We need these birds. In addition to manu tara, 'bird zero'
(Sternata lunata) herself, they were as follows.

|
The names of the age levels of
the sooty tern were earlier used as children's
names (Routledge). These names were (Barthel):
pi(u) riuriu, kava 'eo'eo, te
verovero, and ka 'ara'ara. Fischer. |
|
pi riuriu |
Riuriu,
to go around in a circle. |
|
kava eoeo |
Eoeo. Ashes. Eoeo
reherehe 'weak ashes': a coward. |
|
te verovero |
Verovero, to throw, to
hurl repeatedly, quickly (iterative of vero).
|
|
ka araara |
Ará-ará, to signal, to
send signals with the hand (to another person in
the distance). |
| |
|
kukuru toua |
Tou. In ancient times, a
tou was someone who had recovered from an
epidemic, but whose illness meant that someone
else in the family had to die. The tou
were regarded as portents of evil. Toutou,
lush; fertile (land). Toûa: Egg yolk;
the colour yellow; soft, fibrous part of tree
bark; toûa mahute, mahute fibres. Vanaga.
Toua: Wrath, anger, rage, revenge,
battle, combat, debate, dispute, dissension,
uprising, revolt, quarrel, fight, hostility (taua);
toua rae, to provoke, rae toua, to
open hostilities, toua kakai, to rebuke,
tuki toua, to stir up dissension;
totoua, hostility; hakatoua, fighter,
warrior. P Mgv.: toua, war, battle. Mq.:
toua, war, dispute, quarrel. The form
with o is found only in these three
languages, taua is found in the general
migration, Rapanui is the only speech which has
both. Toutou, fertile (tautau);
hakatoutou, to fertilize. Mq.: taútaú,
fertile. Toùvae, to run; hakauruuru
toùvae, id. Churchill. |
| |
|
makohe |
Fregata minor.
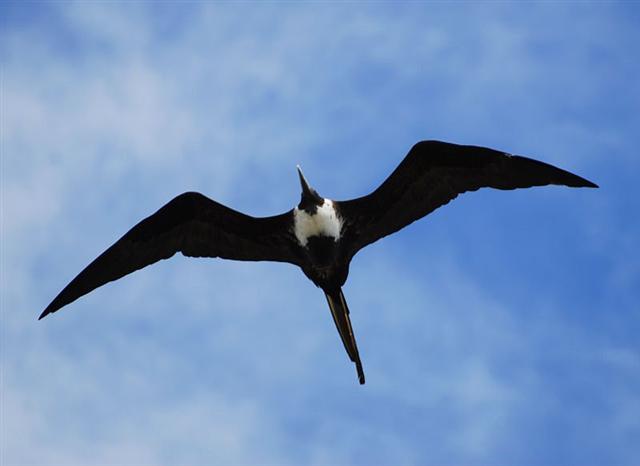 |
|
kena |
Sula dactylatra.
 |
|
tavake |
Phaeton.

"Tavake is the general Polynesian name
for the tropic bird, whose red tail feathers
were very popular. This name is closely
connected with the original population." (The
Eighth Land, p. 151) |
| |
|
ruru |
Sula cyanops. "It should
be pointed out that the combined name ruru-taiko
refers in MAO. to a black petrel (Procellaria
parkinsoni). There are no cultural data
available for ruru, which seems to be
derived from PPN. *lulu 'owl'..." (The
Eighth Land, p. 151.) "There are no cultural data
available for ... taiko (compare RAR.
taiko 'black petril', MGV. tiaku
'petrel?, omen of death', but the textual
association of taiko and spirits should
be dept in mind ..." (The Eight Land, p.151) |
|
taiko |
|
kumara |
"The transference of the name
for sweet potatoes, kumara, to a sea bird
(Oestrelata incerta or
Oestrelata leucoptera) presents a
problem in taxonomy. In a short recitation that
accompanies the string game, the next bird on
the list, kiakia, the white tern, is
associated with the leaves of the sweet potato
..." (The Eight Land, p.152) White tern. Leucanus albus royanus. |
|
kiakia |
| |
|
tuvi |
Grey tern, Tuvituvi (Procelsterna
caerulea skottsbergi). |
|
tuao |
Anous stolidus unicolor.
