25. There was a time when rakau 'lost his nut'.
In order to build a ship wooden planks were needed and Naos (ζ in Argo Navis) was the star at the corner of the shield close to the leftmost of the vertical ropes. It is difficult to see what Hevelius has pictured on this shield but possibly it could be a kind of twisted tree:
Canopus (α) is the great star at the rudder of Argo Navis, below Naos, and there were 26 (= 2 * 13) days from Canopus to Naos (ζ). Probably Ca5-14 illustrates the Egyptian X in order to make clear that Naos coincided with the rakau ahead:
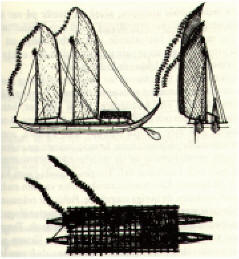
... He cleared the trunks of their branches and bark, hewed them into shape, and with strong fau ropes he and his men drew them down the valley over cliffs and ravines, seeming to feel it merely light work. Thus King Puna was robbed of his fine aha-tea tree, his mara-uri tree, a toi (Alphitonia) tree, and a hauou (pua, Fagraea) tree; and Hiro spared not the trees sacred to the gods around the marae. He cut down a great tamanu (Callophylum), stripped the trunk of its branches and bark, split it up for planks for the bows of his canoe, and trimmed the branches for outriggers and crossbeams. He cut down a most sacred miro (Thespesia) tree for planks for the after part of his canoe, and he took two tall straight breadfruit trees for planks for the deck houses. Then he went into the woods and cut down straight fau trees (Hibiscus tiliaceus) for paddles and for floor planks, and three slim hutu (Barringtonia) trees for masts. After all this depredation, Hiro and his men helped themselves to wood and thatch and reeds and all other material needed for a shed in which to build the canoe and for rollers to place under it, King Puna not daring to oppose them, as Hiro was too powerful and dangerous to vex ... Amid all the required ceremonies and prayers and good omens, they set to work. On rising ground they erected a great shed thirty fathoms long, six wide, and five fathoms high, facing the sea endwise. The builders had their baskets of axes and adzes of stone, gimlets of coconut and sea shells, and sennit of fine tight strands, prepared and consecrated to the god Tane for this special purpose. Hiro marked out the keel, the knees, the beams, and the planks, and the men cut them into shape. All the material for the work was carefully sorted and handily placed in the shed, Hiro passing it to the men as they required it ... They set the keel of avai, toi, and mara wood, polished and firmly spliced together with hard spikes of wood secured with sennit, upon rollers in the shed and painted it with red clay mixed with charcoal so as to preserve it from wood borers. Then they fastened the knees onto the keel with spikes and sennit. Holes were bored into the keel and planks at even distances apart, and the men set to work in the following order: Hotu, the chief of Hiro's artisans, worked on the outer side to the right of the canoe, and Tau-mariari, his assistant, worked on the inner side; Memeru, the royal artisan of Opoa, worked on the outer side to the left of the canoe, and his assistant, Ma'i-hae, worked on the inner side. Each couple faced each other, fixing the planks in their places and drawing the sennit in and out in lacing the wood together; and the canoe soon began to assume form, the bows facing the sea. To make work light they sang ... Every seam and all the little holes in the wood from the keel and upwards were well caulked with fine coconut-husk fiber and pitched carefully with gum, which Hiro drew from sacred breadfruit trees of the marae, and when all the streaks were on the canoe was washed out clean and dried well and painted inside and outside with red clay and charcoal. As the hull of the canoe reached almost to the roof, the builders could work no longer within the shed, and so they broke it away. Then the boards of the deck were set upon the beams and fixed in place with spikes and sennit, and the ama or outrigger of tamanu wood, which had been well steeped in water to preserve it from borers, was polished with limestone and firmly lashed with sennit on to the left side of the canoe, the upper attachment of wood forming across each end of the canoe a beam, called 'iato, and lashed on to the right side in the same manner as on the left side ... Next came the finely carved towering ornaments for a reimua (neck-in-front, the figurehead) and a rei muri (neck-behind, stern ornament), which were fastened on to their respective places, and they were named Rei-fa'aapiapi-fare (Necks-filling-up-the-house), because the shed was broken away to allow placing them and finishing the canoe. The two deck houses, called oa mua and oa muri (fore house and aft house), were then set in their places and thatched with fara leaves, after which Hotu, the chief artisan, cut out the holes in the deck and down in the keel, in which he stood the three masts, before mentioned, which had been steeped in water, well seasoned, dried, and polished. The the canoe was completed. Hiro dedicated it to Tane, naming it Hohoio (Interloper) ... Finally the day arrived for launching the canoe, and a great multitude assembled to see the wonderful sight. The props were removed from the sides of the canoe, and the men held it ready to launch over the rollers. Hotu invoked the gods Ta'aroa, Tane, 'Oro, Ra'a, Ro'o, and Moe, to their aid, and soon their presence was felt impelling the canoe. The rollers began to move, and then the canoe went forwards, slowly at first as the men's hands steadied it and then swiftly and well poised as it gracefully descended alone and sat upon the sea, which rose in great rolling waves caused by a wind sent to meet it by the aster Ana-mua (Antares in Scorpio), the parent pillar of the sky. The spectators greatly admired Hiro's ship and raised deafening shouts. Then the canoe was made to drink salt water; it was dipped forwards and backwards in the waves of the great moving altar of the gods and thus consecrated to Tane. A marae was made for him in the little house aft of the deck, and the three masts were rigged with ropes and strong mats for sails and long tapa pennants streaming from them ... Within a few days the canoe was loaded with provisions. Great fish baskets were made of bamboo, filled with many kinds of fish, and attached to the outside of the canoe so as to be in the water. Bamboos and gourds were filled with water and stowed away on board, and there were fe'i, bananas, taro, and mahi (fermented breadfruit) in abundance. A bed of sand and stones was made upon the deck, upon which to make a fire for cooking the food, and soon Hiro was ready to go to sea. Hiro was the captain and pilot, and he had other competent seamen, who like him were acquainted with the heavenly bodies and their rising and setting. Women and children also accompanied their husbands and fathers on board, and on one fine day, with a strong favorable wind, they set sail, applauded by many spectators, among whom were prisoners of war (called tītī), whose shouts were heard above all others. They saw Hiro's great pahi sail out to sea and disappear beyond the horizon, never again to return to Tahitian shores ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||