13-2. Once again. The Milky
Way was a river of life.
... It is an interesting fact, although
one little commented upon, that myths involving a canoe
journey, whether they originate from the Athapaskan and
north-western Salish, the Iroquois and north-eastern
Algonquin, or the Amazonian tribes, are very explicit about
the respective places allocated to passengers. In the case
of maritime, lake-dwelling or river-dwelling tribes, the
fact can be explained, in the first instance, by the
importance they attach to anything connected with
navigation: 'Literally and symbolically,' notes Goldman ...
referring to the Cubeo of the Uaupés basin,
'the river is a binding thread for the people. It is a
source of emergence and the path along which the ancestors
had travelled. It contains in its place names genealogical
as well as mythological references, the latter at the
petroglyphs in particular.' A little further on ... the same
observer adds: 'The most important position in the canoe are
those of stroke and steersman. A woman travelling with men
always steers, because that is the lighter work. She may
even nurse her child while steering ... On a long journey
the prowsman or stroke is always the strongest man, while a
woman, or the weakest or oldest man is at the helm
...
... Men's spirits were thought to dwell
in the Milky Way between incarnations. This conception has
been handed down as an Orphic and Pythagorean tradition
fitting into the frame of the migration of the soul.
Macrobius, who has provided the broadest report on the
matter, has it that souls ascend by way of Capricorn, and
then, in order to be reborn, descend again through the 'Gate
of Cancer'. Macrobius talks of signs; the
constellations rising at the solstices in his time (and
still in ours) were Gemini and Sagittarius: the 'Gate of
Cancer' means Gemini. In fact, he states explicitly (I,12.5)
that this 'Gate' is 'where the Zodiac and the Milky Way
intersect'. Far away, the Mangaians of old (Austral
Islands, Polynesia), who kept the precessional clock running
instead of switching over to 'signs', claim that only at the
evening of the solstitial days can spirits enter heaven, the
inhabitants of the northern parts of the island at one
solstice, the dwellers in the south at the other ...
Considering the fact that the crossroads of ecliptic and
Galaxy are crisis-resistant, that is, not concerned with the
Precession, the reader may want to know why the Mangaians
thought they could go to heaven only on the two solstitial
days. Because, in order to 'change trains' comfortably, the
constellations that serve as 'gates' to the Milky Way must
'stand' upon the 'earth', meaning that they must rise
heliacally either at the equinoxes or at the solstices. The
Galaxy is a very broad highway, but even so there must have
been some bitter millenia when neither gate was directly
available any longer, the one hanging in midair, the other
having turned into a submarine entrance ...
After the Sun had crossed over the Milky
Way from Betelgeuze to the other side of this River of Life,
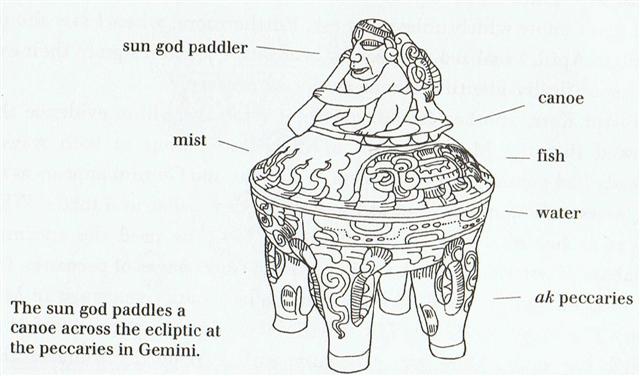
he would reach a fresh New Land:

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
4h (60.9) |
< < < < |
May 22 |
23 |
24 (12 * 12) |
AIN (*65.7) |
|
Ca9-15 (3 * 81) |
Ca9-16 (244) |
Ca9-17 |
Ca9-18 |
Ca9-19 |
Ca9-20 |
|
i te mauga pu hia |
E rima ki te henua |
koia ku honui |
erua maitaki |
ko koe ra |
|
Maitaki, Clean, neat, pure,
pretty, nice, beautiful, handsome; tagata rima
maitaki, clean-handed man, correct man.
Vanaga. 1. Good. Henua maitaki = the good
earth. 2. Shine. Marama maitaki = the shining
moon. Barthel. Ce qui est bon. Jaussen according to
Barthel. Meitaki, good, agreeable,
efficacious, excellent, elegant, pious, valid,
brilliant, security, to please, to approve (maitaki);
ariga meitaki, handsome, of pleasant mien;
mea meitaki ka rava, to deserve; meitaki ke,
marvelous, better. Hakameitaki, to make good,
to amend, to do good, to bless, to establish.
