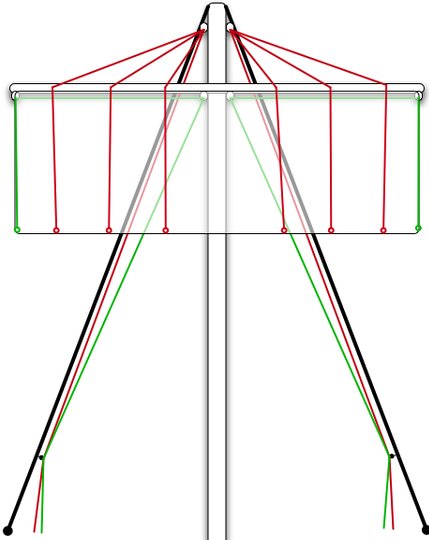
According to Manuscript E the journey of the Sun King across the sea did not begin until after 6 days necessary for loading his canoe: ... During the reign of Matua, the Hanau Eepe came [he ea]. They stole [he toke] one side (etahi painga) of the land of he king of Hanau Momoko and moved [he hakaneke] the border [te tita'a koîa] from their side toward the side of the Hanau Momoko. Five hundred [erima te rau] Hanau Eepe stole the land of the king of the Hanau Momoko. [E:53]. ... 'Oh, you, why [mo-te-aha] have you violated [toke] the borders of my [tooku] land?' The Hanau Eepe answered, 'There is not enough land [he kainga kore] to live on!' WI, adj. Haw., destitute, suffering, starving; s. starvation, famine; wiwi, lean, meagre; hoo-wiwi, to lessen, diminish. Marqu., wiwi, poor, feeble; wiwi-i, solitude. Tah., veve, poor, destitute, bare; v. to be in want. Sanskr., vi, prep. 'compounded with verbs and nouns it implies: 1. separation; 2. privation; 3. wrongness, baseness', &c. (Benfey); as vi-deha, without body; vi-dharâ, without man, a widow; vi-dhantâ, poverty, without wealth. Lat., ve or vi, in compound words, as ve-cors, without reason, frantic; ve-grandis, not large, small; ve-sanus, out of the senses, raving unsound; vi-duus, vi-dua, without husband or wife, widower, widow. Of other things, empty, void, without. Goth, widuwo, A.-Sax., wuduwa, widow. Benfey (Sanskr. Dict., s. v.) leads one to infer that vi is but an aphærsis of dui. It seems to me that the natural inference, and the natural turn of men's thoughts, would be that dui, two, implied addition rather than diminution. It is possible that the Sanskrit dui may have been 'worn down', as Professor Sayce calls it, to a preposition or mere affix, not only in the Sanskrit, but also in the Gothic and Latin; but with a substantial Polynesian wi still alive indicating destitution, deprivation, diminution, I incline to consider the latter as the base of, and proper relative to, the Sanskrit, Gothic, and Latin preposition or affix. (Fornander) Thereupon the king called out [he rangi] to the Hanau Eepe, 'Here I stand, and I tell all of you: I am taking [he too au] you prisoners [he puru] and I am locking you up in the house of prisoners (hare kopu) for fifty [50, erima te kauatu] years!' Then the king called out [he rangi] to his men, 'Seize [ka too] all of them, and lock up all of the Hanau Eepe! Lock them up [ka puru] for good!' [E:55 → right ascension day corresponding to May 15 (365 + 135 = 500)].
