Later, on Easter Island, a new uhi plantation was created
by Ngukuu, alias Kuukuu:
|
E:18 |
| i te kai te uta.hee totoi i te vaka
ki uta he ha(-) |
They went ashore and took
the food [te kai] with them. They pulled the
canoe onto the beach and left it there.
Ira sat down [he noho] with all the other
(companions) and spoke to Makoi [ka ki era kia Makoi]:
'You shall mark the land for me and make it known (by
its name)!'
After that, Ira spoke these words: 'This is the
diggning stick (? ko koko], Kuukuu. You shall
work the land for me and plant the yam roots [te uhi]!' |
| karere.he noho a ira anake.he ki a
Ira.ka ki era |
| kia Makoi.maau e tuki e haite te
kainga.he ki |
| hokoou a Ira.ka ki era.kokoko
e Nguukuu e. |
| maau e keukeu
e oka te uhi. |
| Keu. Communal
enterprise, work done in common: mo te keu. for
the work done in common (for instance: collecting food
mo te keu, to give to the helpers). Keukeu:
1. To work; to work long and steadily: he-keukeu te
aga; tagata keukeu henua, farmer. 2. To get ready,
e.g. for a trip: ka-keukeu koe, ki oho tâtou. get
ready, we are going; ka-keukeu ki turu ki tai, ki hî,
get ready for going down to the sea, to fish. 3. To
approach (of rain): he-keukeu te ûa. Vanaga.
Oka. 1.
Lever, pole; to dig holes in the ground with a sharpened
stick, as was done in ancient times to plant vegetables;
used generally in the meaning of making plantations. 2.
The four sideways poles supporting a hare paega.
Okaoka, to jab, to pierce, to prick repeatedly.
Vanaga. Digging stick, stake, joist; to prick, to
pierce, to stick a thing into, to drive into, to
slaughter, to assassinate; |
| He nape mai a
Makoi.i te ingoa.ko hanga te pau |
Makoi named the place Hanga
Te Pau, 'the landing site of Ira'. So that they would
remember (? he aringa, literally, 'as face'), the
open side [ko mua] of Hanga Te Pau was given this
name. |
| ko te tomonga o
Ira.he aringa.ko mua a hanga |
| te pau.i
nape ai te ingoa. |
|
Pau. 1. To run
out (food, water): ekó pau te kai, te vai, is
said when there is an abundance of food or water, and
there is no fear of running out. Puna pau, a
small natural well near the quarry where the 'hats' (pukao)
were made; it was so called because only a little water
could be drawn from it every day and it ran dry very
soon. 2. Va'e pau, clubfoot. Paupau:
Curved. Vanaga. 1. Hakapau, to pierce (cf.
takapau, to thrust into). Pau.: pau, a cut, a
wound, bruised, black and blue. 2. Resin. Mq.: epau,
resin. Ta.: tepau, gum, pitch, resin. (Paupau)
Hakapaupau, grimace, ironry, to grin. 3. Paura
(powder), gunpowder. 4. Pau.: paupau, breathless.
Ta.: paupau, id. 5. Ta.: pau, consumed,
expended. Sa.: pau, to come to an end. Ma.:
pau, finished. 6. Ta.: pau, to wet one
another. Mq.: pau, to moisten. Churchill. Paua
or pāua
is the Māori name given to three species of large
edible sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs which
belong to the family Haliotidae (genus
Haliotis), known in the USA as abalone, and in the
UK as ormer shells ... Wikipedia |
| he ea.a
Ira.he iri he oho
ki runga anake. |
Ira got up. They all climbed to the top
of the hill. |
| Ea. To rise, to get
up. Ka ea ki táû rikiriki tâtou. Let's get up and
play a little game of war. Vanaga. To go out, to bring
out; ea ki aho, to send away; raa ea mai,
the sun rises; ka ea, be off. Churchill.
Iri. 1. To go up; to go in a boat on the sea
(the surface of which gives the impression of going up
from the coast): he-eke te tagata ki ruga ki te vaka,
he-iri ki te Hakakaiga, the men boarded the boat and
went up to Hakakainga. 2. Ka-iri ki puku toiri
ka toiri. Obscure expression of an ancient curse.
Vanaga. Iri-are, a seaweed. Vanaga.
Ruga.
Upper part, higher part; when used as a locative adverb,
it is preceded by a preposition: i ruga, above,
on; ki ruga, upwards, mai ruga, from
above. When used with a noun the same preposition is
repeated: he-ea te vî'e Vakai, he-iri ki ruga ki te
Ahu ruga, the woman Vakai went, she climbed Ahu
Runga. Ruga nui, high, elevated, lofty: kona
ruga nui, high place, elevated position, high
office; mana'u ruga nui, elevated thoughts.
