Although Manuscript E therefore could seem to define "September 1 as day number
245 (rather than 244), we should not because of that change "September 1
from day 244 to day 245 at Ga6-1.
|
CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
|
AUG 9 |
10 (222) |
11 |
12 |
13 (*145) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga6-1 (141 =
58 + 83) |
Ga6-2 |
Ga6-3 |
Ga6-4 (144 = 12 * 12) |
Ga6-5 (290 /
2) |
|
HEZE
= ζ Virginis
(205.0),
Southern Pinwheel Galaxy = M83 Hydrae
(205.7) |
ε Centauri
(206.3), κ Oct. (206.4)
*165.0 =
*206.4 - *41.4 |
no star
listed (207) |
τ
Bootis (208.2),
BENETNASH
(Leader of the Daughters of the Bier) =
η
Ursae Majoris
(208.5),
ν
Centauri (208.7),
μ
Centauri,
υ
Bootis (208.8) |
no star
listed (209) |
 |
|
Oct 12 (285) |
13 |
14 |
15 (*208) |
16 |
|
°Oct 8 |
9 |
10 |
11 (*204) |
12 (285) |
|
'Sept 15 |
16 |
17 (260) |
18 |
19 (*182) |
|
Hora Nui 1 |
"Sept 2 (245
= 286 - 41) |
3 |
4 |
5 (*168) |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
FEBR 8
(*324) |
9 (40) |
10 |
11 |
12 (365 + 43
= 408) |
|
... On February 9 the
Chorti Ah K'in, 'diviners', begin the
agricultural year. Both the 260-day cycle and the solar
year are used in setting dates for religious and
agricultural ceremonies, especially when those rituals
fall at the same time in both calendars. The ceremony
begins when the diviners go to a sacred spring where
they choose five stones with the proper shape and color.
These stones will mark the five positions of the sacred
cosmogram created by the ritual. When the stones are
brought back to the ceremonial house, two diviners start
the ritual by placing the stones on a table in a careful
pattern that reproduces the schematic of the universe.
At the same time, helpers under the table replace last
year's diagram with the new one. They believe that by
placing the cosmic diagram under the base of God at the
center of the world they demonstrate that God dominates
the universe. The priests place the stones in a very
particular order. First the stone that corresponds to
the sun in the eastern, sunrise position of summer
solstice is set down; then the stone corresponding to
the western, sunset position of the same solstice. This
is followed by stones representing the western, sunset
position of the winter solstice, then its eastern,
sunrise position. Together these four stones form a
square. They sit at the four corners of the square just
as we saw in the Creation story from the Classic period
and in the Popol Vuh. Finally, the center stone is
placed to form the ancient five-point sign modern
researchers called the quincunx ...
 |
|
ACHERNAR
(End of the River) =
α
Eridani
(23.3),
χ
Andromedae (23.6),
τ
Andromedae (23.9) |
ALSEIPH
(Scimitar) =
φ
Persei
(24.5),
τ
Ceti (24.7) |
no star listed (25) |
ANA-NIA-10 (Pillar-to-fish by)
χ
Ceti (26.1),
POLARIS
=
α
Ursae Minoris, BATEN KAITOS (Belly of the Fish) =
ζ
Ceti
(26.6),
METALLAH =
α
Trianguli
(26.9) |
Al Sharatain-1 /
Ashvini-1 (Horse's Head) /
Bond-16 (Dog) /
Mahrū-sha-rishu-ku-1 (Front of the Head of Ku)
SEGIN = ε Cassiopeia, MESARTHIM = γ Arietis,
ψ
Phoenicis (27.2),
SHERATAN
(Pair of Signs) =
β
Arietis,
φ
Phoenicis (27.4)
*351.0 = *27.4 - *41.4 |
|
April 13 |
14 → 41.4 |
15 |
16 (471) |
17 (107) |
|
°April 9 |
10 (100) |
11 |
12 (*22) |
13 |
|
'March 17 |
18 |
19 (78) |
20 (*364) |
0h |
|
"March 3 |
Tarahao 4 (2 * 214) |
5 (64) |
6 (*350) |
7 |
|
Tara,
1. Thorn: tara miro. 2. Spur: tara
moa. 3. Corner; te tara o te hare, corner of
house; tara o te ahu, corner of ahu.
