Beyond *78 came he kape (the bitter plant in contrast to the sweet preceding one, he ti):
In Manuscript E (E:69) has then been listed a pair of trees which did not belong to anyone:
However, it was Taane Mahuta who pushed Father Sky and Mother Earth apart, letting in air and light, enabling life to thrive upon land:
... They were Ranginui, the Sky Father, and Papatuanuku, the Earth Mother, both sealed together in a close embrace. Crushed between the weight of their bodies were their many children, whose oppression deepened. They yearned to be free; they fought their parents and each other to break loose. Tuumatauenga, virile god of war, thrust and shouted; Tangaroa of the oceans whirled and surged; Tawhirirangimaatea, Haumiatiketike and Rongomatane, of wild foods and cultivated crops, tried their best but were not successful; and Ruamoko, god of earthquakes, yet to be born, struggled in the confinement of his mother's womb ... Of them all, Taane Mahuta [cfr Mahute, Boussonetia papyrifera], the god of the forests, was the most determined; he set his sturdy feet upon his father's chest, and braced his upper back and shoulders against the bosom of his mother. He pushed; and they parted. So the world, as the Maori understand it, came into being ... The dark closed embrace which preceded this tearing apart could therefore have been associated with the season of he hauhau.
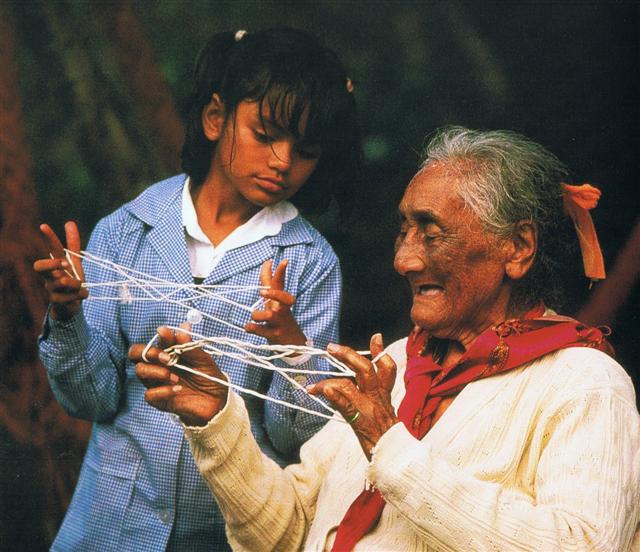
Hau = Thread, line, string, ribbon; this is the name of the fibres of the hauhau tree formerly used to make twine, cloth, etc.; hau kahi, fishing line for tuna; hau here, line for eel trap; hau moroki, strong, tough line, thread; hau paka, fibres of the hauhau tree, which were first soaked in water, then dried to produce a strong thread. Ha'u = Hat. Vanaga. Hat, cord; the tree Triumfetta semitriloba. Van Tilburg. Ta.: The tree Hibiscus tiliaceus. Henry. Hau. 1 a. Hibiscus. b. Wick. P Pau.: fau, hibiscus. Mgv.: hau, id. Mq.: fau, hau, id. Ta.: fau, id. 2. To contribute. Ta.: aufau, to pay, to contribute, to subscribe. 3. Hat, cap, helmet; hakarere ki te hau, to take off the hat. Ta.: fauurumaa, war bonnet. 4. Dew; hakaritorito ki te hau, to bleach in the dew. P Mgv., Mq.,Ta.: hau, dew. 5. To blow freshly, coolness, zephyr, salubrious, breeze, wind (hahau, ahau); kona hauhau, kona hahau, a breezy spot; ahau ora, agreeable breeze; hakahahau, to hang out in the air; hakaahau, to blow. T Mgv.: hau, to blow, blusterous, to breathe. Haua, hoarse. (Hauha); araha hauha, to wait for, to look forward to. Hauhau, 1. dog (onomatopoetic). 2 a. To scratch, to scrape, to rub. b. Wood used in plowing fire. 3. (hau 5). Haumaru (hau 5 - marumaru) cool, cold. Hauł, to replace. Hauva, twin, cut T. Hauvaero (hau 3 - vaero) plume, aigrette, head ornament. Hauvarikapau (hau 3 - varikapau) plume, aigrette, head ornament. Churchill. Pau.: Hau, superior, kingdom, to rule. Mgv.: hau, respect. Ta.: hau, government. Mq.: hau, id. Sa.: sauā, despotic. Ma.: hau, superior. Hauhau, to attack. Ma.: hau, to chop. Churchill. Sa.: fau, to tie together, to fasten by tying, the tree (Hibiscus tiliaceus) whose bast is used for cord, the kava strainer made therefrom, strings in various uses; fafau, to lash on, to fasten with sennit; faufau, to fasten on, to tie together. To.: fau, to fasten up the hair, the name of the hibiscus, the kava strainer made therefrom; faufau, to fasten the outriggers of small canoes; hau, to fasten to; fehauaki, to tie. Fu.: fau, the hibiscus, the kava strainer; fał, fafał, fałfał, to attach, to tie. Niuē: fau, fafau, to make by tying. Fotuna: no-fausia, to tie, to fasten. Ta.: fau, the hibiscus; fafau, to tie together. Pau.: fau, the hibiscus. Nuguria: hau, id. Ma.: hau, to bind, to fasten together; whau, a shrub; whauwhau, to tie. Ha.: hau, name of a tree with a practicable bark. Mq.: hau, the hibiscus. Mgv.: hau, id.; hahau, to join or tie with cords. Nukuoro: hau, the hibiscus, a garland. Mg.: au, the hibiscus. Vi.: vau, the hibiscus; vautha, to bind together. Churchill 2. ... And long did they consider further. At the end of a time no man can measure the five decided that Rangi and Papa must be forced apart, and they began by turns to attempt this deed. First Rongo ma Tane, god and father of the cultivated food of men, rose up and strove to force the heavens from the earth. When Rongo had failed, next Tangaroa, god and father of all things that live in the sea, rose up. He struggled mightily, but had no luck. And next Haumia tiketike, god and father of uncultivated food, rose up and tried without success. So then Tu matauenga, god of war, leapt up. Tu hacked at the sinews that bound the Earth and Sky, and made them bleed, and this gave rise to ochre, or red clay, the sacred colour. Yet even Tu, the fiercest of the sons, could not with all his strength sever Rangi from Papa. So then it became the turn of Tane mahuta. Slowly, slowly as the kauri tree did Tane rise between the Earth and Sky. At first he strove with his arms to move them, but with no success. Then he placed his shoulders against the Earth his mother, and his feet against the Sky. Soon, and yet not soon, for the time was vast, the Sky and Earth began to yield. The sinews [uaua] that bound them stretched and ripped. With heavy groans and shrieks of pain, the parents of the sons cried out and asked them why they did this crime, why did they wish to slay their parents' love? Great Tane thrust with all his strength, which was the strength of growth. Far beneath him he pressed the Earth. Far above he thrust the Sky, and held them there ... Strings from the hauhau tree could initially have bound Sky and Earth close together. Therefore it would not be wise to play with strings before the Sun securely had lifted from the horizon. ... string games could be resumed after it was clear that the Sun had managed to leave the horizon and was rapidly gaining in altitude: 'Before the sun starts to leave the horizon ... when it shows only on the horizon, ... then string games were no longer allowed as they might lacerate the sun. Once the sun had started to go higher and could be seen in its entirety, string games could be resumed, if one so wished. So the restriction on playing string games was only applicable during the period between the sun's return and its rising fully above the horizon ...
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||