Let's repeat. The 5th day was presumably referring to day
360 + 5 = 364 + 1, when the new year had its zero day.
... Nut, whom the Greeks sometimes identified with Rhea, was
goddess of the sky, but it was debatable if in historical times
she was the object of a genuine cult. She was Geb's twin sister
and, it was said, married him secretly and against the will of
Ra. Angered, Ra had the couple brutally separated by Shu and
afterwards decreed that Nut could not bear a child in any given
month of any year. Thoth, Plutarch tells us, happily had pity on
her. Playing draughts with the Moon, he won in the course of
several games a seventy-second part of the Moon's light with
which he composed five new days. As these five intercalated days
did not belong to the official Egyptian calendar of three
hundred and sixty days, Nut was thus able to give birth
successively to five children: Osiris, Haroeris (Horus), Set,
Isis and Nepthys ...
|
he otea he ea a
Makoi.he oho he tuu ki a(-) |
It
grew light [on the 5th day] and Makoi got
up. He set out and came to Apina. When he
arrived there he gave the name |
| pina.he tuu
he nape i te ingoa. |
|
E:38 |
| 1
ko apina iti.ko rapa
kura.he oho mai |
'This is Apina Iti, this is Rapa Kura.'. He
went on and came to Hanga O Ua [Uo].
He gave the name 'This is Hanga O Ua [Uo]
of the beautiful wave (vave renga).'
Makoi went on, giving names, until he had
made a (complete) circle around both sides
(of the island).
In Apina Nui
a stone (maea) was erected [hakatuu],
saying that the naming was done on a (round)
trip during a single day. |
| 2 he
tuu ki hanga o uo.he
nape te ingoa.ko hanga o uo |
|
a vave renga. |
|
he nape he
oho a Makoi .i te ingoa.ka
vari ro |
|
a
arurua.aro i
apina nui i hakatuu ai |
|
te
maea.etahi no raa.i nape he oho ai. |
|
Vari.
1. Menstruation, period (also: tiko).
2. To tack, to veer (nautical);
ku-vari-mai-á te miro, the boat arrives,
have veered [around Rano Kau].
Vanaga. About, circumference, to turn in a
circle; hakavari, pliant, to bend,
square; varivari, about, to go
around; vavari, a garland;
varikapau, circumference, to surround, a
compass, to admire; hiriga varikapau,
to go in a ring; pa varikapau, to
close in; varitakataka (vari-taka
3) to surround. Churchill. Pau.: Vari,
marsh, mire, dirt. Ta.: vari, dirt,
mud. Rar.: vari, mud. Churchill.
Mgv.: Vari, paste well diluted. Mq.:
vaivai, to dilute, to thin. Ha.:
waliwali, soft, pasty. Churchill.
Áruáru, reduplication of aaru: to
grab firmly. Vanaga. 1. To pursue. P Mgv.:
aruaru, to run after, to chase, to
follow. Ta.: aruaru, to pursue. 2. To
raise in waves, undulation. P Pau.:
puhigaru, a bubble of water. Mgv.:
garu, foam, froth. Mq.: naú,
waves. Ta.: aru, billow, wave, flood.
3. (haruharu). Churchill. Haruharu.
To rob, to steal, to arrest, to seize, to
cling, to grasp unexpectedly, to take by
force; robber (aruaru, aaru).
Pau.: haru, to extort, to carry off,
to usurp. Ta.: haru, robber, to seize
by force. Churchill.
Aro. Face, front, side (of a
figure); ki te aro o ..., to the
front of ... Vanaga. Presence, body,
frontispiece; ki te aro, face to
face. P Pau.: aroga, the visage;
ki te aroga, opposite. Mgv.: aro,
presence, before; i te aro, in the
presence of. Mq.: aó, face, in the
presence of, before. Ta.: aro, face,
front, presence, view. It is probable that
more than one word is confounded in alo.
The significations which appear in Southeast
Polynesia are most likely derived from a
Tongafiti alo and do not appear in
Nuclear Polynesia. The alo belly and
alo chief which do occur in Nuclear
Polynesia are also probably Tongafiti, for
in Samoa and Tonga they are honorific and
applied only to folk of rank, a good
indication of borrowing by the Proto-Samoans
from Tongafiti masters. Churchill. In the
Hawaiian group, the western portion or side
of an island was called 'the front', ke
alo, of the land, and the eastern side
was called 'the back', ke kua. The
reason of such designations must be sought
in the fact of the arrival of the
inhabitants from the west. Fornander.