Vanaga. (1. Dollar; moni tara, id.) 2. Thorn,
spike, horn; taratara, prickly, rough, full of
rocks. P Pau.: taratara, a ray, a beam; tare,
a spine, a thorn. Mgv.: tara, spine, thorn, horn,
crest, fishbone. Mq.: taá, spine, needle, thorn,
sharp point, dart, harpoon; taa, the corner of a
house, angle. Ta.: tara, spine, horn, spur, the
corner of a house, angle. Sa.: tala, the round
end of a house. Ma.: tara, the side wall of a
house. 3. To announce, to proclaim, to promulgate, to
call, to slander; tatara, to make a genealogy. P
Pau.: fakatara, to enjoin. Mq.: taá, to
cry, to call. 4. Mgv.: tara, a species of banana.
Mq.: taa, a plant, a bird. Ma.: tara, a
bird. 5. Ta.: tara, enchantment. Ma.: tara,
an incantation. 6. Ta.: tara, to untie. Sa.:
tala, id. Ha.: kala, id. Churchill
Hao. Ta.: to encircle. To.:
hao, id. Ma.: hao, to inclose, to draw
around. Churchill.
 |
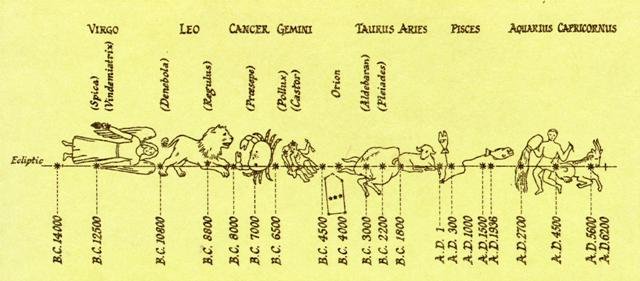
Because the text on side a of the G tablet evidently referred to the heliacal
stars at the time of the Bull - i.e. as observed from a point north of the equator.
|
"June 10 (161) |
82 |
"Sept 1 (244) |
|
83 |
Ga6-1 (141) - 83 = 58 (= 2 * 29) at
Ga2-28 ("June 10 = 'June 24 - 14 =
*118 - *37 = *122 - *41 = *58 + *23):
|
MAY 14 |
15 (365 + 135 = 500) |
16 (136) |
17 |
18 (*58 = 2 * 29) |
19 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga2-24 |
Ga2-25 |
Ga2-26 |
Ga2-27→ π |
Ga2-28 (141 - 83) |
Ga2-29 (59) |
|
φ Gemini (118.4)
*77.0 = *118.4 - *41.4 |
DRUS
(Hard) = χ Carinae
(119.9) |
ω Cancri (120.2) |
8h (121.7)
χ Gemini (121.0),
NAOS
= ζ Puppis
(121.3) |
ρ
Puppis (122.0),
HEAP OF FUEL
= μ Cancri
(122.1),
ζ
Monocerotis (122.3), ψ
Cancri (122.6),
REGOR (Roger backwards) = γ
Velorum
(122.7) |
TEGMINE = ζ Cancri
(123.3) |
|
July 17 |
18 |
19 (200) |
20 (*121) |
21 |
22 / 7 |
|
°July 13 |
14 |
15 (196) |
16 |
(*118 = 4 * 29½) |
18 |
|
'June 20 |
SOLSTICE |
22 (173) |
23 |
ST JOHN'S DAY |
25 (*96) |
|
"June 6 |
7 |
8 |
9 (*80) |
Te Maro 10 (161) |
11 |
|
he ea.a Ira.he iri he oho ki
runga anake.
i te
angahuru o te raa o te maro
i iri ai - Ira got
up. They all climbed to the top
of the hill.
