The flow of sweet waters from the mountains was essential for such planters as Epimenides:
To account for the transportation of rain from the evaporation at sea level the mythical minds used various similarities.
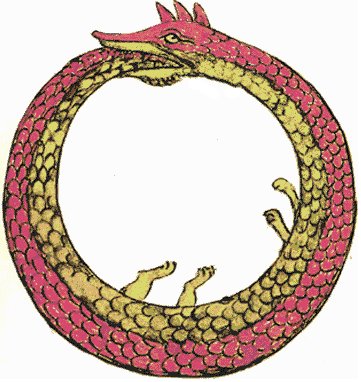
... Men and birds joined forces to destroy the huge watersnake, which dragged all living creatures down to his lair. But the attackers took fright and cried off, one after the other, offering as their excuse that they could only fight on dry land. Finally, the duckler (K.G.: a diver) was brave enough to dive into the water; he inflicted a fatal wound on the monster which was at the bottom, coiled round the roots of an enormous tree. Uttering terrible cries, the men succeeded in bringing the snake out of the water, where they killed it and removed its skin. The duckler claimed the skin as the price of its victory. The Indian chiefs said ironically, 'By all means! Just take it away!' 'With pleasure', replied the duckler as it signalled to the other birds. Together they swooped down and, each one taking a piece of the skin in its beak, flew off with it. The Indians were annoyed and angry and, from then on, became the enemies of birds. The birds retired to a quiet spot in order to share the skin. They agreed that each one should keep the part that was in its own beak. The skin was made up of marvelous colors - red, yellow, green, black, and white - and had markings such as no one had ever seen before. As soon as each bird was provided with the part to which it was entitled, the miracle happened: until that time all birds had had dingy plumage, but now suddenly they became white, yellow, and blue ... The parrots were covered in green and red, and the macaws with red, purple, and gilded feathers, such as had never before been seen. The duckler, to which all the credit was due, was left with the head, which was black. But it said it was good enough for an old bird ... The white egret took its piece [of the skin of 'Keyemen - the rainbow in the shape of a huge watersnake'] and sang, 'ā-ā', a call that it still has to this day. The maguari (Circonia maguari, a stork) did likewise and uttered its ugly cry: 'a(o)-a(o)'. The soco (Ardea brasiliensis, a heron) placed its piece on its head and wings (where the colored feathers are) and sang, 'koro-koro-koro'. The kingfisher (Alcedo species) put its piece on its head and breast, where the feathers turned red, and sang, 'se-txe-txe-txe'. Then it was the toucan's turn. It covered its breast and belly (where the feathers are white and red). And it said: 'kión-he, he kión-he'. A small piece of skin remained stuck to its beak which became yellow. Then came the mutum (Crax species); it put is piece on its throat and sang, 'hm-hm-hm-hm' and a tiny remaining strip of skin turned its nostrils yellow. Next came the cujubin (Pipile species, a piping guan), whose piece turned its head, breast, and wings white: it sang, 'krr' as it has done every morning since. Each bird 'thought its own flute made a pretty sound and kept it.' The richly colored plumage of the macaw is explained by the fact that it seized a large piece of skin and covered its whole body in it ... In the G text there are curious glyphs which might have been used to illustrate the essence of this idea:
The head gear of Ea - in the Mesopotamian illustration above - has 3 'bubbles' (baubles) at left and 4 at right. In Gb2-16 there are 4 such at left and 3 minus 1 at right. Inside at left there are 4 'feathers' (air) marks.
