|
RIGEL
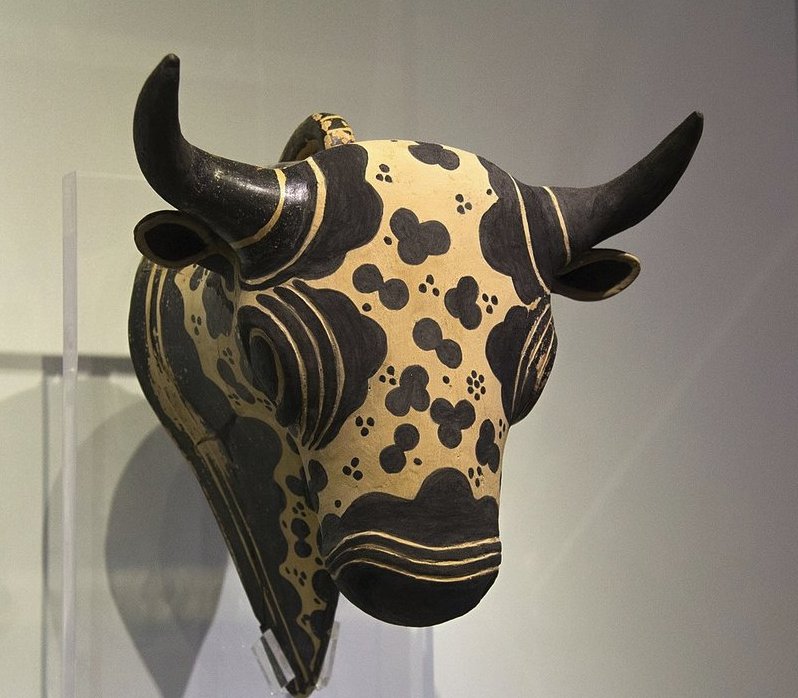
Neither were sacred names chosen haphazardly, for instance should we perhaps read the Easter Island toro in toro-miro as a word fetched from the Spanish toro = bull. ... A man had a daughter who possessed a wonderful bow and arrow, with which she was able to bring down everything she wanted. But she was lazy and was constantly sleeping. At this her father was angry and said: 'Do not be always sleeping, but take thy bow and shoot at the navel of the ocean, so that we may get fire.' The navel of the ocean was a vast whirlpool in which sticks for making fire by friction were drifting about. At that time men were still without fire. Now the maiden seized her bow, shot into the navel of the ocean, and the material for fire-rubbing sprang ashore ...
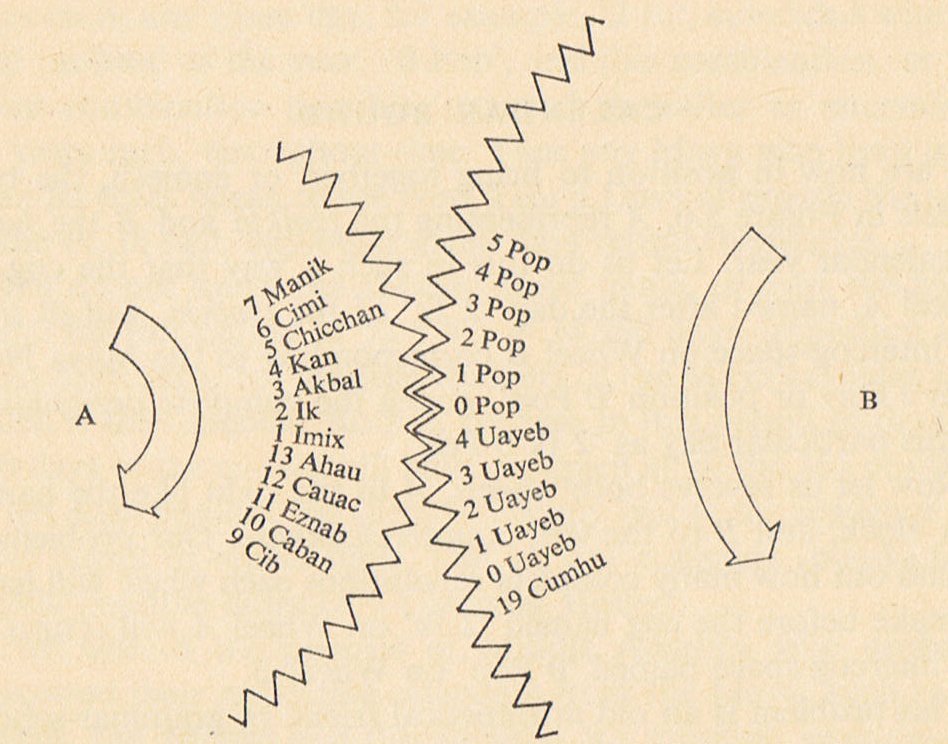
Unavoidably we will here associate this great creative event with the fact that not only the G tablet but also the D tablet seem to have been designed with the origin of the text at the 'Eye of the Bull' - i.e. the star named Ain (ε Tauri, *65):
... About Carmenta we know from the historian Dionysus Periergetis that she gave orcales to Hercules and lived to the age of 110 years. 110 was a canonical number, the ideal age which every Egyptian wished to reach and the age at which, for example, the patriarch Joseph died. The 110 years were made up of twenty-two Etruscan lustra of five years each; and 110 years composed the 'cycle' taken over from the Etruscans by the Romans. At the end of each cycle they corrected irregularities in the solar calendar by intercalation and held Secular Games. The secret sense of 22 - sacred numbers were never chosen haphazardly - is that it is the measure of the circumference of the circle when the diameter is 7. This proportion, now known as pi, is no longer a religious secret; and is used today only as a rule-of-thumb formula, the real mathematical value of pi being a decimal figure which nobody has yet been able work out because it goes on without ever ending, as 22 / 7 does, in a neat recurring sequence [3.142857142857 ...]. Seven lustra add up to thirty-five years, and thirty-five at Rome was the age at which a man was held to reach his prime and might be elected Consul ...
