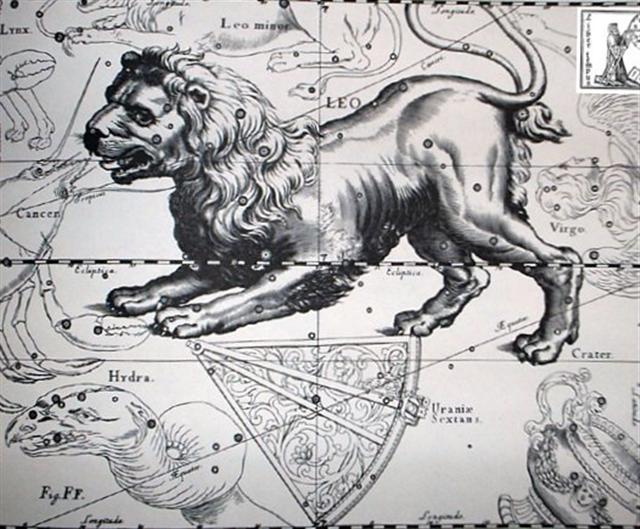
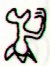It seems clear that Ea had - with help from the Black Diver - conquered the Green Serpent (Keyemen) for we can see how he had placed his foot on top of him:  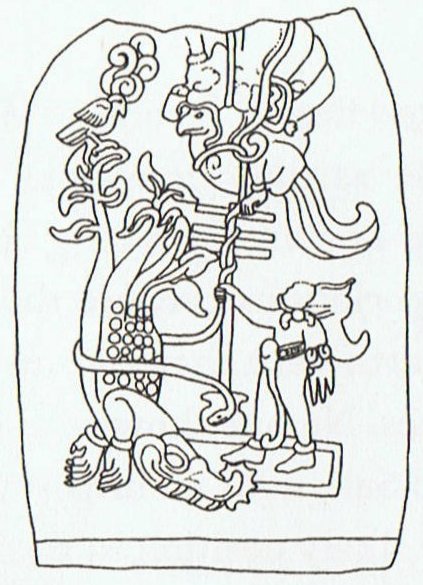 Rei. 1. To tread, to trample on: rei kiraro ki te va'e. 2. (Used figuratively) away with you! ka-rei kiraro koe, e mageo ê, go away, you disgusting man. 3. To shed tears: he rei i te mata vai. 4. Crescent-shaped breast ornament, necklace; reimiro, wooden, crescent-shaped breast ornament; rei matapuku, necklace made of coral or of mother-of-pearl; rei pipipipi, necklace made of shells; rei pureva, necklace made of stones. 5. Clavicle. Îka reirei, vanquished enemy, who is kicked (rei). Vanaga. T. 1. Neck. 2. Figure-head. Rei mua = Figure-head in the bow. Rei muri = Figure-head in the stern. Henry. Mother of pearl; rei kauaha, fin. Mgv.: rei, whale's tooth. Mq.: éi, id. This is probably associable with the general Polynesian rei, which means the tooth of the cachalot, an object held in such esteem that in Viti one tooth (tambua) was the ransom of a man's life, the ransom of a soul on the spirit path that led through the perils of Na Kauvandra to the last abode in Mbulotu. The word is undoubtedly descriptive, generic as to some character which Polynesian perception sees shared by whale ivory and nacre. Rei kauaha is not this rei; in the Maori whakarei designates the carved work at bow and stern of the canoe and Tahiti has the same use but without particularizing the carving: assuming a sense descriptive of something which projects in a relatively thin and flat form from the main body, and this describes these canoe ornaments, it will be seen that it might be applied to the fins of fishes, which in these waters are frequently ornamental in hue and shape. The latter sense is confined to the Tongafiti migration. Reirei, to trample down, to knead, to pound. Pau.: Rei-hopehopega, nape. Churchill.
He stood on the Fish (walked on water):
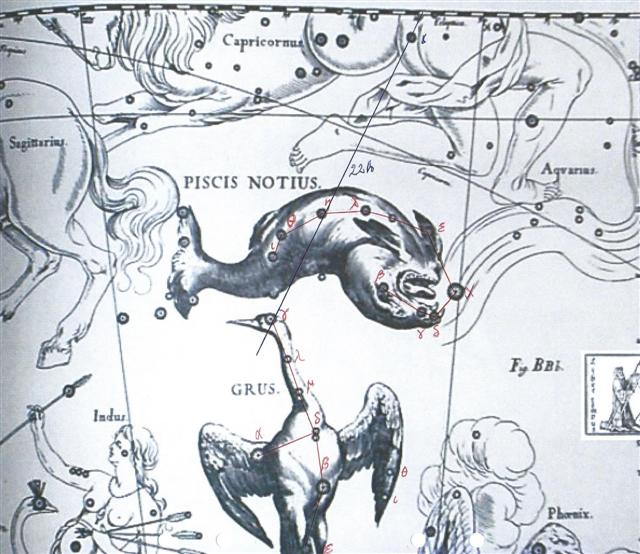
In the C text there were 3 'rats' (kiore) at the star of Weeping (Kuh):
If the beginning of the C text was designed (as I have suggested) to be where Algenib Pegasi (*1) was at the Full Moon in September 22 (264 = 81 + 183) - according to my assumed epoch of rongorongo - then the position 147 days (glyphs) later should be when Kuh (264 + 147 - 80 = *331) was at the Full Moon.
