After the Explorers had slept at Te Pou in Te Anakena 10
(191), they went on:

| i te porima o te
raa.o te anakena.he ea |
On the fifth day of the month of
July ('Anakena'), they all got up, went downhill [he
turu], went on, and reached Hanga Te Pau.
They took their provisions with them, |
| ananake he turu
he oho mai he tuu ki ha(-) |
| nga te pau.he too i
te kai. |
|
Too. 1. To adopt, to
take, to acquire, to admit, to accept, to gather, to
dispose, to seize, to pull up, to extirpate, stripped, to
withdraw, to intercept, to frustrate, to touch, to employ,
to serve; tae too,
to renounce. Mq.: too,
to take, to receive, to accept, to adopt, to seize, to pull
up. 2. Raa too,
noon. 3. Numeral prefix. P Mgv.:
toko, id. Mq.:
toko,
too, id. Ta.:
too, id. Samoa
and Futuna use to'a
and toka, Tonga
and Niuē use toko, and
the remainder of Polynesia uses the latter form. Tooa:
kai tooa, intact, entire, whole; paea tooa, to
deprive. Churchill.
Kai. 1. Ina kai; verbal negation (but not
used with the imperative); ina kai kai matou, we have
not eaten. 2. To eat; meal. 3. Fruits or produces of the
land, vegetables, edible plants. 4. Figuratively: he-kai
ite rogorogo, to recite the inscriptions kohau
rogorogo (as spiritual food). 5. Eclipse: ku-kai-á te
raá, te mahina, the sun, the moon has been eaten
(eclipsed). Vanaga. 1. Negative; kai rogo, to fast;
kai oho, to forego; kai maa, to be ignorant,
to doubt; vave kai kohe, inaccessible; ina kai,
see ina 1. Ta.: ai, no. 2. To undergo, to
suffer. 3. Sharp, cutting. T Mgv.: koi, koikoi,
pointed, sharp, adapted for cutting; kokoi, prickly,
stinging, irritating. Mq.: koi, sharp, cutting. Ta.:
oi, sharp, keen. Since this is the only language
which has kai in this sense the possibility of
typographical error should not be overlooked. The form
koi outside of Southeast Polynesia is found in Maori,
Rarotonga and Hawaii. 4. To eat, to feed, to feast; food,
meat, a meal, repast; kai nui, provision,
intemperate, voracious; kai no iti, sober, temperate;
hue ki te kai, to victual; kai taria te kai,
abundance, to abound; hakapee no kai hoao, abundance,
to abound. Kaia, eaten. P Pau.: kai, food, to
eat. Mgv.: kai, food, nourishment, to eat. Mq.:
kai, ai, food, to eat. Ta.: ai, to eat. 5.
Hakakai, to take, to attack. Mgv.: kai, to
receive. Mq.: ai, to catch some one, to seek to
surprise. Ta.: ai, to receive, to get possession of,
to become master of. Churchill. Kaihue, a heap of
food. Kaikino, selfish, avaricious, faithless,
ingrate, miserly, rascal. Mq.: kaikino, selfish,
stingy, avaricious. Kaipurua, issue, outlet,
egress. Kaitagata, cannibal; paoa kaitagata,
cannibal, savage. Kaiu, nursling, suckling. Pau.:
kaiu, a child at the breast. Mq.: kaiu, child at
the breast, unweaned, suckling, young of animals. Ta.:
aiu, nursling. Churchill. Pau.: Fakakai, earring.
Ta.: faaai, ear ornament. Mq.: hakakai, id.
Ma.: whakakai, id. Kaikaia, a league, a plot.
Mgv.: kaia, cruel, cannibal. Ta.: aiaa, fault,
sin. Mq.: kaia, quarrelsome. Ma.: kaia, to
steal. Kaito, brave, robust. Ta.: aito, brave.
Ma.: kaitoa, a brave man. Kaitoa, well and
good! Ta.: aitoa, good! Ma.: kaitoa, id.
Kaitura, bravery, manhood. Ta.: turatura,
honored, exalted. Churchill. Mgv.: Kaiota, raw food.
Ta.: aiota, raw, ill cooked. Ma.: kaiota, id.
Churchill. Ta.: Ai, a bet, a wager, a game. Mq.:
kai, to throw lots, to lose a game. Sa.: 'ai, a
count toward the score of a game. Ma.: kai, a
puzzling toy. Aihamu, to eat leavings. Mq.:
kaihamu, id. Churchill. Mq.: Kaiheehee, to go
from place to place to enjoy feasts. Sa.: 'aisee, to
beg food at feasts. Kaihue, thief. Ha.: aihue,
to steal. Kaika, a meal, feast. Sa.: 'aiga,
meal. Ha.: aina, id. Kaioto, a sort of
hemorrhage, piles. Sa.: 'ailoto, a cancerous ulcer.
Kaitu, to perfume oneself during a tabu period when
it was forbidden. Ha.: aiku, to break a tabu.