... Ira got up,
climbed up [he ea], went on, and
reached Ruhi Hepii. He drilled a hole into
the stone. After the hole was deep enough,
he took the ornament (rei) and put it
into the hole so that the shiny side (rapa)
was turned outward. [He gave the name Ruhi
Hepii.]
He turned around, climbed down [he turu],
went on, and entered the cave of Pu
Pakakina.
When he arrived there he sat down.
The young kinsmen
arrived and rested. It grew light. On the
second day, Ira said again, 'Go back to
riding the waves!'. They all went back out
there.
Ira got up [he ea a Ira] and again
picked up the (second) ornament. He took it
[he mau], went on, and came to
Apina Nui,
drilled a hole into the stone, put the
ornament in the hole, with the shiny side [te
rapa] to the outside, and gave (the
place) the name 'Pu' ... (E34) |
| 3
hanga roa a tuki
tukau 4
Okahu a
uka ui hetuu. |
MY OWN
IDEAS: |
| Hanga Roa (the
Great Bay) for making landfall (tuki)
in order to multiply (ku-kau)
together with
Okahu (oka-hu), the maiden
star-watcher (uka ui hetuu). |
|
Tutu.
1. Circle of fishing nets arranged in
the shape of a funnels or baskets. 2. To
light a fire; he-tutu i te ahi: to
burn something. 3. To hit, to strike, to
beat. Tûtú, to shake (something)
clean of dust or dirt; he-tûtú te oone o
te nua, to shake the dirt off a nua
cape. Tutuhi, to reject the
responsibility for a mistake onto one
another, to blame one another for a mistake
(see tuhi). Tutuki, to
stumble, to trip. O tutuki te va'e,
in order not to trip. Tutuma,
firebrand, partly burnt stick. Tuturi,
to kneel. Vanaga. 1. To beat bark for cloth.
PS Pau., Mgv., Mq., Ta.: tutu, id.
Sa., To., Fu.: tutu, id. 2. A broom,
to sweep, to clean. Mq.: tutu, to
beat out the dust. 3. To shake, to winnow.
Mgv.: tutu, to tremble, to leap. Mq.:
tutu, to shake. 4. To kindle, to
light, to ignite, to set fire, to burn. Mq.:
tutu, to burn, to set fire. 5. To
stand; hakatutu, to set joists. P
Mgv., Mq.: tutu, to stand upright.
Ta.: tu, id. Tutua (tutu
1): board on which bark is beaten into
cloth. PS Mgv.: tutua, a cloth
beater. Mq., Ta.: tutua, wood on
which cloth is beaten. Sa., Fu.: tutua,
id. Tutui: tutui ohio, chain,
tutui kura, shawl. Mq.: tuitui
kioé, chain. Tutuki: shock,
contusion, to run against, to collide;
tukukia, to run foul of. P Pau.:
tukituki, to strike, to pound, to grind.
Mgv.: tukia, to strike against,
shock, concussion. Mq.: tutuki, id.
Ta.: tui, id. Tutuma: 1. (tutu
- ma) a live coal. 2. Tree trunk T (?
tumu). Tutumata, ligament of
the eye, orbit, eyelid. T (tutumate,
eyelid G). Tutuu, bristling.
Churchill. Kau.1. To move one's
feet (walking or swimming); ana oho koe,
ana kau i te va'e, ka rava a me'e mo kai,
if you go and move your feet, you'll get
something to eat; kakau (or also
kaukau), move yourself swimming. 2. To
spread (of plants): ku-kau-áte kumara,
the sweet potatoes have spread, have
grown a lot. 3. To swarm, to mill around (of
people): ku-kau-á te gagata i mu'a i tou
hare, there's a crowd of people milling
about in front of your house. 4. To flood
(of water after the rain): ku-kau-á te
vai haho, the water has flooded out (of
a container such as a taheta). 5. To
increase, to multiply: ku-kau-á te moa,
the chickens have multiplied. 6. Wide,
large: Rano Kau, 'Wide Crater' (name
of the volcano in the southwest corner of
the island). 7. Expression of admiration:
kau-ké-ké! how big! hare kau-kéké!
what a big house! tagata hakari
kau-kéké! what a stout man! Vanaga. To
bathe, to swim; hakakau, to make to
swim. P Pau., Mgv., Mq.: kau, to
swim. Ta.: áu, id. Kauhaga,
swimming. Churchill.
