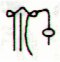
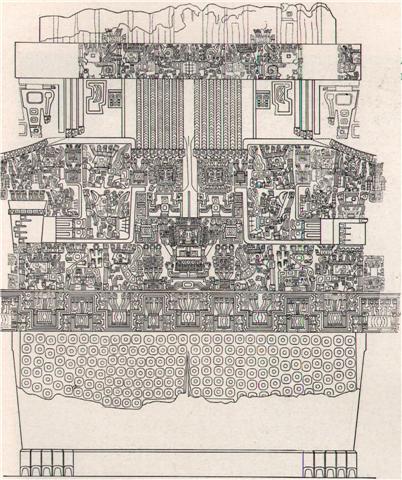
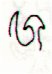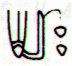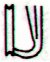206. Then we should consider the tresses of Pacha-mama (the ground, the food-giving earth), because these support my interpretation of an initial time frame based on Betelgeuze (*88) at the Full Moon:
... Counting again in the tresses of Pachamama - after having realized it was probably the number of apexes which mattered - the intended order indeed comes clearly into view ...
At the time of Betelgeuze day 210 counted from 0h would have been at Cb1-1, but counting from the Julian equinox day 210 would have been at Cb1-5:
The central 'tree' - like the wooden shaft of an arrow, a dart, or a spear - which divides the 14 tresses of Pachamama into 7 + 7 could have corresponded to the winter solstice. ... A vestige of the practice of putting the king to death at the end of a year's reign appears to have survived in the festival called Macahity, which used to be celebrated in Hawaii during the last month of the year. About a hundred years ago a Russian voyager described the custom as follows: 'The taboo Macahity is not unlike to our festival of Christmas. It continues a whole month, during which the people amuse themselves with dances, plays, and sham-fights of every kind. The king must open this festival wherever he is. On this occasion his majesty dresses himself in his richest cloak and helmet, and is paddled in a canoe along the shore, followed sometimes by many of his subjects. He embarks early, and must finish his excursion at sunrise. The strongest and most expert of the warriors is chosen to receive him on his landing. The warrior watches the canoe along the beach; and as soon as the king lands, and has thrown off his cloak, he darts his spear at him, from a distance of about thirty paces, and the king must either catch the spear in his hand, or suffer from it: there is no jesting in the business. Having caught it, he carries it under his arm, with the sharp end downwards, into the temple or heavoo. On his entrance, the assembled multitude begin their sham-fights, and immediately the air is obscured by clouds of spears, made for the occasion with blunted ends. Hamamea (the king) has been frequently advised to abolish this ridiculous ceremony, in which he risks his life every year; but to no effect. His answer always is, that he is as able to catch a spear as any one on the island is to throw it at him. During the Macahity, all punishments are remitted throughout the country; and no person can leave the place in which he commences these holidays, let the affair be ever so important ...
The right side of her tresses (182) could therefore be multiplied with 2 and her left side tresses divided by 2. After the solstice there was growth ('multiplication') but before the solstice there was the reverse. Notably, however, 182 * 2 + 214 / 7 = 471 (= 314 * 1.5 = the number of glyphs on the G tablet).