They climbed
up on the tenth day of the month
of June ('Maro’).
(E:18) |
|
DAY 118 - 64 = 54
54
Vai Rapa
a haka remereme |
31 + 24 = 55 |
56 (Sic!) Te Vai Rutu Manu
a koro rupa e haho e hivi e e
runga e te puku ohu kahi e |
57 Hanga Piko (Curved Bay)
a hare utu manu a ana onoono a
pu ngotangota |
58 Ata Popohanga (Morning
Shadow)
toou e to ata hero ē |
59 Ata Ahiahi (Evening Shadow)
toou e honu ē |
|
... The leap day was introduced
as part of the Julian reform.
The day following the Terminalia
(February 23) was doubled,
forming the 'bis sextum -
literally 'double sixth', since
February 24 was 'the sixth day
before the Kalends of March'
using Roman inclusive counting
(March 1 was the 'first day').
Although
exceptions exist, the first day
of the bis sextum
(February 24) was usually
regarded as the intercalated or
'bissextile' day since the third
century. February 29 came
to be regarded as the leap day
when the Roman system of
numbering days was replaced by
sequential numbering in the late
Middle Ages
... |
E:46 |
|
1 Ko Apina Iti |
27 |
29 Ko Te Rano A Raraku |
(30) |
|
29 |
|
30 |
|
31 Oparingi |
11 |
(43) |
1 |
45 Vai ngaere |
8 |
54 Vai Rapa |
(55) |
4 |
60 Apina Nui |
|
12 |
11 |
5 |
|
24 |
|
|
... The
'watering place' where the bird
beats (the rhythm)' - wordplay,
'where a certain chant is being
recited' - is located near Hanga
Piko. A recitation provides the
following information for the
additional name:
'In Koro
Rupa is the house where one is
made to laugh; in Kere Mea is
the house where one is made fun
of' (Barthel 1960:851;
Campbell 1971:400). There the
rule of the new birdman was
celebrated (compare koro
'feast'). In RAP., koro rupa
seems to have the same meaning
as in TUA. kororupo,
which describes a paradise. In
the cosmology of the TUA., the
name also referred to the
entrance to the underworld.
Hivi (maybe the same as
hi ivi 'to fish with a hook
made from bone'; compare the
narrative ME:363) is 'outside',
and 'the elevation from where
(the catch of) the tunafish is
announced' is 'above'. This is a
reference to a large boulder
beside the place where the
canoes docked in Hanga Piko.
There the people waited for the
canoes to return from the
fishing grounds.
'Curved Bay',
the well-known little harbour on
the western shore, is linked
with a 'house where the bird
beats (the rhythm), that is,
where a certain chant is being
recited. This establishes a
cross-connection to the watering
place by the same name and also
to the 'Koro Rupa' motif and the
theme of the birdman cult. It
also suggests the newly
discovered petroglyphs from
Hanga Piko (so far, only
partially published by Barthel
1962:Illustration 2). Ana Onoono
is a cave well-suited as an
overnight shelter; Pu Ngotangota
is a coastal formation where
seawater is allowed to flow in
and out. The three additions,
'house', 'cave', and 'hole',
always describe an enclosed
area.
'Yours is the morning shadow'
refers to an area in Ata Hero
where the house of Ricardo Hero
is now located. 'Yours is the
evening shadow' belongs to a
'turtle'. I could not obtain any
information about the location,
but I suspect that the 'turtle'
refers to a motif in the
narration of Tuki Hakahevari
(the turtle is carved in stone
in a cave along the bay of
Apina) ...
(The Eighth Land, pp.
89-90.) |
|
Kere. To
moor, to make fast. Kerekere,
black, dark, blue, obscure,
gloom; niho kerekere,
blackened teeth. Hakakerekere,
to blacken. P Pau.: kerekere,
black, dark, somber. Mgv.:
kerekere, blue, dark blue
almost black, the color of the
deep ocean, black, somber,
darkness. Mq.: kerekere,
keékeé, black, somber,
livid; ere, blue, azure.