Kaukau. 1. Horizontal poles of a
frame (of a hare paega, or a paina
statue): he-hakatu'u te tama o te
paina, he-kaukau, they erect the
vertical poles of the paina then they
lay upon them the horizontal ones. 2. Group
of people: e-tahi tuitui reipá i Te Pei,
ekó rava'a e-varu kaukau; i-garo ai i
Hiva, i te kaiga, a necklace of
mother-of-pearl is on te Pei, few
will find it (lit: eight groups of people);
it has remained in Hiva, in our
homeland. 3. To go through, to pass through
in unison; he-hogi-mai te ûka i te e'eo o
te pua kaukau-á i roto ite hare, the
girl smelt the fragrance of the pua
wafting inside the house. 4. Newborn baby's
first hand and feet movements (kaukau
or kau). The five stages of a
baby's development are: kaukau, puepe,
tahuri, totoro, mahaga. Puepue =
said of a newborn baby when, a few weeks
old, it begins to distinguish people and
objects: ku-puepue-á te poki.
Tahuri = of a new-born baby, to move
from side to side: ku-tahuri-á te poki.
Totoro = to crawl; ki totoro te
poki, when the baby crawls. Mahaga
= baby when able to stand by itself. Vanaga.
Oka.
1. Lever, pole; to dig holes in
the ground with a sharpened stick, as was
done in ancient times to plant vegetables;
used generally in the meaning of making
plantations. 2. The four sideways poles
supporting a hare paega. Okaoka,
to jab, to pierce, to prick repeatedly.
Vanaga. Digging stick, stake, joist; to
prick, to pierce, to stick a thing into, to
drive into, to slaughter, to assassinate;
kona oka kai, plantation; pahu oka,
a drawer. Okaoka, a fork, to prick,
to dig. Okahia, to prick. Churchill.
Hu. 1. Breaking of wind. T Mgv.,
uu, to break wind. Mq., Ta.: hu,
id. 2. Whistling of the wind, to blow,
tempest, high wind. P Pau.: huga, a
hurricane. Churchill. Mgv.: hu, to
burst, to crackle, to snap. Ha.: hu,
a noise. Churchill.
Uka hoa,
female friend, companion.
Ukauka:
1. Firewood. 2. Leathery, tough. PS Mgv.:
ukauka,
hard to chew. Mq.:
ukakoki,
leathery. Ta.:
uaua, id. Sa.:
u'a,
tough, tenacious, glutinous. To.:
uka,
sticky. Niuē;
uka, tough. Viti: kaukamea,
metal. Churchill.

... The last couple of the seven generations of gods who appeared when
heaven and earth began, Izanagi and Izanami, received the
order to consolidate and fertilize the moving earth. Here Izanagi
stirs the waters of the sea with his celestial lance to produce the island
of Onokoro. The brother and sister then descended to it and
engendered the islands of Japan and numerous deities. Silk painting,
nineteenth century AD ... |
I suggest that both the creators of the text in Manuscript E and
those behind the rongorongo text on the Mamari (Egg)
tablet were well aware of the fact that in a way time
began at the Frond:
...
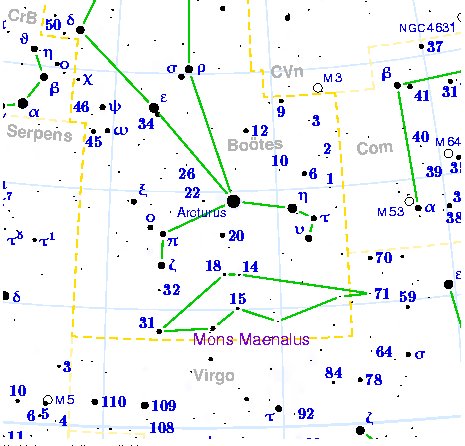
Frond (Coma Berenices & western part of Virgo).
The Frond is represented in the heavens by
the figure of the goddess Erua holding her sacred branch of the Date-palm.
Her constellation rises in the autumn months as the dates are
ripening on the fronds.

