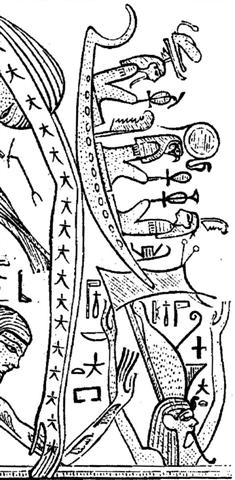
The text on the C tablet has heliacal Polaris at the last glyph on side a. This was the 'pillar-to-fish-by' according to the Tahitian star list, which sounds very much as an allusion to when Maui fished up land. ... This act of Maui's, that gave our people the land on which we live, was an event next in greatness to the separation of the Sky and Earth ... The ancient Egyptians had perceived that the brightest star in the night sky moved at the pace of the Sun, which fact was incorporated into the Julian calendar. ... The Sothic cycle was based on what is referred to in technical jargon as 'the periodic return of the heliacal rising of Sirius', which is the first appearance of this star after a seasonal absence, rising at dawn just ahead of the sun in the eastern portion of the sky. In the case of Sirius the interval between one such rising and the next amounts to exactly 365.25 days - a mathematically harmonious figure, uncomplicated by further decimal points, which is just twelve minutes longer than the duration of the solar year ... In ancient Egypt they thought Sirius was behind the yearly rise of the Nile ... the seasonal cycle, throughout the ancient world, was the foremost sign of rebirth following death, and in Egypt the chronometer of this cycle was the annual flooding of the Nile ... ... At the beginning of 44 B.C. - when Ceasar was still alive - the Senate decided to raise statues of him in all the temples and to sacrifice to him on his birthday in the month Quintilis, which in honour of him was renamed July. He was raised to the status of a god (among the other gods of the state) under the name Jupiter Julius ... Thus Sirius went hand in hand with the Sun and in the G text we have read about this:
... In later research it was postulated that the [Phoenician] alphabet is actually two complete lists, the first dealing with land agriculture and activity, and the second dealing with water, sea and fishing. The first half beginning with Alef - an ox, and ending with Lamed - a whip. The second list begins with Mem - water, and continues with Nun - fish, Samek - fish bones, Ayin - a water spring, Peh - the mouth of a well, Tsadi - to fish, Kof, Resh and Shin are the hook hole, hook head and hook teeth, known to exist from prehistoric times, and the Tav is the mark used to count the fish caught ...
Inspiration from the last pair (Shin and Tav) might have caused a creation of a binome for reaching new land (Alef) in day 88 (MARCH 29) + 64 = 152 (June 1)
... On the twenty-fifth day of the first month (Vaitu Nui), Ira and Makoi set sail; on the first day of June ('Maro'), the bow of Ira's canoe appeared on the distant horizon, came closer and closer on its course, and sailed along, and finally (one) could see the (new home) land ... [E:17] The bow of canoe was its first part and the term for this in MsE was te ihu, possibly a wordplay on ihe in ihe tau. Ihu. 1. Nose; ihu more, snub nose, snub-nosed person. 2. Ihuihu cape, reef; ihuihu - many reefs, dangerous for boats. 3. Ihu moko, to die out (a family of which remains only one male without sons); koro hakamao te mate o te mahigo, he-toe e-tahi tagata nó, ina aana hakaara, koîa te me'e e-kî-nei: ku-moko-á te ihu o te mahigo, when the members of family have died and there remains only one man who has no offspring, we say: ku-moko-á te ihu o te mahigo. To disappear (of a tradition, a custom), me'e ihu moko o te tagata o te kaiga nei, he êi, the êi is a custom no longer in use among the people of this island. 4. Eldest child; first-born; term used alone or in conjunction with atariki. Vanaga. 1. Nose, snout, cape T (iju G). Po ihuihu, prow of a canoe. P Pau.: ihu, nose. Mgv.: ihu, nose; mataihu, cape, promontory. Mq., Ta.: ihu, nose, beak, bowsprit. Ihupagaha, ihupiro, to rap on the nose, to snuffle. 2. Mgv.: One who dives deep. Ta.: ihu, to dive. Churchill. Sa.: isu, nose, snout, bill. Fu., Fakaafo, Aniwa, Manahiki: isu, the nose. Nuguria; kaisu, id. Fotuna: eisu, id. Moiki: ishu, id. To., Niuē, Uvea, Ma., Ta., Ha., Mq., Mgv., Pau., Rapanui, Tongareva, Nukuoro: ihu, id. Rarotonga: putaiu, id. Vaté: tus, id. Viti: uthu, nose. Rotumā: isu, id. ... usu and ngusu ... serve as transition forms, usu pointing to isu the nose in Polynesia and ngusu to ngutu the mouth, which is very near, nearer yet when we bear in mind that ngutu the mouth is snout as well and that isu the nose is snout too ... Churchill 2. Ihe. A fish. Vanaga. 1. Mgv.: ihe, a fish. Mq.: ihe, id. Sa.: ise, id. Ma.: ihe, the garfish. 2. Ta.: ihe, a lance. Ha.: ihe, a spear. Churchill. Tau. Year (ta'u), he-hoa ite ta'u, to confess to a crime committed long ago, by publishing it in the form of a kohau motu mo rogorogo (rongorongo tablet). Vanaga. 1.To hang (tau), to perch (said of chickens on tree branches at night); rock on the coast, taller than others so that something can be deposited on it without fear of seeing it washed away by the waves; hakarere i ruga i te tau, to place something on such a rock; tau kupega, rope from which is hung the oval net used in ature fishing. 2. Pretty, lovely; ka-tau! how pretty! Vanaga. 