Meitakihaga, goodness. PS Pau.: maitaki,
good. Mgv.: meitetaki, beautiful, good. Mq.:
meitai, good, agreeable, fit, wise, virtuous.
Ta.: maitaiki, good, well. Niuē:
mitaki,
good. Maitakia,
clean. Churchill. ...
The pair of restorers of goods (the Gemini twins) once upon
a time had marked the place where the Sun reached the
northern spring *113 - *88 = 25 right ascension days after
the Armpit of Orion (Betelgeuze). The armpit signified
'warming up' (restoring the summer with all its goods). The
Hindu asterism 'Doublegood Pair' (Punarvasu) ought to be
translated into Erua Maitaki ... |
... What happens after (or happened, or
will happen sometime, for this myth is written in the future
tense), is told in the Völuspa, but it is also amplified in
Snorri's Gylfaginning (53), a tale of a strange
encounter of King Gylfi with the Aesir themselves, disguised
as men, who do not reveal their identity but are willing to
answer questions: 'What happens when the whole world has
burned up, the gods are dead, and all of mankind is gone?
You have said earlier, that each human being would go on
living in this or that world.' So it is, goes the answer,
there are several worlds for the good and the bad. Then
Gylfi asks: 'Shall any gods be alive, and shall there be
something of earth and heaven?' And the answer is: 'The
earth rises up from the sea again, and is green and
beautiful and things grow without sowing. Vidar and Vali are
alive, for neither the sea nor the
flames of Surt have hurt them and they dwell on the
Eddyfield, where once stood Asgard.

There come also the sons of Thor, Modi
and Magni, and bring along his hammer. There come also
Balder and Hoder from the other world. All sit down and
converse together. They rehearse their runes and talk of
events of old days. Then they find in the grass the golden
tablets that the Aesir once played with. Two children of men
will also be found safe from the great flames of Surt. Their
names, Lif and Lifthrasir, and they feed on the morning dew
and from this human pair will come a great population which
will fill the earth. And strange to say, the sun, before
being devoured by Fenrir, will have borne a daughter, no
less beautiful and going the same ways as her mother.'
Then, all at once, concludes Snorri's
tale wryly, a thunderous cracking was heard from all sides,
and when the King looked again, he found himself on the open
plain and the great hall had vanished ...
... Ira asked Makoi the following
question: 'How did you fare when you wandered, when you went
searching, when you found yourself on the path of the dream
soul of the father?' Makoi replied, 'There are indeed all
those places. I did not forget them at all (? kai viri
kai viri) when I saw them (text corrected, i-ui-nei).
I alone saw no fewer than four of my places, and I returned
here only because night was falling'. Then Ira spoke again: 'How did you
name them, last-born [hangupotu]?'
Makoi replied, 'This is what happened,
this is how I gave the names. I wrote (ta [?]) 'Te
Manavai A Hau Maka' on the surface of a banana leaf (kaka),
and this is how I left it'.
This is how Makoi remembered it.
No sooner had he said this, when Ira grew angry and
quarreled [he kakai] with Makoi.
He said the following (to him): 'You did not pay attention,
last-born, and you did not [tae] give the (full)
name. This is how it should be [Penei]: the Manavai
of Hau Maka of Hiva, in memory (mo aringa ora)
of the father, of his dream soul'.
Makoi replied, 'In Hiva the land belongs
to him - the land here is mine, not his [tae oona]!'
... [E:21]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Eb3-26 |
Eb3-27 (96) |
Eb3-28 |
Eb3-29 |
Eb3-30 |
Eb3-31 (100) |
|
tagata - e
Tapamea |
ka
pipiri to
ihe |
te
kiore - te
henua |
e
rakau tapamea |
kua tua -
te tino |
kiore - te
henua |
|
Piri.
1. To join (vi, vt); to meet
someone on the road; piriga,
meeting, gathering. 2. To choke:
he-piri te gao. 3. Ka-piri, ka
piri, exclamation: 'So many!'
Ka-piri, kapiri te pipi, so many
shellfish! Also used to welcome
visitors: ka-piri, ka-piri! 4.
