needed it, for culinary and other purposes. This custom is still kept up by a portion of the community, while another portion rely on the matches of Mr. Dutrou-Bornier for their supply. Another portion of the community have learned from Gambier Islanders (who were sent there by the Catholics, to assist the priests) how to make fire: not by rubbing two sticks together, as you ask in your letter, but by rubbing the point of one stick on the side of the other, until it makes a hot groove and eventually fire - a work generally of from five to ten minutes. In order to illustrate this, I have had a photograph taken for you, showing you the natives in the very act of producing fire, and have also sent you the identical sticks used on that occasion. You will notice that the wood is of a soft and spongy nature. It grows abundantly on these islands, and is a variety known as the Hibiscus tiliaceus, and called by the natives 'Purau' and 'Fau', pronounced 'Purow' and 'Fow', 'ow' being sounded as in the word 'how'. You can, if you wish, obtain large quantities of it, by going on board the vessels carrying oranges from these islands to San Francisco; the orange crates are mostly made of it. And you could also get one of the Tahitian or other islanders, sailors on board of such vessels, to make fire for you by the aid of these sticks, and thus practically or ocularly answer your own question, as they are all experienced in the art ...
... Then he went into the woods and cut down straight fau trees (Hibiscus tiliaceus) for paddles and for floor planks ...
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||