"The dark brown tern with a round tail is called
tuao." (The Eight Land, p.152) |
|
tavi |
"I was told that tavi is
a small, lead-colored bird that lives on the
little islets (motu) off the coast. He is
supposed to look like the tuvi, the grey
tern, and owes his name to his call." (The
Eighth Land, p.153) |
1 + 4 + 1 + 3 + 4 + 3 = 16 = 320 / 20.
By the way, we should recognize that 88 (Betelgeuze) + 16 = 104 and 320 + 16
= 336 = 4 * 84 (four quarters) = 48 * 7.
|
Counting the tresses of Pachamama
(the World Mother) from right to left: |
|
1 |
26 |
78 |
1 |
29 |
90 |
|
2 |
26 |
2 |
30 |
|
3 |
26 |
3 |
31 |
|
4 |
25 |
104 |
4 |
34 |
124 |
|
5 |
26 |
5 |
31 |
|
6 |
27 |
6 |
30 |
|
7 |
26 |
7 |
29 |
|
Total = 396 = 182 + 214 |
The mamoth ivory
carving has 88 = 39 (6, 13, 7, 13) + 48 (13, 10, 12,
13) + 1.
And in Manuscript E, we remember, there
were 39 yam varieties:
|
1 |
he tara |
kura |
a Maeha.a Teke |
|
2 |
rau renga |
|
3 |
mahihi |
|
4 |
maito |
|
5 |
nohu |
|
6 |
hetuke |
|
7 |
mama |
|
8 |
titeve |
|
9 |
moamoa tara |
|
10 |
huehue |
|
11 |
he makere |
|
12 |
he mariri |
|
13 |
he tonga |
|
14 |
he pua rau hoho
|
uri |
a Maeha.a Teke |
|
15 |
tea |
|
16 |
mea |
|
17 |
para |
|
18 |
tupere ure |
|
ADHIL (*19) |
|
20 |
ravi hakurakura |
|
21 |
naku |
|
22 |
takatore |
|
23 |
ravei |
|
24 |
he papa |
uri |
|
25 |
tea |
|
26 |
he papaki |
kahukahu |
|
27 |
vehivehi |
|
28 |
papa kura |
|
29 |
he mamari |
kioe |
|
30 |
he tutae |
|
31 |
he kunekune |
|
32 |
he tahe |
a Maeha. a Teke |
|
MIRA (*33) |
|
34 |
he taha |
|
35 |
he apuka |
|
36 |
he apuka heu |
|
37 |
he tuitui koviro |
|
38 |
he rai atea |
|
39 |
he rai atanga |
|
40 |
he ravi kana |
|
41 he ravi pako
(BHARANI *41) |
I.e., on side a of the G tablet we will find APRIL
14 (104) at the place where *64 precessional days
earlier - at the time of the Bull (the Golden Calf)
- Betelgeuze would have returned to visibility after
its close encounter with the Sun.