In other words, when Makoi began with
Apina Iti this should have corresponded to a day
zero, to the time of Coma Berenices (α
and β).
| Hetu erua |
tagata rere ki te ragi |
|
Hetu 1. To (make) sound; figuratively:
famous, renowned. 2. To crumble into embers (of a bonfire). Hetu'u. Star, planet; hetu'u popohaga
morning star; hetu'u ahiahi evening star; hetu'u viri meteorite. Vanaga Hetu 1. Star (heetuu); hetu rere, meteor; hetu pupura, planet. P Pau.: hetu, star. Mgv.: etu, id. Mq.: fetu, hetu, id. Ta.: fetu, fetia, id. The alternative form fetia in Tahiti, now the only one in common use, need not be regarded as an anomaly in mutation. It seems to derive from Paumotu fetika, a planet. Its introduction into Tahiti is due to the fashion of accepting Paumotu vocables which arose when the house of Pomare came into power. 2. Capital letter (? he tu). 3. To amuse. 4. To stamp the feet. Hetuhetu, to calk, to strike the water. Hetuke, sea urchin. Churchill. |
 |
 |
 |
| Cb8-1 (172 → solstice) |
Cb8-2 (565 = 392 + 173) |
Cb8-3 |
| CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
| APAMI-ATSA (Child of Waters) = θ Virginis, ψ Hydrae (198.5), DIADEM = α Com. Ber. (198.9) |
AL DAFĪRAH (Tuft) = β Com. Ber. (199.4) *158.0 = *199.4 - *41.4 |
σ Virginis (200.4)
*159.0 = *200.4 - *41.4 |
|
... Apami-Atsa ('Child of Waters', θ Virginis) at 13h maybe should be contrasted with Apam Napat ('Grandson of Waters') ... θ is on the front of the garment, below the girdle ... Moderns have no name for it, but in the Surya Siddhanta it was Apami-Atsa, the Child of the Waters ... Apam Napat is an eminent figure of the Indo-Iranian pantheon. In Hinduism, Apām Napāt is the god of fresh water, such as in rivers and lakes. In Zoroastrianism, Apąm Napāt is also a divinity of water ... Apām Napāt in Sanskrit and Apąm Napāt in Avestan mean 'grandson of waters' ... Sanskrit and Avestan napāt ('grandson') are cognate to Latin nepōs and English nephew, but the name Apām Napāt has also been compared to Etruscan Nethuns and Celtic Nechtan and Roman Neptune. In Yasht 19 of the Avesta Apąm Napāt appears as the Creator of mankind. Here, there is an evident link between the glory of sovereignty (Khvarenah) and Apąm Napāt who protects Khvarenah as the royal glory of Iranian kings. Apām Napāt is sometimes, for example in Rigveda book 2 hymn 35 verse 3, described as a fire-god who originates in water ... The reference to fire may have originally referred to flames from natural gas or oil seepages surfacing through water, as in a fire temple at Surakhany near Baku in Azerbaijan ... There is a conjecture that the word 'naphtha' came (via Greek, where it meant any sort of petroleum) from the name 'Apampat' ...

|
| Oct 5 |
6 |
7 (280) |
| 'Sept 8 |
9 |
10 (253 = 280 - 27) |
| "Aug 25 (237 = 8 * 29½ + 1) |
Hora iti 26 |
27 |
| AUG 2 (237 - 23 = 214 = 172 + 42) |
3 |
4 (280 - 64 = 216) |
|
... Once upon a time there was an old woman who owned a great potato field (mara) where she planted her potatoes in spring and harvested them in autumn. She was famous all around for her many varieties of wonderful potatoes, and she had enough of them to sell at the market place. She planted her potatoes 7 in a row, placing her foot in front of her as a measure from one potato to the next. Then she marked the place with a bean - which would also give nourishment to the surrounding potatoes. Next she changed variety and planted 7 more followed by another bean, and this was the pattern she followed until all her 214 varieties had been put down in their proper places. She had drawn a map which she followed and from where each sort of potato could be located at the proper time for its harvest ... |
| DAY 198 |
199 |
200 (= 216 + 64) |
| (PAPA O PEA) |
AHU AKAPU |
|
Here above I have moved Ahu Akapu 1 day ahead, compared to my earlier presentations, in order to make it begin when the Full Moon reached Cb8-3 (→ 24).
Aka. 1. Anchor: he-hoa te aka, to drop anchor. 2. Root of certain plants (banana tree, taro, sugar-cane). 3. To be paralyzed by surprise. Vanaga. 1. Root; aka totoro, to take root. P Pau., Mq.: aka, root. Ta.: aa, id. 2. (āka) anchor. 3. Causative (haka). Churchill.