Ta.: ereere, black.
Churchill.
ELE¹,
v. Haw., be dark, black;
adj. dark-coloured,
black, blue, dark-red, brown;
ele-ele, id. Tah.,
ere-ere, dark, black, blue.
Rarot., kerekere, id.
Marqu., kekee, id.;
kee-voo, darkness, gloom.
The application of this word to
colour is doubtless derivative
from the Polynes. Haw. kele,
mud, mire (quod vide),
Tong. kèle-kere, earth,
soil, dirt, Sam. 'ele and
'ele-ele, red earth, dirt,
rust; elea, Tong.,
kelea, rusty, dirty;
probably all akin to ala,
ara, in ala-ea,
earth, clay ... Jav., iran,
black. N. Celebes (Kema),
hirun, id. In the following
Greek words the first
constituent proclaims their
affinity to the Polynesian
ere, ele: -
ερεβος, darkness of the
grave, the dark passage from
earth to Hades; ερεβεννος,
dark, gloomy; ερεμνος,
sync. fr. previous word, black,
swarthy; ερεφω, to cover;
ορφνη, darkness of night;
ορφνος, dark, dusty;
οροφη, roof of a house.
Sanskr., aruņa,
tawny, dark, red; s.
the dawn, the sun;
aruņita,
made red. Benfey refers the
Sanskrit word to arus,
a wound. Lidell and Scott refer
the Greek words to
ερεφω,
to cover. They are plausible;
but are they the true roots of
stems, in view of the Polynesian
ele,
ere?
Dr. J. Pickering, in his Greek
Lexicon, derives
ερεβος
'from ερα
(the earth) or ερεφω
(to cover)'. The former seems to
me the better reference.
ELE²,
prefix.
Haw., an intensitive added to
many words, imparting a meaning
of 'very much, greatly';
ele-u,
alert, quick;
ele-ma-kule,
old, aged, helpless;
ele-mio,
tapering to a point;
ele-ku,
easily broken, very brittle;
ele-hei,
too short. Tah.,
ere-huru,
encumbered, too much of a thing.
A. Pictet ... says, apropos of
the derivation of the word
Erin:
'L'irlandais er
comme adjectif magnus, nobilis,
paraît être identique à l'er
intensitif de l'irlandais et du
cymrique, considéré comme une
particule inséparable, et qui
serait ainsi proprement un
adjectif. Il est à remarquer en
confirmationm, que le zend
airya
= sanskr. arya
avec l'acception de bon, juste,
est également devny ér
dans les composés du Pârsi,
comme ér-maneshu,
bon esprit, er-tan,
bon corps (Spiegel, Avesta, i.
6). De là à un sens intensitif,
transition était facile.' Why
not widen the philological
horizon by admittning the
Polynesian ere,
ele,
to consideration as well as the
Irish, Welsh, or Parsi? And why
may not the O. Norse
ar,
early, first; aerir,
messengers; the Sax.
er,
before, in time, go up to the
same root as those others?
(Fornander) |
However, on side b of the C tablet the text might
possibly have been designed in order to let there be
84 days from the Full Moon at glyph number 176 - 84
= 92 (= 2 * 46 = 184 / 2):
|
"June 10 (161) |
83 |
"Sept 1 (245) |
|
84 |
| te
hokohuki |
te moko |
vero hia |
tagata honui |
e
ha mata |
|
Ha. 1. Four.
2. To breathe. Hakaha'a, to
flay, to skin. Vanaga. 1. Four. P Mgv., Mq., Ta.: ha, id.
2. To yawn, to gape. 3. To heat. 4.
Hakaha, to skin, to flay;
unahi hakaha, to scale fish.