|
APRIL 11 |
12 |
4-13 → 14 * 29½ |
4-14→
*41.4 (104) |
15 |
16 (*26) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-21 |
Ga1-22 |
Ga1-23 |
Ga1-24 |
Ga1-25 |
Ga1-26 |
|
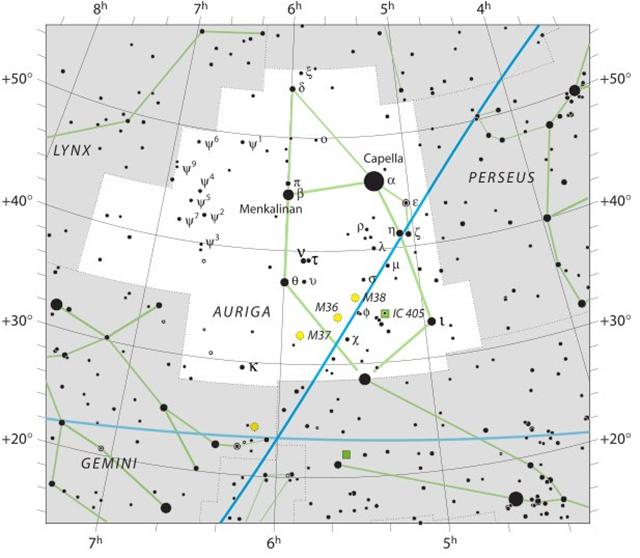
ο Aurigae (85.8), γ Leporis (85.9)
YANG MUN (α
Lupi)
|
μ
Columbae,
SAIPH
(Sword) =
κ
Orionis
(86.5),
τ
Aurigae,
ζ
Leporis (86.6) |
υ Aurigae (87.1), ν Aurigae (87.2),
WEZN (Weight) = β Columbae,
δ Leporis (87.7),
TZE (Son) = λ Columbae
(87.9) |
Ardra-6 (The Moist One) /
ANA-VARU-8 (Pillar to sit by)
χ¹
Orionis,
ξ
Aurigae (88.1),
BETELGEUZE
=
α
Orionis
(88.3),
ξ
Columbae (88.5),
σ
Columbae (88.7) |
η
Leporis (89.0),
PRAJA-PĀTI (Lord of Created Beings) =
δ
Aurigae,
MENKALINAN (Shoulder of the Rein-holder)
= β Aurigae, MAHASHIM (Wrist) = θ
Aurigae,
and
γ
Columbae (89.3),
π
Aurigae (89.4),
η
Columbae (89.7)
*48.0 = *89.4 - *41.4 |
μ Orionis (90.3), χ² Orionis (90.5) |
|
June 14 (165) |
15 |
16 |
17 (168) |
18 |
19 |
|
°June 10 (161) |
11 |
12 |
13 (164) |
14 |
15 (*86) |
|
'May 18
(*58) |
19 |
20 (140) |
21 |
22 |
23 (*63) |
|
"May 4 (*54) |
5 |
6 |
7 (127) |
8 |
9 (*49) |
|
DAY 85 - 64 = 21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
|
21 Ko
Roto Kahi
a touo renga |
22 Ko
Papa Kahi
a roro (ko pa) |
23 Ko
Puna A Tuki
hauhau renga |
24 Ko
Ehu Ko Mahatua
a piki rangi a hakakihikihi mahina |
25 Ko Maunga
Teate(t)a
a pua katiki |
26 Ko
Te Hakarava
a hakanohonoho |
|
4
he toa ruma |
5 he toa tuitui koviro |
6 he toa vitiviti |
7 he toa marikuru |
he ngaatu |
he tavari |
|
Hata. 1. Table,
bureau. P Pau.: afata, a chest,
box. Mgv.: avata, a box, case,
trunk, coffin. Mq.: fata, hata,
a piece of wood with several branches
serving as a rack, space, to ramify, to
branch; fataá, hataá,
stage, step, shelf. Ta.: fata,
scaffold, altar. 2. Hakahata, to
disjoint; hakahatahata, to
loosen, to stretch. P Pau.: vata,
an interval, interstice. Mgv.: kohata,
the space between two boards, to be
badly joined; akakohata, to leave
a space between two bodies badly joined;
hakahata, to be large, broad,
wide, spacious, far off. Mq.:
hatahata, fatafata, having
chinks, not tightly closed, disjointed.
Ta.: fatafata, open. 3.
Hatahata, calm, loose, prolix, vast.
Mgv.: hatahara, broad, wide,
spacious, at one's ease. Ta.:
fatafata, free from care. Mq.:
hatahata, empty, open. 4.
Hatahata, tube, pipe, funnel.
Churchill. Sa.: fata, a raised
house in which to store yams, a shelf, a
handbarrow, a bier, a litter, an altar,
to carry on a litter; fatāmanu,
a scaffold. To.: fata,
a loft, a bier, a handbarrow, to carry
on a bier; fataki,
a platform. Fu.: fata,
a barrow, a loft; fatataki,
two sticks or canes attached to each
other at each side of a house post to
serve as a shelf. Niuē: fata,
a cage, a handbarrow, a shelf, a stage,
(sometimes) the upper story of a house.