The Explorers stayed for 2 days in Ahu Akapu and Cb8-6 (→ 48) should therefore correspond to "September 29 when the Full Moon reached Spica. |
| CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
| April 5 (365 + 95 = 460) |
6 (96 = 80 + 16) |
7 |
|
1h (15.2)
β Phoenicis (15.1), υ Phoenicis, ι Tucanae (15.6), η Ceti, ζ Phoenicis (15.7) |
Al Batn Al Hūt-26 (Belly of the Fish) / Revati-28 (Prosperous) / 1-iku (Field Measure)
MIRACH (Girdle) = β Andromedae, KEUN MAN MUN (Camp's South Gate) = φ Andromedae (16.0), ANUNITUM = τ Piscium (16.5), REVATI (Abundant) = ζ Piscium (16.9)
REGULUS (α Leonis) |
ν Phoenicis (17.4), κ Tucanae (17.6)
*342.0 = *383.4 - *41.4
= *159.0 + *183.0 |
| 'March 9 (68) |
10 |
11 |
| "Febr 23 (54) |
24 (365 + 55 = 420) |
25 |
|
... The leap day was introduced as part of the Julian reform. The day following the Terminalia (February 23) was doubled, forming the 'bis sextum - literally 'double sixth', since February 24 was 'the sixth day before the Kalends of March' using Roman inclusive counting (March 1 was the 'first day'). Although exceptions exist, the first day of the bis sextum (February 24) was usually regarded as the intercalated or 'bissextile' day since the third century. February 29 came to be regarded as the leap day when the Roman system of numbering days was replaced by sequential numbering in the late Middle Ages ... |
According to Barthel (The Eighth Land, p. 77)
the place Okahu was located next to the
cemetary of Hanga Roa, a piece of information
which when regarded isolated appears to be rather trivial.
However, in view of how in Manuscript E the full
stop sign which otherwise ought to have followed the item
for Hanga Roa is absent, whereas the item
for Okahu ends with such a full stop, the idea
could be to connect item 3 with item 4 (= 7 - 3).
A full stop sign was used at October 10 (100 + 183) as if to
point out where Mons Maenalus (the Primeval
Mound) was beginning:
... Ta'aroa tahi tumu,
'Ta'aroa origl. stock' - most commonly Ta'aroa
or Te Tumu - existed before everything except
of a rock (Te Papa) which he compressed and
begat a daughter (Ahuone) that is Vegetable
Mole. Ahuone means 'earth heaped up' - a
widespread name for the Polynesian first woman. It
sounds as if Cook also heard the term applied to the
banks of humus and rotting material on which taro
is grown. In the English of his day this was known
as 'vegetable mould' ...
In the diagram over the nested cycles of Mercury in
the year 1933 AD we should notice that this day
might have been considered to be special (written as
1Okt instead of 1 Okt):
| te hokohuki |
te moko |
vero hia |
tagata honui |
e ha mata |
|
Ha. 1. Four. 2. To breathe. Hakaha'a, to
flay, to skin. Vanaga. 1. Four. P Mgv., Mq., Ta.: ha, id. 2. To yawn, to gape. 3. To heat. 4. Hakaha, to skin, to flay; unahi hakaha, to scale fish. Mgv.: akaha, to take to pieces, to take off the bark or skin, to strip the leaves off sugarcane. 5. Mgv: ha, sacred, prohibited. Mq.: a, a sacred spot. Sa.: sa, id. Churchill. 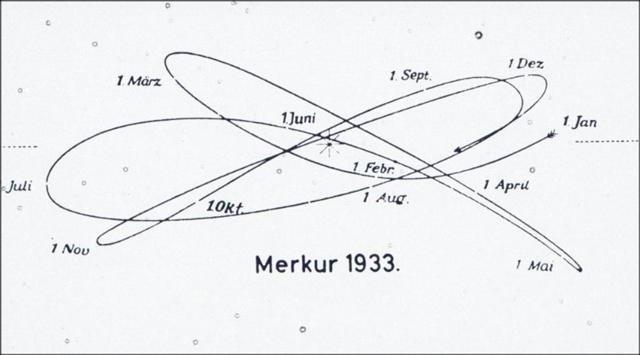
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Cb8-4 |
Cb8-5 (172 + 4) |
Cb8-6 (177 = 6 * 29½) |
Cb8-7 (392 + 178 = 570) |
Cb8-8 (1½ * 314 + 100) |
| CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
| γ Hydrae (201.0), ι Centauri (201.4) |
Al Simāk-12 (Lofty) / Chitra-14 (Bright One) / Horn-1 (Crocodile) / Sa-Sha-Shirū-20 (Virgin's Girdle) / ANA-ROTO-3 (Middle pillar)
MIZAR = ζ Ursae Majoris (202.4), SPICA = α Virginis, ALCOR = 80 Ursae Majoris (202.7)
SADALMELIK (α Aquarii)
*161.0 = *202.4 - *41.4 |
71 VIRGINIS (203.6) |
no star listed (204) |
HEZE = ζ Virginis (205.0), Southern Pinwheel Galaxy = M83 Hydrae (205.7) |
|
... Proclus informs us that the fox star nibbles continuously at the thong of the yoke which holds together heaven and earth; German folklore adds that when the fox succeeds, the world will come to its end. This fox star is no other than Alcor, the small star g near zeta Ursae Majoris (in India Arundati, the common wife of the Seven Rishis, alpha-eta Ursae ...