Mgv.: akaha, to take to
pieces, to take off the bark or
skin, to strip the leaves off
sugarcane. 5. Mgv: ha,
sacred, prohibited. Mq.: a, a
sacred spot. Sa.: sa, id.
Churchill. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Cb8-4 |
Cb8-5 (172 + 4) |
Cb8-6 (177 = 6 * 29½) |
Cb8-7 (392 + 178 = 570) |
Cb8-8 (1½ * 314 + 100) |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
γ Hydrae (201.0), ι Centauri (201.4)
*160.0 = *201.4 - *41.4 |
Al Simāk-12 (Lofty) /
Chitra-14 (Bright One) /
Horn-1 (Crocodile) /
Sa-Sha-Shirū-20
(Virgin's Girdle) /
ANA-ROTO-3 (Middle pillar)
MIZAR = ζ Ursae Majoris
(202.4),
SPICA
= α Virginis,
ALCOR
= 80 Ursae Majoris
(202.7)
SADALMELIK (α Aquarii)
*161.0 = *202.4 - *41.4 |
71 VIRGINIS
(203.6) |
no star listed (204) |
HEZE
= ζ Virginis
(205.0),
Southern Pinwheel Galaxy = M83
Hydrae
(205.7) |
|
... Proclus informs us that the fox
star nibbles continuously at the
thong of the yoke which holds
together heaven and earth; German
folklore adds that when the fox
succeeds, the world will come to its
end. This fox star is no other than
Alcor, the small star g near
zeta Ursae Majoris (in India
Arundati, the common wife of the
Seven Rishis, alpha-eta Ursae
...
 |
|
Oct 8 (240 + 41) |
9 |
10 |
11 (364
- 80) |
12 (285) |
|
'Sept 11
(354 - 100) |
12 |
13 (256 = 4 * 64) |
14 |
15 |
|
"Aug 28 (240) |
HORA ITI 29 |
30 (242 = 2 * 11 * 11) |
31 |
HORA NUI 1 |
|
AHU AKAPU |
PU PAKAKINA A IRA |
|
Paka.
1. Dry; to become dry (of
things); pakapaka, to dry
out. Te paka is also the name
of the moss-covered areas, between
the small lakes of volcano Rano
Kau, through which one can pass
without getting one's feet wet. 2.
To go, to depart; he-paka-mai,
to come; he-oho, he-paka,
they go away. 3. To become calm (of
the sea): ku-paka-á te tai.
Pakahera, skull, shell,
cranium; pakahera puoko tagata,
human skull; pakahera pikea,
shell of crab or crayfish.
Gutu pakapaka, scabbed lips.
Hau paka, fibres of the
hauhau tree, which were first
soaked in water, then dried to
produce a strong thread. Moa gao
verapaka, chicken with bald
neck. Ariki Paka, certain
collateral descendents of Hotu
Matu'a, who exercised religious
functions. Vanaga. 1. Crust, scab,
scurf; paka rerere, cancer;
pakapaka, crust, scabby. 2.
Calm, still. 3. Intensive; vera
paka, scorching hot; marego
paka, bald; nunu paka,
thin. 4. To arrive, to come. 5. To
be eager. 6. To absorb. 7. Shin T.
Pakahera, calabash, shell,
jug. Pakahia, to clot,
curdle, coagulate. Pakapaka,
dry, arid, scorching hot, cooked too
much, a desert, to fade away, to
roast, a cake, active; toto
pakapaka, coagulated blood;
hakapakapaka, to dry, to broil,
to toast. Pakahera pikea,
shell of crab or crayfish.
Churchill.
Kinana,
s. Haw., a hen that has
hatched chickens.
Sam.,
tina, a mother.
Tong.,
tina-manu, a sow that had
litter.
Tah.,
ti'a, the lower part of the
stomach, below the navel.
Fiji.,
tina, mother; tina-tina,
mother of inferior animals.
N.
Zeal., tinana, the buttocks,
trunk, body.