Uvea: fata,
a barrow, a bier. Fotuna: fata,
a stage. Ta.: fata,
an altar, a scaffold, a piece of wood
put up to hang baskets of food on;
afata,
a chest, a box, a coop, a raft, a
scaffold. Pau.: fata,
a heap; afata,
a box, a chest. Ma.: whata,
a platform or raised storehouse for
food, an altar, to elevate, to support.
Moriori: whata,
a raft. Mq.: fata,
hata,
hataá,
shelves. Rapanui: hata,
a table. Ha.: haka,
a ladder, an artificial henroost;
alahaka,
a ladder. Mg.: ata,
a shelf; atamoa,
a ladder; atarau,
an altar. Mgv.: avata,
a coffer, a box. Vi.: vata,
a loft, a shelf; tāvata,
a bier. The Samoan fata
is a pair of light timbers pointed at
the ends and tied across the center
posts of the house, one in front, the
other behind the line of posts; rolls of
mats and bales of sennit may be laid
across these timbers; baskets or
reserved victuals may be hung on the
ends. The litter and the barrow are two
light poles with small slats lashed
across at intervals. The Marquesan
fata
is a stout stem of a sapling with the
stumps of several branches, a hat tree
in shape, though found among a barehead
folk. These illustrations are sufficient
to show what is the common element in
all these fata
identifications, light cross-pieces
spaced at intervals. With this for a
primal signifaction it is easy to see
how a ladder, a raft, a henroost, an
altar come under the same stem for
designation. Perhaps Samoan
fatafata
the breast obtains the name by reason of
the ribs; it would be convincing were it
not that the plumpness of most Samoans
leaves the ribs a matter of anatomical
inference. Churchill 2.
Vao.
Mgv.: vao, uninhabited land.
Ta.: ? [obliterated text] ... of the
valleys. Mq.: vao, bottom of a
valley. Sa.: vao, the bush. Ma.:
wao, the forest. Churchill. |

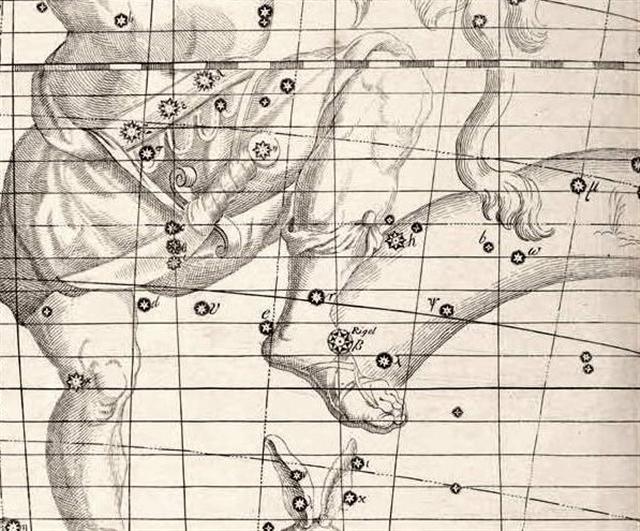
... The
earliest depiction that has been linked
to the constellation of Orion is a
prehistoric (Aurignacian) mammoth ivory
carving found in a cave in the Ach
valley in Germany in 1979.
Archaeologists have estimated it to have
been fashioned approximately 32,000 to
38,000 years ago ... The artist cut,
smoothed and carved one side (A)
and finely notched the other side (B)
and the edges. Side A contains
the half-relief of an anthropoidal
figure, either human or a human-feline
hybrid, known as the 'adorant' because
its arms are raised as if in an act of
worship.
|
Egyptian jubilation |
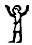 |
Phoenician
he |
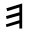 |
Greek
epsilon |
Ε (ε) |
|
Wikipedia
points at the Egyptian
gesture with arms held high
as a Sign of jubilation,
which may have been the
origin (via Phoenician he)
of epsilon.