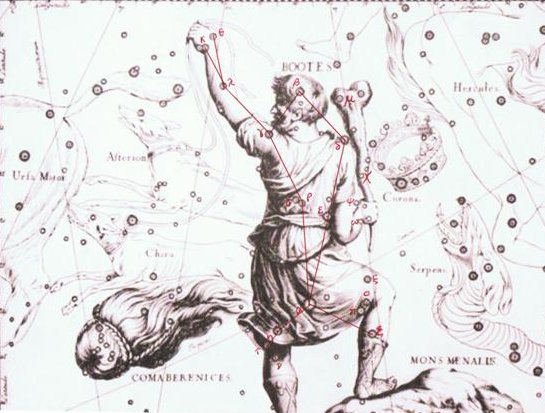
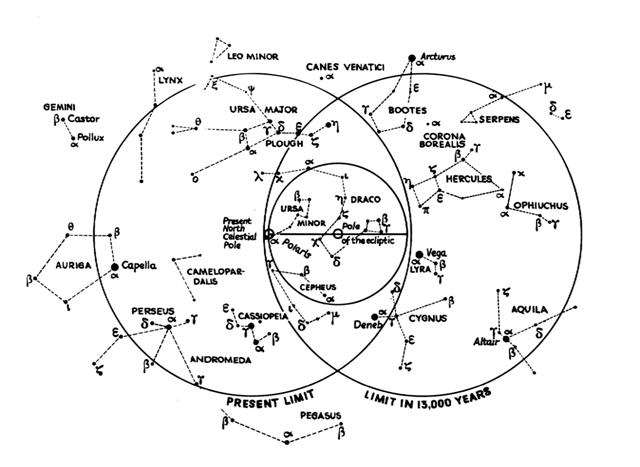
Arcturus is at the 'tail' of Bootes. ... Mons Maenalus, at the feet of Boötes, was formed by Hevelius, and published in his Firmamentum Sobiescianum; this title coinciding with those of neighboring stellar groups bearing Arcadian names. It is sometimes, although incorrectly, given as Mons Menelaus, - perhaps, as Smyth suggested, after the Alexandrian astronomer referred to by Ptolemy and Plutarch. The Germans know it as the Berg Menalus; and the Italians as Menalo. Landseer has a striking representation of the Husbandsman, as he styles Boötes, with sickle and staff, standing on this constellation figure. A possible explanation of its origin may be found in what Hewitt writes in his Essays on the Ruling Races of Prehistoric Times: The Sun-god thence climbed up the mother-mountain of the Kushika race as the constellation Hercules, who is depicted in the old traditional pictorial astronomy as climbing painfully up the hill to reach the constellation of the Tortoise, now called Lyra, and thus attain the polar star Vega, which was the polar star from 10000 to 8000 B.C. May not this modern companion constellation, Mons Maenalus, be from a recollection of this early Hindu conception of our Hercules transferred to the adjacent Bootes? Once upon a time Thuban had been the star at the pole.
The vertical shaft between 182 and 214 could have pointed at the winter solstice and towards the star at the north pole - which was outside the rising and setting in the east respectively in the west, outside the cycles of birth and death. At first I tried to count also the fractional parts of the tresses and then my result became 400:
This could be interpreted as a statement saying that there were 4 extra nights outside the regular order of the calendar structure, corresponding to a measure for the shaft of the 'ridgepole': ... The Sacred Book of the ancient Maya Quiche, the famous Popol Vuh (the Book of Counsel) tells of Zipacna, son of Vucub-Caquix (= Seven Arata). He sees 400 youths dragging a huge log that they want as a ridgepole for their house. Zipacna alone carries the tree without effort to the spot where a hole has been dug for the post to support the ridgepole. The youths, jealous and afraid, try to kill Zipacna by crushing him in the hole, but he escapes and brings down the house on their heads. They are removed to the sky, in a 'group', and the Pleiades are called after them ... 4 meant death: ... Delta (uppercase Δ, lowercase δ) ... is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 4. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Dalet ... Dalet (dāleth, also spelled Daleth or Daled) is the fourth letter of many Semitic alphabets ... The letter is based on a glyph of the Middle Bronze Age alphabets, probably called dalt 'door' (door in Modern Hebrew is delet), ultimately based on a hieroglyph depicting a door ... ... Tammuz was a month in the Babylonian calendar, named for one of the main Babylonian gods, Tammuz (Sumerian: Dumuzid, 'son of life'). Many different calendar systems have since adopted Tammuz to refer to a month in the summer season. In the Hebrew calendar, Tammuz is the tenth month of the civil year and the fourth month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar. It is a summer month of 29 days. Tammuz is also the name for the month of July in the Gregorian calendar ... ... The two great stars, which marks the summit and the foot of the Cross, having nearly the same right ascension, it follows that the constellation is almost perpendicular at the moment when it passes the meridian. This circumstance is known to the people of every nation situated beyond the Tropics or in the southern hemisphere. It has been observed at what hour of the night, in different seasons, the Cross is erect or inclined. It is a time piece, which advances very regularly nearly four minutes a day, and no other group of stars affords to the naked eye an observation of time so easily made. How often have we heard our guides exclaim in the savannahs of Venezuela and in the desert extending from Lima to Truxillo, 'Midnight is past, the Cross begins to bend' ... Crux lies in the Milky Way, - here a brilliant but narrow stream three or four degrees wide, - and is noticeable from its compression as well as its form, being only 6º in extent from north to south, and less in width, the upper star a clear orange