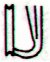The structure of the A text is not the same as that of the 3 closely correlated texts on the H, P, and Q tablets. The fish-hook on the A tablet is in line a1 and the long oar of ash seems to have induced 8 lines of glyphs on each side of the tablet.
Barthel has assigned the side carrying the fish-hook we have discussed as the front side (a), and that may well be so. However, when Metoro was reading for Bishop Jaussen he began with side b.
The counting was probably to begin at the little viri in Ab1-1, viz. 60 right ascension days after the old 'head-off' one on side a. We should think in terms of right ascension days instead of such days which were defined in the Sun calendar. Right ascension days are more general in character, more useful.
The diurnal night-and-day cycle could be observed to replicate itself in the winter-and-summer cycle of the year.
... If my suggestion be admitted that the Babylonians dealt not with the daily fight but the yearly fight between light and darkness - that is, the antithesis between day and night was expanded into the antithesis between the summer and the winter halves of the year - then it is clear that at the vernal equinox Scorpio setting in the west would be watching the sunrise; at the autumnal equinox rising in the east, it would be watching the sunset; one part would be visible in the sky, the other would be below the horizon in the celestial waters. If this be so, all obscurity disappears, and we have merely a very beautiful statement of a fact, from which we learn that the time to which the fact applied was about 3000 B.C., if the sun were then near the Pleiades ... The words of Metoro at the beginning of line Ab1 were certainly in agreement with his words early on side b on the C tablet:
The drums were sounding (rutua te pahu) - when light went down it meant sound became more important - Rutu. 1. To read, to recite, to pronounce words solemnly; he-rutu i te kohau motu, to read the rongorongo tablets; hare rutu rogorogo mo hakama'a ki te ga poki ite kai, i te rogorogo, rongorongo school, house in which children were taught reading and writing the rongorongo signs. 2. To pelt with stones. 3. To gather in great numbers (of people). Vanaga. Sound. Rutu-rongorongo = the sound of recitation. Barthel. T. Beat. Henry. To recite; tae rutu, irreverence. Churchill. Pau.: rutu, a drum. Mgv.: rutu, to beat, to cause to resound. Ta.: rutu, a drum, to drum. Mq.: utu, to drum. Sa.: lutu, to shake a rattle. Churchill. Pahu. Drum. Pahu-rutu-roa = Long-beating-drum. Barthel. M. Pahū. Tree gong. Starzecka. Pahu uma, coffin; in modern usage, any sort of jar. Pahupahu = To dig a hole. Vanaga. A trough, barrel, cask, cradle, drum, chest, box; pahu nui, a kettle; pahu oka, a drawer; pahu papaku, coffin; pahu rikiriki, sheath; pahu viriviri, hogshead. Pahupahu, box. Churchill. A trough, barrel, cask, cradle, drum, chest, box; pahu nui, a kettle; pahu oka, a drawer; pahu papaku, coffin; pahu rikiriki, sheath; pahu viriviri, hogshead; pahupahu, box. P Mgv., Ta.: pahu, a drum. Mq.: pahu, a drum, a large cylindrical container. (To.: bahu, a hollow tree set in water as a filter.) Sa.: pusa, a box. To.: buha, id. Fu.: pusa, id. Niue: puha, id. Pau.: puha, id. Pahuahi, lantern, beacon. Paukumi, closet, cupboard. Pahupopo, a mould; pahupopokai, cupboard for food. Pahure: 1. To sweep everything away. 2. To wound, to lacerate, scar, bruise, lesion, sore; pahurehure, to wound, to scratch; hakapahure, to wound. T Pau.: pahure, to be skinned; pahore, to peel off, to scale. Mgv.: pahore, to cut off, to chop, to slice. Ta.: pahore, to flay, to skin. Churchill 2.
... The [tun] glyph is nearly the same as that for the month Pax (T549), except that the top part of the latter is split or divided by two curving lines. Brinton, without referring to the Pax glyph, identified the tun glyph as the drum called in Yucatec pax che (pax 'musical instrument'; che < *te 'wooden). Yucatec pax means 'broken, disappeared', and Quiche paxih means, among other things, 'split, divide, break, separate'. It would seem that the dividing lines on the Pax glyph may have been used as a semantic/phonetic determinative indicating that the drum should be read pax, not tun (cf. de Gruyter 1946, p. 27). Thus, one may expect that this glyph was used elsewhere meaning 'to break' and possibly for 'medicine' (Yuc. pax, Tzel., Tzo. pox) ... and, it seems, the sky was responding. Maeva. T. 1. Move. Rangi-maeva = Moving Sky (name of a marae). 2. Greet, greeting. Henry. ... It was 4 August 1968, and it was the feast day of Saint Dominic, patron of Santo Domingo Pueblo, southwest of Santa Fe. At one end of the hot, dusty plaza, a Dominican priest watched nervously as several hundred dancers arranged in two long rows pounded the earth with their moccasined feet as a mighty, collective prayer for rain, accompanied by the powerful baritone singing of a chorus and the beat of drums. As my family and I viewed this, the largest and in some ways the most impressive Native American public ceremony, a tiny cloud over the Jémez Mountains to the northwest got larger and larger, eventually filling up the sky; at last the storm broke, and the sky was crisscrossed by lightning and the pueblo resounded with peals of rolling thunder ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||