Pu. 1. To come forward to greet someone met on the road; to walk in front, to go in front: ka-pú a mu'a, let them go first. 2. Pú a mu'a, to intervene, to come to someone's rescue; he-pú-mai a mu'a, he-moaha, he came to my rescue and saved my life. 3. Ancient expression: ai ka-pú, ai ka-pú, tell us frankly what you think. 4. Hole, opening, orifice; well; circumference, rotundity; swirling water; pú-haga, vaginal orifice; pú-henua (also just henua), placenta. He pú henua nó te me'e aau, he-oti-á; ina-á me'e ma'u o te rima i-topa-ai koe, a placenta was all you had, it is a past thing now; you held nothing in your hands when you were born (stern words said to children to make them realize that they must not be demanding, since they were born naked and without possessions). 5. To dig out (tubers): he-pú i te uhi, to dig out yams. Vanaga. 1. A trumpet. P Mgv.: pu, a marine shell. Mq.: pu, conch shell. Ta.: pu, shell, trumpet. 2. A small opening, hole, mortise, stirrup, to pierce, to perforate, to prick; pu moo naa, hiding place; taheta pu, fountain, spring; hakapu, to dowel, to pierce, to perforate. PS Sa., Fu., Niuē: pu, a hole. Churchill. Mq.: Pu, source, origin. Ma.: pu, root, origin, foundation. Churchill. Aue. Ah, alas. Aueue, oh. P Pau., Ta.: aue, alas. Mgv.: aue, auhe, alas. Mq.: aue, oh, alas; auhe, a sigh. Exclamation in general representing the most primordial type of speech, it seems that this may be reduced to recognizable elements. The e is throughout these languages a vocative or hailing sign, commonly postpositive in relation to the person hailed. In the examination of au we have shown that the primal first person singular designation is u. With the comparatively scanty material afforded by this vocabulary we may not attempt ot define the use of a but we have no hesitation in noting that proof based on wider studies will show it to have, inter alia, a characteristic function as a word-maker. In a very high degree, then, a-u-e is represented by a common English interjection 'oh my!' in which oh = a, my = u, and e = !. Churchill. What is this cry which our primitive islanders share with the animals? Look at its elements, all full-throated. First we have a, the sound of mouth open, fauces open, lungs full of air. As air expires the sound recedes in the mouth towards the palate and we find the u. Last comes the conscious finish of the utterance, the muscles begin to retract, the sound-making point is forced forward and the sound is e. If the man had but a few more cubic centimeters of lung capacity he could attain cow volumne for his cry, or interjection, since it amounts to the same thing. Churchill 2. When the new moon appeared women assembled and bewailed those who had died since the last one, uttering the following lament: 'Alas! O moon! Thou has returned to life, but our departed beloved ones have not. Thou has bathed in the waiora a Tane, and had thy life renewed, but there is no fount to restore life to our departed ones. Alas ... (Makemson) The Egyptian X (as in Ca5-14) has taught us that we can regard each such 'bubble' as a star (for marking time peiods). ... Among the Nahyssan of S. Carolina time was measured and a rude chronology arranged by means of strings of leather with knots of various colour, like the Peruvian quipos. The Dakota use a circle as the symbol of time, a smaller one for a year and a larger one for a longer period: the circles are arranged in rows, thus: OOO or O-O-O. The Pima of Arizona make use of a tally. The year-mark is a deep notch across the stick ... And strings of leather can be used for whips: ... At the beginning of 44 B.C. - when Ceasar was still alive - the Senate decided to raise statues of him in all the temples and to sacrifice to him on his birthday in the month Quintilis, which in honour of him was renamed July. He was raised to the status of a god (among the other gods of the state) under the name Jupiter Julius. Marcus Antonius, who this year was consul together with Caesar, became high priest and responsible for the ceremonies. In the middle of February [February 15], at the time of the old feast of Lupercalia [Lupus = Wolf], he ran around naked and whipped the Roman ladies with thongs made from goat-skin [februa], in order to promote their fertility ...
We have so far encountered Gb2-12 repeatedly: ... All these exercises are necessary for making sure that order is preserved in all directions.
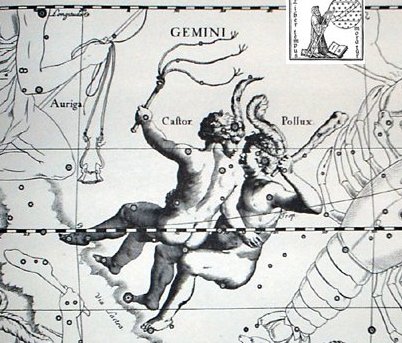
(Castor Fiber) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||