Vanaga. High up; a ruga, above; ki ruga,
on, above, upon; ma ruga, above; o ruga,
upper; kahu o ruga, royal (sail); ruga iho,
celestial. Hakaruga, to accumulate, to draw up. P
Pau., Mgv.: ruga, above. Mq.: úna, úka,
id. Ta.: nua, nia, id. Churchill. |
| i te angahuru o
te raa o te maro |
They climbed up on the tenth
day of the month of June ('Maro).
They reached the side crater (te manavai) and looked
around carefully.
Makoi said, 'This is the Manavai of Hau Maka'. |
| i iri ai.he tuu ki te manavai hee
rarama. |
| he ki a Makoi.ko
te manavai a hau maka |
| Manavai. Hollow
where rainwater accumulates; anciently, small, round
gardens, preferably situated in low shady spots, where
the mahute tree was grown. Vanaga. 1. Brain. 2.
Valley, ravine, river, torrent, brook; manavai miro,
orchard, Mq.: manavai, valley, brook. Ta.:
anavai, river, brook. It scarcely appears that these
are fully coordinate. In Tahiti anavai has a
clear etymology, ana meaning the bed of a stream.
In Rapanui and in the Marquesas mana most readily
associates with maga, as water in a forked bed.
Churchill.
Mahute. A tree (Boussonetia papyrifera)
formerly more abundant on the island, the fibres of
which were used for clothing (see nua and hami).
Vanaga. The tree Broussonetia papyrifera,
indispensible for all types of fasteners (lines, twine,
ropes, and rigging). Barthel 2. Maute, paper
mulberry (mahute G). P Mgv.: eute, ute,
id. Mq.: ute, id. Ta.: aute, Hibiscus
rosa-sinensis. Pau.: aute, id. Mahutehute
(mahute - tutu 1) bast cloth in the last
stage of preparation (maute). Churchill. |
| he iri he oho he tuu ki runga he ui i
te poko uri |
They climbed farther and
reached the top. They saw the dark abyss and the large
hole (of the crater Rano Kau).
They all said, 'Here it is, young men [repa],
the dark abyss of Hau Maka.' |
| he tikea
te pakonga he ki anake i ana nei |
| e kau a repa e a
te poko uri a hau maka. |
|
Tikea. To see,
to perceive, to examine, to find; (also: tikera).
Vanaga. To see, to feel, to recognize, to perceive, to
know, manifest, to appreciate; tikea mai, to
appear, visible; tikea horahorau, to skim a book;
tae tikea, unknown, invisible, misunderstand,
unperceived, unheard; tikeahaga, science, a
dream; hakatikea, to announce, to make known, to
prove, to propose, to prejudice, to show, immodest;
hakatikeahaga, instruction. Churchill.
Poko. 1.
Fragrant; to smell, to give off a smell: he-poko te
eo, it gives off a pleasant smell. 2. To hunt, to
catch with a trap, to snare. He-kî e Tori: maaku-á
e-ea ki te manu, e-poko i te po i ruga i te opata.
Tori said: I shall go and catch birds at night, up on
the cliff. 3. Thunder (also hatutiri). 4. (Also:
pokopoko.) Hollow, hole, depression, any deep,
concave object; to leave in a hole, in a depression.
Pokoga, chasm; summit. Pokohata, female rat:
kio'e pokohata. Pokopoko, woman bent under
the weight of her years: vî'e pokopoko. Vanaga.
1. Sound of the sea; tai poko, breakers.
Pokopoko, to slap water. Mgv.: pokokina,
resonant, clear-toned. Mq.: poko, to slap the
water in imitation of drumming; pokokina, sound
of water. 2. Rut, beaten path. P Pau.: poko,
hollow; pokopoko, concave, to excavate. Mgv.:
poko, to dig, to excavate, to hollow out. Mq.:
pokoko, to crack open; pokona, to hollow out,
to excavate. Ta.: poópoó, hollow, deep. 3.
Infernal; pokoga, hell, infernal cave; topa ki
te pokoga, to damn (lit: to go down to hell.) Mq.:
pokona, cavity, hole. Churchill. Pokopoko:
1. Womb. PS Sa.: po'opo'o, clitoris. Mq.:
pokopoko, pudendum muliebre. 2. Pokopoko
vae, footprints. 3. Concave, deep, ditch,
mysterious; pokopoko ihu, nostril (Ta.:
poópoó ihu); pokopoko ke,
fathomless; pokopoko taheta, concave.
Hakapokopoko, to deepen. Chuchill.
Uri.