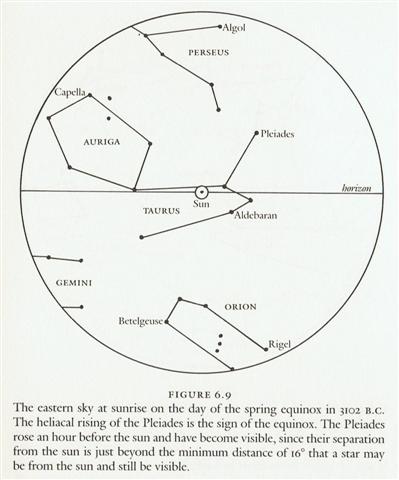
Thus, in August 16 (227 + 1 = 80 + 148) these 3 sitting 'rats' would have been visible close to the Full Moon. ... In ancient times the priest-astronomers (Brahmans) determined the recurrence of the solstices and equinoxes by the use of the gnomon. Later they developed the Nakshatra system of star reference to determine the recurrence of the seasons, much as the Greeks used the heliacal rising of some star for the same purpose. An example of the operation of the Nakshatra system in antiquity can be seen in figure 6.9.
Here we see that the spring equinox occurred when the sun was at its closest approach to the star Aldebaran (called Rohini by the Hindus) in our constellation Taurus. But, of course, the phenomenon would not have been visible because the star is too close to the sun for observation. The astronomers would have known, however, that the equinoctial point was at Aldebaran by observing the full moon falling near the expected date or near a point in the sky exactly opposite Aldebaran (since the full moon is 180º from the sun), that is, near the star Antares ... And according to the epoch of Bharani their position would have been in day 228 - 41 = 187 ("July 6) = *107 (= 472 - 365 = 41 + 66). The stars could not be observed when they were close to the Sun and therefore the nakshatra stars must be observed instead. These should therefore be illustrated in the rongorongo text rather than those stars which were hidden by the fierce rays from the Sun.
The feathers at the back side - not visible - on these 3 wet Moon 'rats' are in contrast to their taking in water which can be seen in front.
... In the calendar of daylight the morning sun is growing in strength up to noon, and here the kai hand gesture is therefore used:
The nutrition sun is taking in may be far from obvious, but not so for the ancient mind: ... The life-force of the earth is water. God moulded the earth with water. Blood too he made out of water. Even in a stone there is this force, for there is moisture in everything. But if Nummo is water, it also produces copper. When the sky is overcast, the sun's rays may be seen materializing on the misty horizon. These rays, excreted by the spirits, are of copper and are light. They are water too, because they uphold the earth's moisture as it rises. The Pair excrete light, because they are also light ... 'The sun's rays,' he went on, 'are fire and the Nummo's excrement. It is the rays which give the sun its strength. It is the Nummo who gives life to this star, for the sun is in some sort a star.' It was difficult to get him to explain what he meant by this obscure statement. The Nazarene made more than one fruitless effort to understand this part of the cosmogony; he could not discover any chink or crack through which to apprehend its meaning. He was moreover confronted with identifications which no European, that is, no average rational European, could admit. He felt himself humiliated, though not disagreeably so, at finding that his informant regarded fire and water as complementary, and not as opposites. The rays of light and heat draw the water up, and also cause it to descend again in the form of rain. That is all to the good. The movement created by this coming and going is a good thing. By means of the rays the Nummo draws out, and gives back the life-force. This movement indeed makes life. The old man realized that he was now at a critical point. If the Nazarene did not understand this business of coming and going, he would not understand anything else. He wanted to say that what made life was not so much force as the movement of forces. He reverted to the idea of a universal shuttle service. 'The rays drink up the little waters of the earth, the shallow pools, making them rise, and then descend again in rain.' Then, leaving aside the question of water, he summed up his argument: 'To draw up and then return what one had drawn - that is the life of the world' ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||