|
|
... Mons Maenalus, at the feet of Boötes, was formed by Hevelius, and published in his Firmamentum Sobiescianum; this title coinciding with those of neighboring stellar groups bearing Arcadian names. It is sometimes, although incorrectly, given as Mons Menelaus, - perhaps, as Smyth suggested, after the Alexandrian astronomer referred to by Ptolemy and Plutarch. The Germans know it as the Berg Menalus; and the Italians as Menalo. Landseer has a striking representation of the Husbandsman, as he styles Boötes, with sickle and staff, standing on this constellation figure. A possible explanation of its origin may be found in what Hewitt writes in his Essays on the Ruling Races of Prehistoric Times: The Sun-god thence climbed up the mother-mountain of the Kushika race as the constellation Hercules, who is depicted in the old traditional pictorial astronomy as climbing painfully up the hill to reach the constellation of the Tortoise, now called Lyra, and thus attain the polar star Vega, which was the polar star from 10000 to 8000 B.C. May not this modern companion constellation, Mons Maenalus, be from a recollection of this early Hindu conception of our Hercules transferred to the adjacent Bootes?
|
| Oct 8 (240 + 41) |
9 |
10 |
11 (364 - 80) |
12 (285) |
| 'Sept 11 (354 - 100) |
12 |
13 (256 = 4 * 64) |
14 |
15 |
| "Aug 28 (240) |
HORA ITI 29 |
30 (242 = 2 * 11 * 11) |
31 |
HORA NUI 1 |
| AHU AKAPU |
PU PAKAKINA A IRA |
|
Paka. 1. Dry; to become dry (of things); pakapaka, to dry out. Te paka is also the name of the moss-covered areas, between the small lakes of volcano Rano Kau, through which one can pass without getting one's feet wet. 2. To go, to depart; he-paka-mai, to come; he-oho, he-paka, they go away. 3. To become calm (of the sea): ku-paka-á te tai. Pakahera, skull, shell, cranium; pakahera puoko tagata, human skull; pakahera pikea, shell of crab or crayfish. Gutu pakapaka, scabbed lips. Hau paka, fibres of the hauhau tree, which were first soaked in water, then dried to produce a strong thread. Moa gao verapaka, chicken with bald neck. Ariki Paka, certain collateral descendents of Hotu Matu'a, who exercised religious functions. Vanaga. 1. Crust, scab, scurf; paka rerere, cancer; pakapaka, crust, scabby. 2. Calm, still. 3. Intensive; vera paka, scorching hot; marego paka, bald; nunu paka, thin. 4. To arrive, to come. 5. To be eager. 6. To absorb. 7. Shin T. Pakahera, calabash, shell, jug. Pakahia, to clot, curdle, coagulate. Pakapaka, dry, arid, scorching hot, cooked too much, a desert, to fade away, to roast, a cake, active; toto pakapaka, coagulated blood; hakapakapaka, to dry, to broil, to toast. Pakahera pikea, shell of crab or crayfish. Churchill.
Kinana, s. Haw., a hen that has hatched chickens. Sam., tina, a mother. Tong., tina-manu, a sow that had litter. Tah., ti'a, the lower part of the stomach, below the navel. Fiji., tina, mother; tina-tina, mother of inferior animals. N. Zeal., tinana, the buttocks, trunk, body. This word, with somewhat varying but not far separate meanings, I am inclined to consider as related to the Goth., kwens, kwino, a woman; kwina-kunds and kwineins, female; and possibly kwithus, the womb, the stomach, if that is syncope of an original kwinthus. Greek, γυνη, woman ... |
| CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
| April 8 |
9 |
10 (100) |
11 |
12 |
| no star listed (18) |
ADHIL (Garment's Train) = ξ Andromedae (19.3), θ Ceti (19.7) |
KSORA (Knee) = δ Cassiopeiae (20.1), ω Andromedae (20.6), γ Phoenicis (20.8) |
δ Phoenicis (21.5) |
υ Andromedae (22.9) |
| 'March 12 |
13 |
14 (73) |
15 |
16 |
| "Febr 26 |
TE-HETUU-PU 27 |
28 (59) |
29 |
"March 1 |
 |
3 and 4 are complementary concepts:
... The ancient Chinese said:
One generates Two, Two generates Three, and Three
generates Everything.