1. Dark; black-and-blue. 2. Green;
ki oti te toga, he-uri te maúku o te kaiga, te kumara,
te taro, te tahi hoki me'e, once winter is over, the
grasses grow green, and the sweet potatoes, and the
taro, and the other plants. Uriuri, black; very
dark. Vanaga. Uriuri, black, brown, gray, dark,
green, blue, violet (hurihuri). Hakahurihuri,
dark, obscurity, to darken. P Pau.: uriuri,
black. Mgv.: uriuri, black, very dark, color of
the deep sea, any vivid color. Mq.: uiui, black,
brown. Ta.: uri, black. Churchill. Uli, s.
Haw., the blue sky; adj., blue, cerulean, green;
uli-uli, verdure; adj., green, dark-coloured, black.
Sam., Tong., Fak., uli; Tah., uri,
blue-black, any dark colour. Fornander. |
| he noho o(i)ra he hakatuu i te
hare.he ea a |
They made camp and
constructed a house [te hare]. Kuukuu got up,
worked the ground, and heaped up the earth for the yam
roots [he puke i te uhi]. |
| kuukuu he
keukeu he puke i te uhi. |
They climbed up to the top of the hill and here a house was
constructed and here a yam plantation was created - for at the
top there was a square piece of fertile land, a Field:
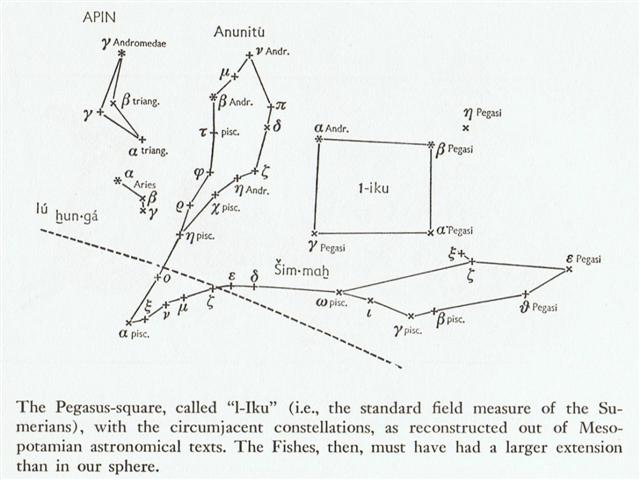
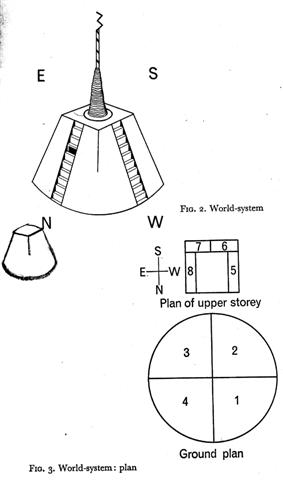

... I walked towards it now, and spent some
time strolling around it and clambering over it. Originally it
had been a clean-sided step-pyramid of earth faced with large
andesite blocks. In the centuries since the conquest, however,
it had been used as a quarry by builders from as far away as La
Paz, with the result that only about ten per cent of its superb
facing blocks now remained. What clues, what evidence, had those
nameless thieves carried off with them? As I climbed up the
broken sides and around the deep grassy troughs in the top of
the Akapana, I realized that the true function of the
pyramid was probably never going to be understood. All that was
certain was that it had not been merely decorative or
ceremonial. On the contrary, it seemed almost as though it might
have functioned as some kind of arcane 'device' or machine. Deep
within its bowels, archaeologists had discovered a complex
network of zigzagging stone channels, lined with fine ashlars.
These had been meticulously angled and jointed (to a tolerance
of one-fiftieth of an inch), and had served to sluice water down
from a large reservoir at the top of the structure, through a
series of descending levels, to a moat that encircled the entire
site, washing against the pyramid's base on its southern side
...
And here was a door leading to the interior.
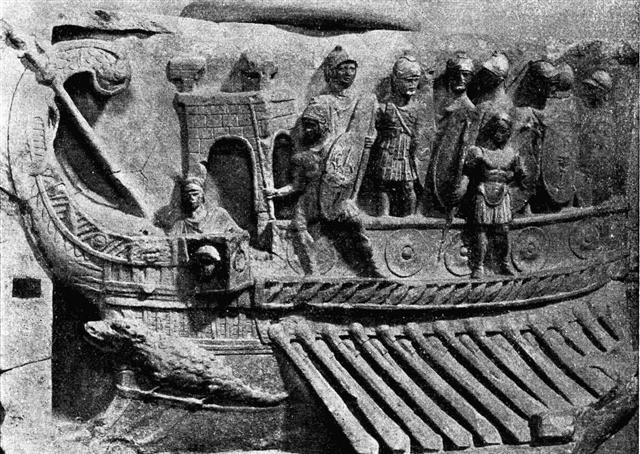

... Then the canoe was made to drink salt
water; it was dipped forwards and backwards in the waves of the
great moving altar of the gods and thus consecrated to Tane.