Ai-ka-piri ta'a me'e ma'a,
expression used to someone from whom one
hopes to receive some news, like saying
'let's hear what news you bring'. 5.
Kai piri, kai piri, exclamation
expressing: 'such a thing had never
happened to me before'. Kai piri, kai
piri, ia anirá i-piri-mai-ai te me'e
rakerake, such a bad thing had never
happened to me before! Piripiri,
a slug found on the coast, blackish,
which secretes a sticky liquid. Piriu,
a tattoo made on the back of the hand.
Vanaga. 1. With, and. 2. A shock, blow.
3. To stick close to, to apply oneself,
starch; pipiri, to stick, glue,
gum; hakapiri, plaster, to
solder; hakapipiri, to glue, to
gum, to coat, to fasten with a seal;
hakapipirihaga, glue. 4. To
frequent, to join, to meet, to
interview, to contribute, to unite, to
be associated, neighboring; piri mai,
to come, to assemble, a company, in a
body, two together, in mass,
indistinctly; piri ohorua, a
couple; piri putuputu, to
frequent; piri mai piri atu,
sodomy; piri iho, to be addicted
to; pipiri, to catch; hakapiri,
to join together, aggregate, adjust,
apply, associate, equalize, graft, vise,
join, league, patch, unite. Piria;
tagata piria, traitor. Piriaro
(piri 3 - aro), singlet,
undershirt. Pirihaga, to ally,
affinity, league. Piripou (piri
3 - pou), trousers. Piriukona,
tattooing on the hands. Churchill.
Rakau.
Raau, medicine, remedy, drug.
Ra'a'u, scratch on the skin.
Rakau, a plant. Râkau, goods,
property. Vanaga. 1. Wood; rakau ta,
cudgel, stick. P Pau.: rakau,
tree, to dress a wound. Mgv.: rakau,
wood, timber, a tree; medicine, a
remedy; an object. Mq.: ákau,
wood, tree. Ta.: raáu, id. 2.
Medicine, remedy, potion, ointment,
furniture, any precious object,
resources, baggage, riches, heritage,
dowry, merchandise, treasure, wealth;
rakau hakaneinei, purgative;
rakau nui, rich, opulent; rakau
kore, poor, beggar, indigent,
miserable, an inferior; hakakamikami
ki te rakau, to impoverish; rakau
o te miro, ballast. Mq.: akau,
anything in general. The medicine sense
is particularized in Tonga, Nukuoro,
Hawaii, Tahiti, Mangareva, Paumotu. In
no other speech does wood stand so fully
for wealth of possessions, but it will
be recalled that Rapanui is
destitute of timber and depends wholly
upon driftwood. Churchill.
Tino.
1. Belly (as reported by a
Spaniard in 1770). 2. Genitalia (modern
usage). 3. Trunk (of a tree), keel (of a
boat); tino maîka, banana trunk;
tino vaka, keel. Vanaga. Body,
matter; mea tino, material;
tino kore, incorporeal. P Pau.:
tino, a matter, a subject. Mgv.:
tino, the body, trunk. Mq.: tino,
nino, the body. Ta.: tino,
id. Churchill.
 |
*9 |
 |
|
MAY 1 |
July 13 |
|
Eb3-20 |
Eb3-29 |
|
MULIPHEIN |
PROCYON |
|
 |
*15 |
 |
|
kua tuo te tino |
kua tua - te tino |
|
Eb3-15 (84) |
July 14 (195) |
Tuo.
Mgv.: tuo, to speak long without an
answer. Ta.: tuo, to cry out loudly. Ha.: kuo,
to cry with a loud voice. Churchill.
... Long ago in the very beginning of
time there dwelt within a shell an infant god whose name
was Ta'aroa. He was Ta'aroa the unique
one, the ancestor of all gods, the creator of the
universe whose natures were myriad, whose backbone was
the ridgepole of the world, whose ribs were its
supporters. The shell was called Rumia, Upset.