I.e., before the invention of the
alphabet - ABC - there was 123. But we have mostly forgotten:
... Most ingenious Thoth, said
the god and king Thamus, one man has the ability to
beget arts, but the ability to judge of their
usefulness or harmfulness to their users belongs to
another; and now you, who are the father of letters,
have been led by your affection to ascribe to them a
power the opposite of that which they really
possess. For this invention will produce
forgetfulness in the minds of those who learn to use
it, because they will not practise their memory.
Their trust in writing, produced by external
characters which are no part of themselves, will
discourage the use of their own memory within them.
You have invented an elixir not of memory, but of
reminding; and you offer your pupils the appearance
of wisdom, not true wisdom, for they will read many
things without instruction and will therefore seem
to know many things, when they are for the most part
ignorant and hard to get along with, since they are
not wise, but only appear wise ...

... Interestingly, since another
meaning of shi is 'death', the number 4 is
considered unlucky.

... The practice of turning down
the fingers, contrary to our practice, deserves
notice, as perhaps explaining why sometimes savages
are reported to be unable to count above four. The
European holds up one finger, which he counts, the
native counts those that are down and says 'four'.
Two fingers held up, the native counting those that
are down, calls 'three'; and so on until the white
man, holding up five fingers, gives the native none
turned down to count. The native is nunplussed, and
the enquirer reports that savages can not count
above four ... For example, the
floor numbering in hotels
sometimes jumps mysteriously from 3 to 5; it is also
considered unlucky to give four of something as a
present ...
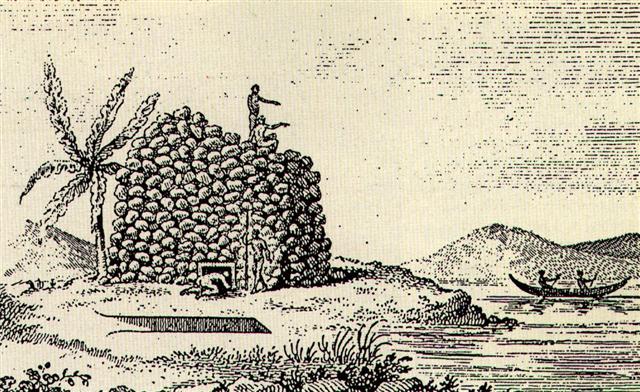
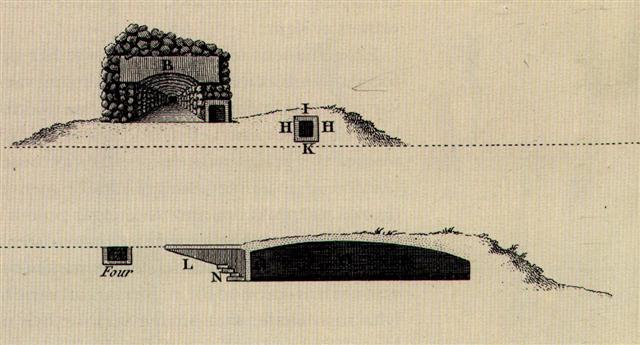
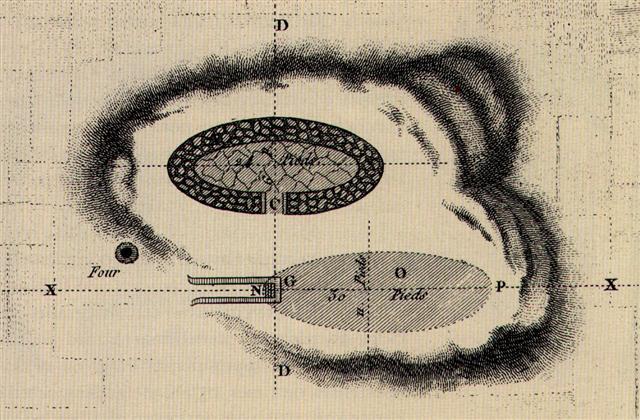
Barthel (a.a.):
"Okahu is located next to the cemetary of Hanga Roa
(HM:238). The place is famous because of the large
Tupa structure, seen by Cook and by La Pérouse (see
also Thomson, PH:Fig. 9, the indication of the
location is unreliable), which Métraux was still
able to describe (ME:189), and which was not
destroyed until 1941, when the stones were needed to
build a cemetary wall."