A marae was made for him in the little house aft of the
deck, and the three masts were rigged with ropes and strong mats
for sails and long tapa pennants streaming from them
...

And this (female) entrance should be hidden by a piece of cloth:


... There is still more to the barkcloth. The
barkcloth which provides access for the god/chief and signifies
his sovereignity is the preeminent feminine valuable (i yau)
in Fiji. It is the highest product of woman's labor, and as such
a principal good of ceremonial exchange (soolevu). The
chief's accession is mediated by the object that saliently
signifies women ... That Fijian
barkcloth, woman's good, which provides the path for the god
also functions in everyday life as a loincloth, concealing -
culturalizing - the primary site of male power. There is a
contradiction latent in the chief's appropriation of 'the
barkcloth of the land'. As Hocart puts it, barkcloth is used to
'catch' the spirit' ...
The date given in Manuscript E for creating the yam plantation
on Easter Island was "June 10 (Te Maro 10) - i te angahuru o
te raa o te maro.Thus it
was the beginning of the Dark month of Father Light (Jus
Piter).
... Midsummer is the flowering season of the
oak, which is the tree of endurance and triumph, and like the
ash is said to 'court the lightning flash'. Its roots are
believed to extend as deep underground as its branches rise in
the air - Virgil mentions this - which makes it emblematic of a
god whose law runs both in Heaven and in the Underworld ...
The month, which takes its name from Juppiter the oak-god,
begins on June 10th and ends of July 7th. Midway comes St.
John's Day, June 24th, the day on which the oak-king was
sacrificially burned alive. The Celtic year was divided into two
halves with the second half beginning in July, apparently after
a seven-day wake, or funeral feast, in the oak-king's honour ...
On Easter Island the winter solstice was in June, and they
were surely aware of the fact that the ocean floor was very
far down - only the top of the great Rapa Nui mountain
which was resting on
this floor constituted inhabitable land, viz. 'the little
clod of earth' (Te Pei) - close to
Te Pou.
... Hau Maka told about his dream: 'I was sleeping, and this is
what happened: My dream soul moved on, and, through the power of
her mana, my dream soul reached seven [ehitu]
lands, which were lying in the midst of a dim twilight. My dream
soul looked around searchingly, but these lands were not very
good at all. In the midst of dim twilight there is Te Pei, the
residence. Not even eight [evaru] groups of people (i.e.,
countless boat crews) can find the small piece (of land?) again
once it has been lost ... (E:12)
... He went off to further explore the area. He went along and
came to the 'dark rat'.
He looked around and said [he ki]:
'Here we are at the dark rat of Hau Maka'. He gave it the name [he
nape i te ingoa] 'Te Kioe Uri A Hau Maka'. He went on
[again, hokoou] and came to Te Piringa Aniva. When he
arrived there, he looked around and gave the name 'Te Piringa
Aniva'. He went on and came to Te Pei, looked around, and said,
'Here it is!' So he gave the name 'Te Pei A Hau Maka'. He went
on, all alone [hokotahi] he went on, and came to Te Pou.
When he arrived there, he looked around and again said 'Here it
is!' [he ki hokoou i ana nei] and gave the name 'Te Pou A
Hau Maka'
... (E:20)
Rapa. 1. To shine;
shiny, polished; he-rapa te moai miro, the wooden
figurine is shiny, polished. 2. Emblem, badge of timo îka
(person entrusted with putting a death spell on an assassin).
Rapahago, name of a spirit (akuaku), anciently
considered as benevolent; rapahago, a fish. Raparapa,
to dazzle; dazzled: he-raparapa te mata. Marîa
raparapa, calm, smooth shiny sea. Vanaga. 1. Pau.: rapa,
a fool, madness. Ma.: rapa, a familiar spirit. 2. Pau.:
rapa, blade of a paddle. Mgv.: raparapahoe, id.
Ta.: rapa, id. Mq.: apa, id. Sa.: lapa,
flat. Ma.: rapa, flat part of a shovel. 3. Pau.: rapae,
a sand-pit. Ta.: rape, arapai, id. 4. Mgv.:
rapahou, primipara. Ma.: rapoi, id. 5. Mgv.:
raparapa, green. Ta.: rapa, id. 6. Mgv.: raparapa,
flat. Ta.: rapa, a flat rock. Sa.: lapalapa, a
flat coral. Ma.: raparapa, the flat part of the foot. 7.
Ta.: raparapa, square. To.: labalaba, id. Ha.:
lapalapa, square (of timber, of a bottle, of a cow yard).
Churchill.

|











 1
winter solstice
1
winter solstice