in color, and the rest white; the general effect being that of a badly made kite, rather than a cross ... ... Barthel informs us that the Maori singers in New Zealand, where the breadfruit did not grow, 'translated' kuru (= breadfruit) in the old songs - from the times when their forefathers lived in a warmer climate - into poporo. He points out that in the Marquesas they counted the fruits from the breadfruit trees in fours, perhaps thereby explaining the four 'berries' in this type of glyph. The breadfruit did not grow on Easter Island but the berries of Solanum nigrum were eaten in times of famine. Barthel compares with the word koporo on Mangareva. The poor crop of breadfruits at the end of the harvest season was called mei-koporo, where mei stood for breadfruit. On other islands breadfruit was called kuru, except in the Marquesas which also used the word mei. Koporo was a species of nightshade ... ... The four of them (corrected for 'the six of them') went out and picked up leaves (on branches) to give signals. They picked them up, went and arrived at Te Hikinga and saw the canoe. Raparenga got up, picked up the leaves, took them in his hands, and waved, waved, waved, waved ... Lau, s. Haw., to feel for, spread out, expand, be broad, numerous; s. leaf of a tree or plant, expanse, place where people dwell, the end, point; sc. extension of a thing; the number four hundred ... ... On the south-western tip of Easter Island, at Orongo, up near the ragged edge of the Rano Kau crater, are four small holes very precisely pecked through the bedrock just beside a large Ahu. Since Orongo is known to have been an important ritual centre, these holes attracted the attention of the Norwegian Archaeological Expedition which visited the island in 1955-56. They were studied by Dr Edwin Ferdon. After making detailed observations at the solstices and the equinoxes he concluded: 'it can definitely be stated that the complex of four holes constituted a sun-observation device' ... ... The king, wearing the belt with her four faces and the tail of her mighty bull, moved in numerous processions, preceded by his four standards, from one temple to the next, presenting favors (not offerings) to the gods ... The king, wearing now a short, stiff archaic mantle, walks in a grave and stately manner to the sanctuary of the wolf-god Upwaut, the 'Opener of the Way', where he anoints the sacred standard and, preceded by this, marches to the palace chapel, into which he disappears. A period of time elapses during which the pharaoh is no longer manifest. When he reappears he is clothed as in the Narmer palette, wearing the kilt with Hathor belt and bull's tail attatched. In his right hand he holds the flail scepter and in his left, instead of the usual crook of the Good Shepherd, an object resembling a small scroll, called the Will, the House Document, or Secret of the Two Partners, which he exhibits in triumph, proclaiming to all in attendance that it was given him by his dead father Osiris, in the presence of the earth-god Geb. 'I have run', he cries, 'holding the Secret of the Two Partners, the Will that my father has given me before Geb. I have passed through the land and touched the four sides of it. I traverse it as I desire.' ... the shift in the date of the equinox that occurred between the 4th and the 16th centuries was annulled with the Gregorian calendar, but nothing was done for the first four centuries of the Julian calendar. The days of 29 February of the years AD 100, AD 200, AD 300, and the day created by the irregular application of leap years between the assassination of Caesar and the decree of Augustus re-arranging the calendar in AD 8, remained in effect ... ... All four of them felt like turning back at once, but Maui by his enchantments made the sea stretch out between their canoe and the land, and by the time they had turned the canoe round they saw that they were much further out than they had thought. 