Churchill. AI, v. Haw., to eat; s. food,
vegetable food, in distinction from ia, meat;
ai-na, for ai-ana, eating, means of eating,
fruits of the land; hence land, field, country.New Zeal.,
kai, to eat; kainga, food, meal, home, residence,
country. Tong., kai, to eat. Sam., 'ai, to
eat; ainga, family, kindred. Marqu., kaika,
kainga, food, meal. Tagal., cain, to eat. Zend.,
gaya, life; gaetha, the world; gava,
land, country. Vedic, gaya, house, family (A.
Pictet). Sanskr., ghâsa, food; ghas, devour.
Greek, αία,
γαια, γη,
different forms occurring in Homer, land, country,
cultivated land; γειος,
indigenous; γειτων,
a neighbour; ήια,
provisions for a journey. Goth., gawi,
gauja, country,
region. Germ., gau.
Lat., ganea,
eating-house; ganeo,
glutton. Lith., goyas;
Ant. Slav. and Russ., gai,
'past-rage', nemus. Polish, gay,
id. Mr. A. Pictet, in his 'Les Origines Indo-Europ.',
vol. II. p. 15, says that the Vedic and Zend gay
'n'ont surement aucun rapport avec le grec γαια.'
This assertion evokes a doubt, inasmuch as, as late a in
Homer's time, two other dialectical variations of this word
existed in the Greek, viz. αία and δα
or δη, in
δη-μητηρ, contracted
from some ancient form in δαια,
as γη and
γα, from γαια.
As neither of these can be supposed to be derived from, or
to be a phonetic corruption of, the other, it seems to me
that they must have come down abreast from primeval times,
thus indicating that the original root was differently
pronounced by various sections of the still united Aryan
stock; and I believe that this root, in its archaic forms,
still survives in the Polynesian ai
and kai, to eat.
The Sanskrit go,
land, the earth, from which Benfey derives a hypthetical
gavyd and a Greek
γαfια - by
elimination γαια
- is probably itself a contraction from the Vedic and Zend
gaya, as the
Greek γη and
γα, as the
ancient Saxon gâ
and gô, pagus,
regio, and the ancient Slav. gai,
nemus, are contractions from derivations of that ancient
root still found in Polynesia. The above derivatives in
sound and sense certainly refer themselves better to some
ancient ai of
kai, food, the
fruits of the forest or the roots of the field, than to the
Sanskrit go,
bull, cow, cattle; for the Aryan family undoubtedly had one
or more names for eating and for food before its various
divisions applied themselves to the herding of cattle. The
Sanskrit ghas,
ghâsa, the Latin
ganea,
ganeo, point strongly to
the underlying original sense of eating and food. According
to Professor A. H. Sayce, in 'Introduction to the Science of
Language', vol ii. p. 19, it is probable that the Latin
edere, to eat, is
a compound word = e-dere,
like ab-dere,
con-dere,
cre-dere, and others,
thus leaving e as
the root. How far that e
may have been a dialectical variant or a phonetic decay of
an older form more nearly allied to the Polynesian
ai, kai,
I leave to abler philologists to determine. Fornander. |
|
E:22 |
| he amoamo he oho he tuu ki
te pou he noho |
carrying them on their shoulders
[he amoamo], went on, and reached Te Pou. They made
camp and slept in Te Pou on the tenth day of the month of
July ('Anakena'). |
| he moe i te pou.i
te angahuru o te raa.ko te |
| anakena. |
| he ea ananake.he amoamo i te kai he oho |
Then they all got up, carried
their provisions [te kai] on their shoulders, went
straight ahead, and followed the path [he oho i te ara]
of the dream soul of Hau Maka. |
| he hakatika he oho i te ara.oho mai era.o |
| Atiga. Angle, corner.
Mgv.: hatiga, the corner of a house; hatiga,
hatihatiga, the joints or articulation of a limb.
Mq.: fatina, hatika, joint, articulation,
link. Ta.: fatiraa, articulation. Churchill.
 |
| te kuhane o Hau maka.he tuu ki hua reva |
They came to Hua Reva and said,
'This is Hua Reva A Hau Maka!' They went on and reached [he
tuu] Akahanga, took a look at it [he ui] and
looked around [he tikea]. They said: 'This is it!'
and gave the name [he nape i te ingoa] 'Akahanga A
Hau Maka'.
They went on and came to Hatinga Te Kohe and saw that in
this place the kohe plant had been broken [hati].
They all said [he ki anake], 'Here it is, the
kohe plant, troop of young men!'
This kohe plant had been broken by the feet [te
vae]of the dream soul and therefore they gave the name
'Hatinga Te Kohe A Hau Maka'.