This
word, with somewhat varying but not
far separate meanings, I am inclined
to consider as related to the
Goth.,
kwens, kwino, a woman;
kwina-kunds and kwineins,
female; and possibly kwithus,
the womb, the stomach, if that is
syncope of an original kwinthus.
Greek,
γυνη, woman ... |
|
CLOSE TO THE
SUN: |
|
April 8
no star listed (18) |
9
ADHIL
(Garment's Train) = ξ Andromedae
(19.3),
θ
Ceti (19.7) |
10 (100)
KSORA (Knee) = δ Cassiopeiae
(20.1),
ω
Andromedae (20.6),
γ
Phoenicis (20.8) |
11 (364
- 263)
δ Phoenicis (21.5) |
12
υ Andromedae (22.9) |
|
'March 12 |
13 |
14 (73) |
15 |
16 |
|
"Febr 26 |
27 |
28 (59) |
29 |
"March 1 |
 |
Regor (Roger in reverse) was at glyph number
488 - 392 = 96 (= 176 - 80 = 2 * 48 = 192 /
2) due to the unfortunate change by the Pope G-
regor -y XIII to a new day for spring
equinox.
... When the Pope had decided to abandon day
84 (Julian equinox) in favour of day 80
(Gregorian equinox) it implied counting from
the December solstice in order to reach day
11 + 80 = 91 = 364 / 4 = 7 * 13 (ºMarch 21),
instead of the previous 84 = 336 / 4 = 7 *
12 (ºMarch 25) as counted from the beginning
of the year ...
... When the Pope Gregory XIII updated the
Julian calendar he changed the date for
spring equinox from day 84 to day 80,
although the astronomically more adequate
date was day 79 (when the majority of
equinoxes occurred). There were 5 days from
Polaris to Hamal and there were 5 days from
79 to 84 ...
... When the Pope Gregory
XIII updated the Julian calendar he did not
revise what had gone wrong before 325 AD
(when the Council of Nicaea was held). Thus
the stars were still 3-4 days 'out of tune'
compared to the calendar ... the Gregorian
'canoe' was 'crooked'. His calendar was not
in perfect alignment with the ancient star
structure. Because he had avoided to adjust
with the effects of the precession between
the creation of the Julian calendar and the
Council of Nicaea in 325 AD. [The Julian
equinox was in the 3rd month of the year and
in its 25th day; 3-25.]
...
... They go inland at the
land. The child nursed and tended grows up,
is able to go and play. Each day he now goes
off a bit further away, moving some distance
away from the house, and then returns to
their house. So it goes on and the child is
fully grown and goes to play far away from
the place where they live. He goes over to
where some work is being done by a father
and son. Likāvaka is the name of the
father - a canoe-builder, while his son is
Kiukava. Taetagaloa goes right
over there and steps forward to the stern of
the canoe saying - his words are these: 'The
canoe is crooked.' (kalo ki ama).
Instantly Likāvaka is enraged at the
words of the child. Likāvaka says:
'Who the hell are you to come and tell me
that the canoe is crooked?' Taetagaloa
replies: 'Come and stand over here and see
that the canoe is crooked.' Likāvaka
goes over and stands right at the place
Taetagaloa told him to at the stern of
the canoe. Looking forward, Taetagaloa
is right, the canoe is
crooked. He slices
through all the lashings of the canoe to
straighten the timbers. He realigns the
timbers. First he must again position the
supports, then place the timbers correctly
in them, but Kuikava the son of
Likāvaka goes over and stands upon one
support. His father Likāvaka rushes
right over and strikes his son Kuikava
with his adze. Thus Kuikava dies.
Taetagaloa goes over at once and brings
the son of Likāvaka, Kuikava,
back to life. Then he again aligns the
supports correctly and helps Likāvaka
in building the canoe. Working working it is
finished ...
|
Cb5-2 (96 = 161 - 65)
"June 10 (161) |
83 |
Cb8-5 (176 = 241 - 65)
"Sept 1 (245) |
|
85 |
|