'You might as well let me stay now; I can do the bailing', said Maui, picking up the carved wooden bailing scoop that was lying beside the bailing-place of the canoe. The brothers exchanged glances and shrugged their shoulders. There was not much point in objecting, so they resumed their paddling, and when they reached the place where they usually fished, one of them went to put the stone achor overboard ... ... In Andean thought both world and time were divided into four sectors or directions unified under a presiding fifth principle. The Tawantinsuyu - 'the indivisible four quarters' - was unified and presided over by Cusco, the center. Similarly, history was divided into four previous ages, presided over by a fifth, the present. In his book, Waman Puma organizes the history of both Old and New worlds according to this scheme. The Old Testament and the pre-Inca times are each divided into four equivalent and parallel ages. The 'present' age in Peru begins with the appearance of Manku Qhapaq, the first Inca, a being of supernatural origin. And in the Old World the 'present' starts with the birth of Jesus Christ ... ... Quetzalcoatl, her child, who is known both as the Son of the Lord of the High Heavens and as the Son of the Lord of the Seven Caves, was endowed at birth with speech, all knowledge, and all wisdom, and in later life, as priest-king, was of such purity of character that his realm flourished gloriously throughout the period of his reign. His temple-palace was composed of four radiant apartments: one toward the east, yellow with gold; one towards the west, blue with turquoise and jade; one toward the south, white with pearls and shells; one towards the north, red with bloodstones - symbolizing the cardinal quarters of the world over which the light of the sun holds sway. And it was set wonderfully above a mighty river that passed through the midst of the city of Tula; so that every night, precisely at midnight, the king descended into the river to bathe; and the place of his bath was called 'In the Painted Vase', or 'In the Precious Waters' ... The king remained four days in his underground tomb, and when he came forth he wept and told his people that the time had come for his departure to the Red Land, the Dark Land, the Land of Fire. Having burned his dwellings behind him, buried his treasures in the mountains, transformed his chocolate trees into mesquite, and commanded his multicolored birds to fly before him, Quetzalcoatl, in great sorrow, departed. Resting at a certain place along the way and looking back in the direction of Tula, his City of the Sun, he wept, and his tears went through a rock [creating sinkholes]; he left in that place the mark of his sitting and the impress of his palms. Farther along, he was met and challenged by a company of necromancers, who prevented him from proceeding until he had left with them the arts of working silver, wood, and feathers, and the art of painting. As he crossed the mountains, many of his attendants, who were dwarfs and humpbacks, died of the cold. At another place he met his dark antagonist, Tezcatlipoca, who defeated him at a game of ball. At still another he aimed with an arrow at a large pochotl tree; and the arrow too was a pochotl tree, so that when he shot it through the first they formed a cross. And so he passed along, leaving many signs and place-names behind him, until, coming at last to where the sky, land, and water come together, he departed. He sailed away on a raft of serpents, according to one version, but another has it that his remaining attendants built a funeral pyre, into which he threw himself, and while the body burned, his heart departed and after four days appeared as the rising planet Venus. All agree, however, that he will presently return. He will arrive with a fair-faced retinue from the east and resume sway over his people; for although Tezcatlipoca had conquered, those immutable laws that had determined the destruction of Tula assigned likewise its restoration. Quetzalcoatl was not dead. In one of his statues he was shown reclining, covered with wrappings, signifying that he was absent or 'as one who lays him down to sleep, and that when he should wake from that dream of absence, would rise to rule again the land'. He had built mansions underground to the Lord of Mictlan, the lord of the dead, but did not occupy these himself, dwelling, rather, in that land of gold where the sun abides at night. This too, however, is underground. Certain caverns lead to it, one of which, called Cincalco, 'To the Abode of Abundance', is south of Chapultepec; and through its gloomy corridors men can reach that happy land, the habitation of the sun, which is still ruled by Quetzalcoatl. Moreover, that land is the land from which he came in the beginning ... ... The name [Benetnash] derives from the Arabic phrase meaning 'The leader of the daughters of the bier'. The daughters of the bier, i.e. the