Becoming aware at last of his own existence and
oppressed by a yearning loneliness Ta'aroa broke
open his shell and, looking out, beheld the black
limitless expanse of empty space. Hopefully, he shouted,
but no voice answered him. He was alone in the vast
cosmos. Within the broken Rumia he grew a new
shell to shut out the primeval void ...
|
|
VISIBLE CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
July 10 |
11 |
12 (193) |
13 |
14 |
15 (196) |
 |
|
ALUDRA (Virgin) =
η
Canis Majoris
(111.1),
PROPUS = ι
Gemini (111.4),
GOMEISA (Water-eyed) = β Canis Minoris
(111.6)
*70.0 = *111.4 - *41.4 |
ρ Gemini
(112.1),
Eskimo Nebula
= NGC2392 Gemini
(112.2)
ANTARES (α Scorpii) |
Al Dhirā'-5 (Forearm)
/
Punarvasu-7 (The Two Restorers of Goods)
/
Mash-mashu-Mahrū-10 (Western One of the Twins)
CASTOR (Beaver) = α Gemini (113.4)
*113.4 = *41.4 + *72.0 |
ANA-TAHUA-VAHINE-O-TOA-TE-MANAVA-7
(Pillar for Elocution)
υ Gemini (114.0),
MARKAB PUPPIS = κ Puppis
(114.7), ο Gemini (114.8),
PROCYON = α Canis Minoris
(114.9) |
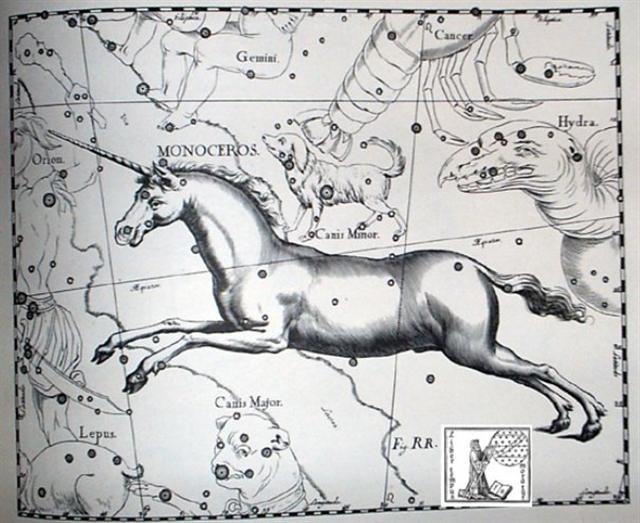
α
Monocerotis (115.4), σ Gemini (115.7)
*74.0 = *115.4 - *41.4 |
Mash-mashu-arkū-11 (Eastern One of the Twins)
κ Gemini (116.1),
POLLUX = β Gemini
(116.2), π Gemini (116.9) |
|
... In Hindu legend
there was a mother goddess called Aditi, who had
seven offspring. She is called 'Mother of the Gods'.
Aditi, whose name means 'free, unbounded, infinity'
was assigned in the ancient lists of constellations as
the regent of the asterism Punarvasu.
Punarvasu is dual in form and means 'The Doublegood
Pair'. The singular form of this noun is used to refer
to the star Pollux. It is not difficult to surmise that
the other member of the Doublegood Pair was Castor. Then
the constellation Punarvasu is quite equivalent
to our Gemini, the Twins. In far antiquity (5800 B.C.)
the spring equinoctial point was predicted by the
heliacal rising of the Twins ...
 |
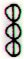 |
 |
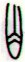 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Eb3-32 |
Eb3-33 |
Eb3-34 |
Eb3-35 (104) |
Eb3-36 |
Eb3-37 |
Eb3-38 |
Eb4-1 (108) |
|
te
maitaki |
te
tagata moko |
te
henua |
te
maitaki |
tagata moko |
te
henua |
Te
maitaki |
te
henua - te
kiore |
|
Moko.
1. Lizard; moko manu uru,
figurine of a
lizard (made of wood). 2. To throw oneself on
something, to take quickly, to snatch; to flee into
the depths (of fish); tagata moko,
interloper, intruder, someone who seizes something
quickly and swiftly, or cleverly intrudes somewhere;
ka-moko ki te kai, ka-moko, ka-aaru, quickly
grab some food, grab and catch. 3. To throw oneself
upon someone, to attack: he-moko, he-reirei,
to attack and kick. 4. Moko roa: to make a
long line (of plantation); moko poto, to make
a short line. 5. Ihu moko; to die out (a
family of which remains only one male without sons);
koro hakamao te mate o te mahigo, he-toe e-tahi
tagata nó, ina aana hakaara, koîa te me'e e-kî-nei:
ku-moko-á te ihu o te mahigo. when the members
of family have died and there remains only one man
who has no offspring, we say: ku-moko-á te ihu o
te mahigo; to disappear (of a tradition, a
custom), me'e ihu moko o te tagata o te kaiga
nei, he êi, the êi is a custom no longer
in use among the people of this island. Vanaga. 1.