1. Year, season, epoch, age. P Pau.: tau, a season, period. Mgv.: tau, a year, the season of breadfruit. Mq.: tau, year. Ta.: tau, season, time. 2. Fit, worthy, deserving, opportune; tae tau, impolite, ill-bred, unseemly; pei ra tau, system. PS Mgv.: tau, fit, suitable, proper. Sa.: tau, right, proper. To.: tau, becoming, fit, proper, agreeable. Fu.: tau, fit, proper. 3. To perch. P Pau.: tau, a perch for a bird. Mgv.: tau, to mount on a person's back. Mq.: tau, to perch, to rest on. Ta.: tau, to perch, to alight on. 4. To hang; hakatau, necklace; hakatautau, to append. P Pau.: fakatautau, to hang up. Mq.: tautau, id. Ta.: faatautau, id. 5. Anchor; kona tau, anchorage, port. P Mq.: katau, anchor. Ta.: tau, id. 6. To fight; hakatau, challenge, to defy, to incite; hakatautau, to rival. P Ma.: whakatatau, to quarrel. Churchill. Pau.: fakatau, indolent. Ta.: faatau, id. Fakatautau, to delay, to defer. Ta.: haatautau, id. Churchill. The Malay word for 'year' is taun or tahun. In all Polynesian dialects the primary sense is 'a season', 'a period of time'. In the Samoan group tau or tausanga, besides the primary sense of season, has the definite meaning of 'a period of six months', and conventionally that of 'a year', as on the island of Tonga. Here the word has the further sense of 'the produce of the year', and derivatively 'a year'. In the Society group it simply means 'season'. In the Hawaiian group, when not applied to the summer season, the word keeps its original sense of 'an indefinite period of time', 'a life-time, an age', and is never applied to the year: its duration may be more or less than a year, according to circumstances. So far our authority (Fornander, I, 124; cp. 119). It seems however to be questionable whether the original sense is not the concrete 'produce of the seasons', rather than the abstract 'period of time'. It is significant that on the Society Islands the bread-fruit season is called te tau, and the names of the other two seasons, te tau miti rahi and te tau poai, are formed by adding to this name. Nilsson. The word tau could be used for 'hanging', and a hanging fish (ika reva) is what Metoro saw at Bb1-1. Here. 1. To catch eels in a snare of sliding knots; pole used in this manner of fishing, with a perforation for the line. 2. To tie, to fasten, to lash; rasp made of a piece of obsidian with one rough side; cable, tie; figuratively: pact, treatise. Vanaga. 1. To lash, to belay, to knot the end of a cord, to lace, to tie, to fasten, to knot; to catch in a noose, to strangle, to garrote; here pepe, to saddle; moa herea, a trussed fowl; hehere, collar, necklet; herega, bond, ligament; heregao, scarf, cravat. 2. Hakahere. To buy, to sell, to barter, to part with, to pay for, to do business, to compensate, to owe, to disburse, to expiate, to indemnify, to rent out, to hire, to traffic, to bargain, to bribe; merchant, trader, business, revenge; tagata hakahere, merchant, trader; hakahere ki te ika, to avenge; hakaherega, ransom, redemption; hakahererua, to exchange, to avenge. 3. Here ei hoiho, incense. Churchill. Hereke, festering wound, cracked skin. Barthel 2. A 'hanging fish' (kua reva te ika)
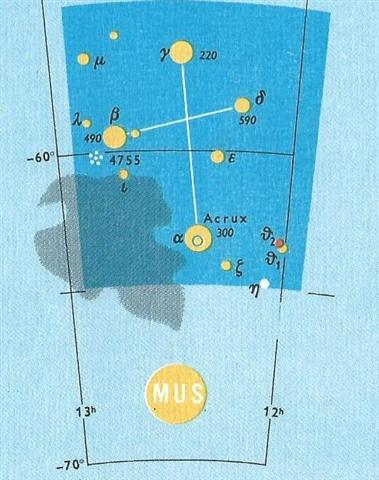
could also have referred to as rau hei. Mimosa was β (490) Crucis:
Thus there were several stars which could be referred to as 'pillar-to-fish-by'. The name of the 10th and last star in the Tahitian list, Ana-nia (Polaris), should probably be read as Ana-nika. Nika. 'Savage tribes knew the Pleiades familiarly, as well as did the people of ancient and modern civilization; and Ellis wrote of the natives of the Society and Tonga Islands, who called these stars Matarii, the Little Eyes: The two seasons of the year were divided by the Pleiades; the first, Matarii i nia, the Pleiades Above, commenced when, in the evening, those stars appeared on the horizon, and continued while, after sunset, they were above. The other season, Matarii i raro, the Pleiades Below, began when, at sunset, they ceased to be visible, and continued till, in the evening, they appeared again above the horizon. Gill gives a similar story from the Hervey group, where the Little Eyes are Matariki, and at one time but a single star, so bright that their god Tane in envy got hold of Aumea, our Aldebaran, and, accompanied by Mere, our Sirius, chased the offender, who took refuge in a stream. Mere, however, drained off the water, and Tane hurled Aumea at the fugitive, breaking him into the six pieces that we now see, whence the native name for the fragments, Tauono, the Six, quoted by Flammarion as Tau, both titles singularly like the Latin Taurus. They were the favorite one of the various avelas, or guides at sea in night voyages from one island to another; and, as opening the year, objects of worship down to 1857, when Christianity prevailed throughout these islands.' (Allen) From Polaris (471) to Tau-ono (500) there were 29 right ascension days.
Although fishing in ancient Egypt (where everything was upside down - with up in the south and down in the north) was done with a net:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||