And we can see this also from the beginning of the C text. For the dates in the Sun calendar remained unchanged against the background of the fixed stars - although apparently moving in the calendar due to the precession of the equinoxes and solstices:
I am suggesting we should provisionally read toro in the 'Tree' named toro-miro as an allusion to the Spanish word for Bull. In which case this 'Bull Tree' would grow for 260 days after MARCH 22.
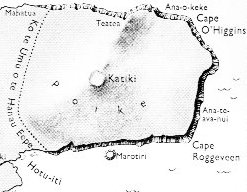
In Chile the official language was Spanish. ... On the following day, 20 November 1770, Commander José Bustillo took formal possession of Easter Island 'in the name of the King and of Spain, our Lord and Master Don Carlos the third', renaming the island 'San Carlos'. Several hundred Rapanui - probably members of the Koro 'o 'Orongo tribe of the eastern 'Otu 'Iti - observed the ceremony not far from Poike's parasitic cones Parehe, Teatea, and Vai 'a Heva, on the tops of which the Spaniards had planted three crosses ...
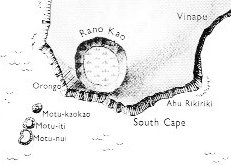
We can perceive a contrast between these 3 'dry trees' planted high up on the Poike (place aloft) peninsula in comparison to the single still living toromiro tree down in the watery crater of Rano Kau on the opposite side of Easter Island.
Kau. 1. To move one's feet (walking or swimming); ana oho koe, ana kau i te va'e, ka rava a me'e mo kai, if you go and move your feet, you'll get something to eat; kakau (or also kaukau), move yourself swimming. 2. To spread (of plants): ku-kau-áte kumara, the sweet potatoes have spread, have grown a lot. 3. To swarm, to mill around (of people): ku-kau-á te gagata i mu'a i tou hare, there's a crowd of people milling about in front of your house. 4. To flood (of water after the rain): ku-kau-á te vai haho, the water has flooded out (of a container such as a taheta). 5. To increase, to multiply: ku-kau-á te moa, the chickens have multiplied. 6. Wide, large: Rano Kau, 'Wide Crater' (name of the volcano in the southwest corner of the island). 7. Expression of admiration: kau-ké-ké! how big! hare kau-kéké! what a big house! tagata hakari kau-kéké! what a stout man! Vanaga. To bathe, to swim; hakakau, to make to swim. P Pau., Mgv., Mq.: kau, to swim. Ta.: áu, id. Kauhaga, swimming. Churchill. The stem kau does not appear independently in any language of Polynesian proper. For tree and for timber we have the composite lakau in various stages of transformation. But kau will also be found as an initial component of various tree names. It is in Viti that we first find it in free existence. In Melanesia this form is rare. It occurs as kau in Efaté, Sesake, Epi, Nguna, and perhaps may be preserved in Aneityum; as gau in Marina; as au in Motu and somewhere in the Solomon islands. The triplicity of the Efaté forms [kasu, kas, kau] suggests a possible transition. Kasu and kas are easy to be correlated, kasu and kau less easy. They might be linked by the assumption of a parent form kahu, from which each might derive. This would appear in modern Samoan as kau; but I have found it the rule that even the mildest aspirate in Proto-Samoan becoming extinct in modern Samoan is yet retained as aspiration in Nuclear Polynesia and as th in Viti, none of which mutations is found on this record. Churchill 2 Kahu. Clothing, dress, habit, cloth, curtain, vestment, veil, shirt, sheet; kahu hakaviri, shroud; kahu nui, gown; rima o te kahu, sleeve; kahu rahirahi, muslin; hare kahi, tent; horega kahu, shirt; hakarivariva ki te kahu, toilet; rakai ki te kahu, toilet; patu ki te kahu, to undress; kahu oruga, royal sail; kahu hakatepetepe, jib; kahu nui, foresail; hakatopa ki te kahu, to set sail; (hecki keho, canvas T.) P Pau.: kahu, dress, garment, native cloth. Mgv.: kahu, cloth, stuff, garment, clothing. Mq.: kahu, habit, vestment, stuff, tunic. Ta.: ahu, cloth in general, vestment, mantle. Chuchill.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||