 |
On side B together with the
four edges is a series of notches that
are clearly set in an intentional
pattern. The edges contain a total of 39
notches in groups of 6, 13, 7 and 13. A
further 49 notches on side B
are arranged in four vertical lines of
13, 10, 12 and 13 respectively plus a
further notch that could be in either of
the middle two lines ... The grouping of
the notches on the plate suggests a
time-related sequence. The total number
of notches (88) not only coincides with
the number of days in 3 lunations (88.5)
but also approximately with the number
of days when the star Betelgeuse (α Ori)
disappeared from view each year between
its heliacal set (about 14 days before
the spring equinox around 33,000 BP) and
its heliacal rise (approximately 19 days
before the summer solstice).
Conversely, the nine-month period when
Orion was visible in the sky
approximately matched the duration of
human pregnancy, and the timing of the
heliacal rise in early summer would have
facilitated a ‘rule of thumb’ whereby,
by timing conception close to the
reappearance of the constellation, it
could be ensured that a birth would take
place after the severe winter half-year,
but leaving enough time for sufficient
nutrition of the baby before the
beginning of the next winter. There is a
resemblance between the anthropoid on
side A and the constellation Orion. None
of these factors is convincing when
taken in isolation, because of the high
probability that apparently significant
structural and numerical coincidences
might have arisen fortuitously. However,
taken together they suggest that the
anthropoid represented an asterism
equivalent to today’s constellation of
Orion, and that the ivory plate as a
whole related to a system of time
reckoning linked to the moon and to
human pregnancy. If so, then
ethnographic comparisons would suggest
that the Geißenklösterle culture
related their ‘anthropoid’ asterism to
perceived cycles of cosmic power and
fertility ...
 |
21 (sweet potato variants) followed the 39 kinds
of yam, making a total of 60 (= 88 -
28). Although in that case the nights for Adhil (*19) and
Mira (*33) were not accounted for. By counting
also these the sum (39 + 21 + 2) will point at
Bharani (*41), as the star at the end of the
season of yams.
*41 + *21 (kumara) = *62 (= 88 - 26). Here
we will find Beid (*62). In Manuscript E this
kind of 'sweet potato' was named he mamari
kiakia (instead of he kumara kiakia)
- it was not a potato below the surface of the
earth but an egg.
|
kumara |
"The transference of the name
for sweet potatoes, kumara, to a sea bird
(Oestrelata incerta or
Oestrelata leucoptera) presents a
problem in taxonomy. In a short recitation that
accompanies the string game, the next bird on
the list, kiakia, the white tern, is
associated with the leaves of the sweet potato
..." (The Eight Land, p.152) White tern. Leucanus albus royanus. |
|
kiakia |

The final of the season of 'close embrace' (he hauhau)
seems to have been 5 (bananas) + 12 (taro) + 1
(Elnath, *80) = 18 right ascension days after He Mamari
Kiakia. *62 + *5 + *12 + *1 = *80.

|
APRIL 5 |
6 (96) |
7 |
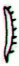 |
 |
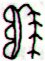 |
|
Ga1-15 (Ga1-3 + 12) |
Ga1-16 |
Ga1-17 |
|
λ Aurigae (79.0), λ Leporis (79.6),
ρ Aurigae (79.7)
ARCTURUS (α Bootis) |
Shur-narkabti-sha-iltanu-5 (Star in
the Bull towards the north)
σ
Aurigae (80.4),
BELLATRIX (Female Warrior) = γ
Orionis, SAIF AL JABBAR (Sword of
the Giant) = η Orionis
(80.7),
ELNATH
(The Butting One) =
β
Tauri = γ Aurigae
(80.9) |
ψ
Orionis (81.1),
NIHAL (Thirst-slaking Camels) = β
Leporis
(81.7) |
|
June 8 |
9 |
10 (161) |
|
... The month, which takes its name
from Juppiter the oak-god, begins on
June 10th and ends of July 7th.