Lizard. P Pau., Mgv., Mq.: moko, id. Ta.
moó, id. 2. To stun, to be dizzy. PS Sa.:
mo'o, to be surprised. Hakamoko, to
accomplish. Mokohi, grain, full-grown berry (mokoi);
mokohi haraoa, grain. Mgv.: mokohe,
food. Mokoimokoi, heart T, kidney.
Mokomoko, sharp, pointed, slender, cape,
headland; gutu mokomoko, pointed lips.
Churchill. Mgv.: mokora, a duck. Ta.:
moora, id. Churchill.

... Maui
at first assumed the form of a kiore, or rat,
to enter the body of Hine. But tataeko,
the little whitehead, said he would never succeed in
that form. So he took the form of a toke, or
earth-worm. But tiwaiwaka the fantail, who
did not like worms, was against this. So Maui
turned himself into a moko huruhuru, a kind
of caterpillar that glistens. It was agreed that
this looked best, and so Maui started forth,
with comical movements. The little birds now did
their best to comply with Maui's wish. They
sat as still as they could, and held their beaks
shut tight, and tried not to laugh. But it was
impossible. It was the way Maui went in that
gave them the giggles, and in a moment little
tiwaiwaka the fantail could no longer contain
himself. He laughed out loud, with his merry, cheeky
note, and danced about with delight, his tail
flickering and his beak snapping. Hine nui
awoke with a start. She realised what was happening,
and in a moment it was all over with Maui. By
the way of rebirth he met his end ... ...
The Hawaiians also called the Milky Way Kuamoo,
Backbone of the Lizard. Many Polynesian names for
the Milky Way may be reminiscent of the crocodiles
of Western Melanesia, the moko-roa, 'long
lizards' of legend, for the same motif is found in
various parts of the Pacific. The Tuamotuans termed
the Milky Way Vaero-o-te-moko, Tail of the
Lizard, and Mango-roa, Long Shark. The
Mangaian name Moko-roa-i-ata,
Long-lizard-of-morning, not only sounds the lizard
or crocodile note but also refers to the method of
determining the small hours of the night before the
rising of the morning star. The Maori used the same
term contracted to Mokoroiata. Again they
called the Galaxy Mango-roa, Long
Shark, and Mangoroiata, Long-shark-of-dawn
...

... A une certaine saison, on
amassait des vivres, on faisait fête On emmaillotait
un corail, pierre de défunt lezard, on l'enterrait,
tanu. Cette cérémonie était un point de
départ pour beacoup d'affaires, notamment de
vacances pour le chant des tablettes ou de la
priére, tanu i te tau moko o tana pure,
enterrer la pierre sépulcrale de lézard de sa prière
... |
|
VISIBLE CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
July 16 |
17 (*118) |
18 |
19 |
20 (*121) |
21 |
22 |
23 (204) |
|
AZMIDISKE (Little Shield) =
ξ
Puppis
(117.4)
*116.0 = *117.4 - *41.4 |
Φ
Gemini
(118.4)
*117.0 = *118.4 - *41.4 |
DRUS (Hard) = χ Carinae
(119.9) |
ω Cancri (120.2) |
8h (121.7)
χ
Gemini (121.0),
NAOS (Ship) =
ζ
Puppis
(121.3) |
ρ
Puppis (122.0),
HEAP OF FUEL =
μ
Cancri
(122.1),
ζ
Monocerotis (122.3), ψ
Cancri (122.6),
REGOR (Roger backwards) =
γ
Velorum
(122.7) |
TEGMINE (The Cover) =
ζ
Cancri
(123.3) |
AL TARF (The End) =
β
Cancri
(124.3)
RAS ALGETHI (α Herculis) |
 |
South of the equator, on Easter Island, the seasons of the year
were reversed as compared to the situation north of the equator.
Therefore they could always look at the face of the Full Moon
against the stars of the night in order to see the season which
corresponded to where the Sun was north of the equator. Thus in
July (high summer north of the equator) the Full Moon would be
visible close to the stars which were positioned in January.
I.e. July was a winter month. And when in July the Full Moon was
visible close to Gemini it meant it was high summer on Easter
Island. There were 2 kinds of dance paddles:
 
|

