... Matua [A Taana] said to Hotu [A Matua], 'Take along the Hanau Eepe and let them work the land!' Hotu called out to Heke: 'Go and bring the 500 prisoners on board the canoe!' He took all of them along, led them on board the canoe, and left them there. For six days (po ono), mats (moenga) were taken on board the canoe (i.e., the loading of the canoe took six days) ... [E:73-74] These 6 days ought to correspond to the first 6 glyphs in line Ga7:
The first glyph in the line is a viri:
Presumably we should in this case translate viri with 'clew': Viri. 1. To wind, to coil, to roll up; he viri i te hau, to wind, coil a string (to fasten something). 2. To fall from a height, rolling over, to hurl down, to fling down. Viriviri, round, spherical (said of small objects). Viviri te henua, to feel dizzy (also: mimiro te henua). Vanaga. To turn in a circle, to clew up, to groom, to twist, to dive from a height, to roll (kaviri). Hakaviri, crank, to groom, to turn a wheel, to revolve, to screw, to beat down; kahu hakaviri, shroud. Viriga, rolling, danger. Viriviri, ball, round, oval, bridge, roll, summit, shroud, to twist, to wheel round, to wallow. Hakaviriviri, to roll, to round; rima hakaviriviri, stroke of the flat, fisticuff. P Pau.: viriviri, to brail, to clew up; koviriviri, twisting. Mgv.: viri, to roll, to turn, to twist; viviri, to fall to the ground again and again in a fight. Mq.: vii, to slide, to roll, to fall and roll. Ta.: viri, to roll up, to clew up. Viritopa, danger. Mgv.: Viripogi, eyes heavy with sleep. Mq.: viipoki, swooning, vertigo. Churchill.Viti: vili, to pick up fallen fruit or leaves ... In Viti virimbai has the meaning of putting up a fence (mbai fence); viri does not appear independently in this use, but it is undoubtedly homogenetic with Samoan vili, which has a basic meaning of going around; virikoro then signifies the ring-fence-that-goes-about, sc. the moon. In the Maori, aokoro is the cloud-fence ... Churchill 2.
... The substitution of the sun for the sail, both of which are called ra or raa in Polynesia, is a remarkable feature in Easter Island art ... LA, s. Haw., sun, light, day. N. Zeal., ra, sun, day. Marqu., a, id. Sam., la, id. Deriv.: Haw., lae, be light, clear, shining; lai, shining as the surface of the sea, calm, still; laelae and lailai, intens. Sam., lelei, something very good; lala, to shine; lalangi, to broil. Fiji., rai, to see, appear; rai-rai, a seer, a prophet. Teor., la, sun. Aru Islands, lara, id.; rarie, bright, shining. Amblaw., laei, sun, day. Irish, la, lae, day. Laghmani (Cabul), la'e, day. Sanskr., laj, lanj, to appear, shine; râj, to shine. Ved., to govern; s. a king. If, as Benfey intimates, the Sanskrit verb bhrâj, to shine, to beam, is 'probably abhi-râj', an already Vedic contraction, then the Polynesian root-word al and lae will reappear in several of the West Aryan dialects. Lat., flagrare, flamma, flamen. Greek, φλεγω, φλοξ. A.-Sax., blac, blæcan, &c. Probably the universal Polynesian lani, langi, rangi, ra'i, lanits (Malg.) designating the upper air, sky, heaven, and an epithet of chiefs, refers itself to the same original la, lai, lanj, referred to above, to which also be referred: Welsh, glan, clean pure, bright, holy. Sax. clæne, clean, pure. Swed., ren, clean. pure; grann (?), fine, elegant. It may be noted in connection with this word, either as a coincidence or as an instance of ancient connection, that in the old Chaldean the name of the sun and of the Supreme Deity was Ra, and that in Egypt the sun was also named Ra. LA², s. Haw., Sam., Tong., ra. N. Zeal., the sail of a canoe; abbreviated from, or itself an older form of, the Fiji. laca, a sail, also the mats from which the sails were made. Sunda., Mal., layar, sail. Malg., laï, sail, tent, flag. Sanskr., lâta (Pictet), a cloth; latâ (Benfey), a creeper, a plant; lak-taka, a rag. As mats and clothing in primitive times were made of bark or flexible plants, the connection between the Sanskrit latâ and Polynesian laca, la, becomes intelligible. Armen., lôtig, a mantle. Lat., lodix, a blanket. Irish, lothar, clothing. (Fornander) To which should be added Leech. ... Likāvaka is the name of the father - a canoe-builder, while his son is Kuikava...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



.jpg)