Midway comes St. John's Day, June
24th, the day on which the oak-king
was sacrificially burned alive. The
Celtic year was divided into two
halves with the second half
beginning in July, apparently after
a seven-day wake, or funeral feast,
in the oak-king's honour
... |
|
°June 4 |
5 (156) |
6 (*77) |
|
'May 12 |
13 |
14 (*54) |
|
"April 28 |
29 (*39) |
30 |
|
DAY 79 - 64 = 15 |
16 |
17 |
|
15 Ara Koreu
a pari maehaeha |
16 Hanga Kuokuo
a vave renga |
17 Opata Roa
a mana aia |
|
He hatu i te
vanaga rivariva ki te kio o poki ki
ruga ki te
opata, they gave the
refugees the good advice not to
climb the precipice.
He-kî e Tori:
maaku-á e-ea ki te manu, e-poko i te
po i ruga i te
opata. Tori said: I shall
go and catch birds at night, up on
the cliff. |
|
1 he kape |
1 he hauhau |
1 he mahute |
|
Ti by lying
with Tattooing made the ti
plant (he ti ki ai ki roto ki a
he ta ka pu te ti). Burnt ti
leaves were used to produce the
black dye for tattooing.
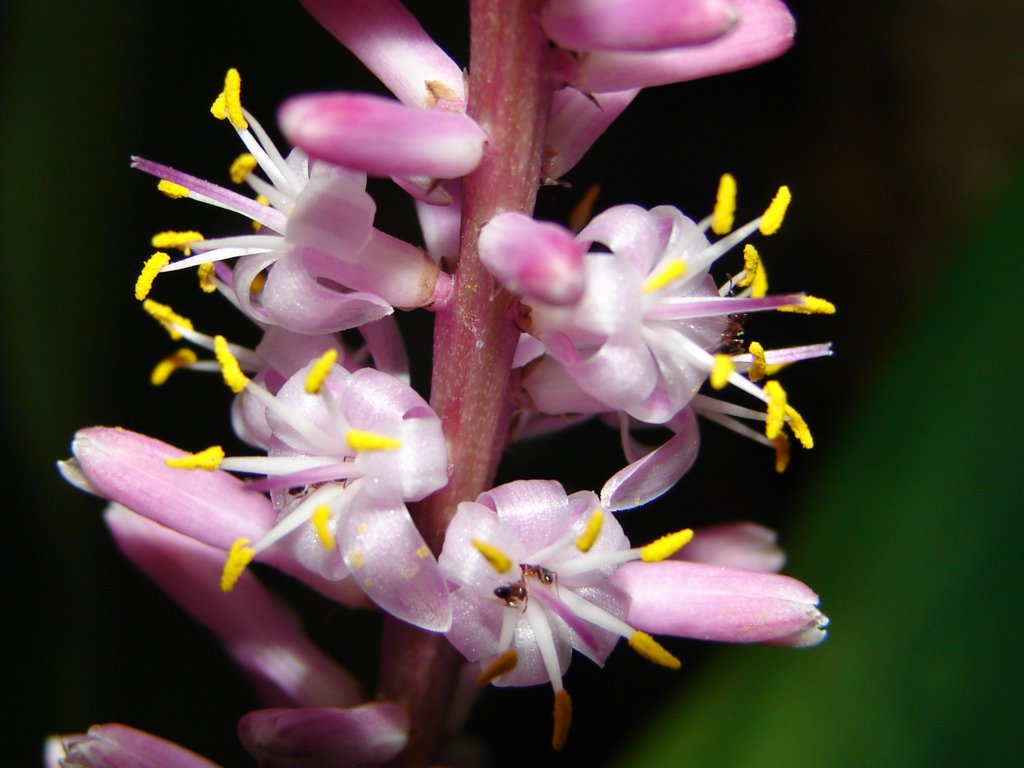

Kape.
'Bitter-taro' (Alocasia
macrorrhiza). In 1957 kape
was still cultivated in much the
same way as dry taro. It is a type
of food to be eaten during times of
famine. According to Fuentes
(1960:856), the tubers had to be
kept in the earth-oven for 15 (sic)
days in order to eliminate some of
the poisonous components. Barthel
2. Arum, yam. Churchill. Bitterness
by doing it with Bad-taste produced
the kape (mangeongeo ki ai
ki roto he rakerake ka pu te kape). |
|