mourning maidens, are the three stars of the handle of the Big Dipper, Alkaid, Mizar, and Alioth; while the four stars of the bowl, Megrez, Phecda, Merak, and Dubhe, are the bier ... ... The manik, with the tzab, or serpent's rattles as prefix, runs across Madrid tz. 22 , the figures in the pictures all holding the rattle; it runs across the hunting scenes of Madrid tz. 61, 62, and finally appears in all four clauses of tz. 175, the so-called 'baptism' tzolkin. It seems impossible, with all this, to avoid assigning the value of grasping or receiving. But in the final confirmation, we have the direct evidence of the signs for East and West. For the East we have the glyph Ahau-Kin, the Lord Sun, the Lord of Day; for the West we have Manik-Kin, exactly corresponding to the term Chikin, the biting or eating of the Sun, seizing it in the mouth ... ... 4 March 1779. The British ships are again at Kaua'i, their last days in the islands, some thirteen months since their initial visit. A number of Hawaiian men come on board and under the direction of their women, who remain alongside in the canoes, the men deposit navel cords of newborn children in cracks of the ships' decks (Beaglehole 1967:1225). For an analogous behavior observed by the missionary Fison on the Polynesian island of Rotuma, see Frazer (1911, 1:184). Hawaiians are connected to ancestors (auumakua), as well as to living kinsmen and descendants, by several cords emanating from various parts of the body but alike called piko, 'umbilical cord'. In this connection, Mrs. Pukui discusses the incident at Kaua'i: I have seen many old people with small containers for the umbilical cords... One grandmother took the cords of her four grandchildren and dropped them into Alenuihaha channel. 'I want my granddaughters to travel across the sea!' she told me. Mrs. Pukui believes that the story of women hiding their babies' pikos in Captain Cook's ship is probably true. Cook was first thought to be the god Lono, and his ship his 'floating island'. What woman wouldn't want her baby's piko there? ... The four bereaved and searching divinities, the two mothers and their two sons, were joined by a fifth, the moon-god Thoth (who appears sometimes in the form of an ibis-headed scribe, at other times in the form of a baboon), and together they found all of Osiris save his genital member, which had been swallowed by a fish. They tightly swathed the broken body in linen bandages, and when they performed over it the rites that thereafter were to be continued in Egypt in the ceremonial burial of kings, Isis fanned the corpse with her wings and Osiris revived, to become the ruler of the dead. He now sits majestically in the underworld, in the Hall of the Two Truths, assisted by forty-two assessors, one from each of the principal districts of Egypt; and there he judges the souls of the dead. These confess before him, and when their hearts have been weighed in a balance against a feather, receive, according to their lives, the reward of virtue and the punishment of sin ... ... Alphard was the 4th star 'pillar' in the Tahitian list and from there to Antares there were *249 - *142 = 107 days. 471 (number of glyphs on the G tablet) - 107 = 364 (= 52 weeks) ... Interestingly, since another meaning of shi is 'death', the number 4 is considered unlucky. For example, the floor numbering in hotels sometimes jumps mysteriously from 3 to 5; it is also considered unlucky to give four of something as a present ... Etc., etc. ... As soon as one has mastered the elementary grammar and accidence of myth, and built up a small vocabulary, and learned to distinguish seasonal myths from historical and iconotropic myths, one is surprised how close to the surface lie the explanations, lost since pre-Homeric times, of legends that are still religiously conserved as part of our European cultural inheritance. For example, the various legends of the halcyon, or kingfisher which like the wren, is associated in Greek myth with the winter solstice. There were fourteen 'halcyon days' in every year, seven of which fell before the winter solstice, seven after, peaceful days when the sea was smooth as a pond and the hen-halcyon built a floating nest and hatched out her young. According to Plutarch and Aelian, she had another habit, of carrying her dead mate on her back over the sea and mourning him with a peculiarly plaintive cry ...
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||