... Tupa.
Ancient buildings found scattered along the
coast; made of stone, and almost all of them round,
they served as shelters for fishermen. Tupatupa,
to carry (someone) on a stretcher; to carry (a load)
with the help of several people. Vanaga. 1. Land
crab. PS Mgv.: tutupa, a large crayfish. Mq.,
Ta.: tupa, land crab. Sa., To., Fu.: tupa,
a land crab with large claws. 2. Mixture, to carry,
tupatupa, to bring in one dead or wounded.
Tupapaku, corpse. T Pau.: tupapaku,
corpse, ghost. Mgv.: tupapaku, corpse, sick
person. Mq.: tupapaku, tupapaú, id.
Ta.: tupapau, corpse, ghost, specter.
Churchill.
... Compare also the type of structure, mainly in
the Lake Titicaca basin area, called chullpa
and Easter Island's tupa, both apparently
built as 'adoratorios', in which mummies,
skeletons, and skulls were displayed and worshipped
… where tupa would be the expected
Polynesian revaluation of chullpa ...
Thus there was reason for naming the 4th
place Okahu - the prominent place for recycling
(birth - death - birth - death etc).
|
3 (toru) |
4 (ha) |
|
Hanga Roa |
Okahu |
|
* |
† |
... They prepared a soft bed for
him in the cave and let him rest there. They stayed
there, rested, and lamented the severely injured
Kuukuu. Kuukuu said, 'Promise me, my
friends, that you will not abandon me!' They all
replied, 'We could never
abandon you!' They stayed there twenty-seven [27]
days in Oromanga. Everytime Kuukuu
asked, 'Where are you, friends?' they immediately
replied in one voice, 'Here we are!' They all sat
down and thought. They had an idea and Ira
spoke, 'Hey, you! Bring the round stones (from the
shore) and pile them into six heaps of stones!' One
of the youths said to Ira, 'Why do we want
heaps of stone?' Ira replied, 'So that we can
all ask the stones to do something.' They took (the
material) for the stone heaps (pipi horeko)
and piled up six heaps of stone at the outer edge of
the cave. Then they all said to the stone heaps,
'Whenever he calls, whenever he calls for us, let
your voices rush (to him) instead of the six (of us)
(i.e., the six stone heaps are supposed to be
substitutes for the youths). They all drew back to
profit (from the deception) (? ki honui) and
listened. A short while later, Kuukuu called.
As soon as he had asked, 'Where are you?' the voices
of the stone heaps replied, 'Here we are!' All (the
youths) said, 'Hey, you! That was well done!' ...
KUPA, v. Haw., to dig out, hollow out,
as a canoe or a trench; kupa-paku, a place
deep down in the ground. Tah., tupa, to dig
out, hollow out, scoop out. Fiji., cuva, to
stoop, bow down. Mal., kubur, grave, tomb.
Sunda., tumbuk, a hook, a staple.
Sanskr., kûpa, a well, a pit.; kûpa-kara,
a well-digger; kub-ja, humpbacked, crooked;
kumbha, a pot, jar. Benfey (Sanskr. Dict.)
refers the two latter to a lost verb kubh,
with an original signification of 'to be crooked'.
He offers no etymon, however, for kûpa, well,
pit. The Polynesians reconcile the two. The Sanskrit
kûpa finds its kindred in the Hawaiian and
Tahitian kupa, and the Sanskrit kumbha,
ku-ja, and kubh, with a primary sense
of 'crooked', refer themselves to the Fijian cuva,
'to stoop, low down', a sense now lost within the
Polynesian dialects proper.
Pers., kuftan, kaftan, to dig, cleave;
kuft, kâf, fissure. Armen., kup,
pit, cistern. Greek, κυπτω,
to bend forward, to stoop down; κυφος,
humpbacked; κυμβη,
a cup, a boat, a wallet; σκυφος,
a cup; κυψελη,
any hollow vessel. Lat., cubo, lie,
recline: concumbo, incumbo; cupa,
a vat, cask. Goth., kumbjan, lie down,
recline; hups, the hips, loins. A.-Sax.,
cop, a hollow vessel, cup. Anc. Slav., kâpona,
a goblet. Russ., kopati, to dig; a cistern.
Welsh, cwb or cwpan, a hollow place,
kennel or cote. Gael., tubag, tub.
(Fornander)

|

