They went on and came to Roto Iri Are. Again [hokoou]
they said,'Here it is, Roto Iri Are' and named (the place)
'Roto Iri Are A Hau Maka'. |
| he ki i ana nei ko
hua reva a Hau maka.he oho |
| hokoou he tuu ki akahanga he ui he tikea.he
ki |
| ki i (a)na nei he
nape i te ingoa.ko akahanga.a |
| hau maka.(h)e
oho hokoou he tuu ki hatinga te |
| kohe.he ui ko te kohe ku hati ana he ki
anake |
| i ana nei te kohe e kau a repa e tau kohe
hati |
| era i te vae o te kuhane.he
nape i te ingoa ko |
| hatinga te kohe a
Hau maka.he oho hokoou |
| he tuu ki roto iri are.he ki hokoou i ana
nei |
| a roto iri are he
nape i te ingoa ko roto iri are |
| a Hau maka. |
In
overview:
|
Nga Kope Ririva Tutuu
Vai |
A Te Taanga |
|
Hanga Te Pau (named
in Te Maro 1, 152) |
Ko Te Tomonga O Ira
|
|
3 Pu Mahore |
A Hau Maka O Hiva
|
|
Counting from the preceding "January 1
this was day 531 (= 365 + 166). In other words Pu
Mahore A Hau Maka O Hiva was at the position of 18
lunar synodic months. Here was 18 * 29½ = 531.
Here was 'the fish Mahore, who was in
a (water) hole to spawn'.
...
he oho mai te kuhane o hau maka.he tomo ki uta ki te
kainga.he ui te kuhane ko te mahore
ka noho i roto i te pu ...
... P
Pau.: kake, to climb, to ascend. Mgv.:
kake, the arrival of
shoals of spawning fish. Mq.: kake, to
climb up a valley ...
 |
 |
|
manu kake |
Ga3-1 (60) |
|
|
HE HURI MAI TE ARINGA
(He turned his face around)
 |
|
2 Poko Uri |
A Hau Maka I [Sic!]
Hiva |
|
I. 1. Preposition denoting the
accusative: o te hanau eepe i-hoa i te pureva mai
Poike ki tai, the hanau eepe threw the stones
of Poike into the sea. Te rua muraki era i a Hotu
Matu'a. the grave where they buried Hotu Matu'a. 2.
Preposition: for, because of, by action of, for reason
of..., ku-rari-á te henua i te ûa the ground is
soaked by the rain; i te matu'a-ana te hakaúru i te
kai mo taana poki huru hare, the mother herself
carries (lit.: by the mother herself the taking...) the
food for her son secluded in the house. 3. Preposition:
in, on, at (space): i te kaiga nei, on this
island. 4. Preposition: in, on (time): i mu'a,
before; i agataiahi, yesterday; i agapó,
tonight; i te poá, in the morning. 5.
Preposition: in the power of: i a îa te ao, the
command was in his power. 6. Adverb of place: here. i
au nei, I am here (also: i au i, here I am,
here). Vanaga. Î. Full; ku-î-á te kete i te kumara,
the bag is full of sweet potatoes. 2. To abound, to
be plentiful; ki î te îka i uta, as there are
lots of fish on the beach. 3. To start crying (of a
baby): i-ûi-era te ma-tu'a ku-î-á te poki mo tagi,
he-ma'u kihaho, when a mother saw that her baby was
starting to cry she would take it outside. Vanaga.
Toward; i muri oo na, to accompany. Churchill.
Ii, to deteriorate, to go bad. Churchill.
 |
|
1 Te Manavai |
A Hau Maka O Hiva |
|
Manava, Abdomen, belly, (fig.)
affection, sensitivity, feelings; manava more,
grief; manava mate, infatuated, in love (with
something); ku-ká-á te manava, flared up,
infuriated, irate; he-kava te manava, offended,
to turn sour, embittered. See also hatu (manava
hatu). Vanaga. Belly, abdomen, entrails, interior;
manava ahuahu, indigestion; manava hanohano,
high tempered, to annoy; manava itiiti, frugal;
manava karavarava, colic; manava mate, to
be in ecstasy, passion, intensity of affection;
manava more, to desolate; manava ninihi,
colic; manava nuinui, appetite; manava pagaha,
affected, to complain; manava rakerake, bad
character; manava riri, anger; manava ru,
complaint; manava ruru, alarm, consternation,
emotion, swoon; manava tagi, eager; manava
tiha, out of breath; manava topa ki raro,
humble, to humiliate; manava vai, simpleton, to
have dull senses; meniri ko manava, little
finger; kakari manavai,
waist; manava eete, to shudder, to
tremble, to astonish; anger, fright, consternation;
manava eete ki te mau mea ananake,
susceptible; eete manava, affected, moved;
manava pohi, hasty, cruel, penitent; contrition,
indignation; kokoma hanohano manava pohi, to
abhor; manava pohi nunui ke, implacable. P Pau.:
manava, the interior, affected, touched. Mgv.:
manava, the belly, spirit, conscience. Mq.:
menava, respiration, pulse. Ta.: manava,
belly, entrails. Churchill. |
|
Te Kioe Uri (named in
Te Maro 15, 166) |
A Hau Maka |
|
Te Piringa Aniva
(named in Te Maro 15, 166) |
- |
|
Te Pei (named in Te
Maro 15, 166) |
A Hau Maka |
|
Te Pou (named in Te
Maro 15, 166) |
A Hau Maka |
|
Hua Reva |
A Hau Maka O Hiva
|
|
Akahanga (named by
all) |
|
Hatinga Te Kohe
(named by all) |
|
Roto Iri Are (named
by all) |
|
Tama He Ika Kino He
Ihu Roroa |
|
One Tea |
A Hau Maka O Hiva |
|
Hanga Takaure |
|
Poike |
|
Pua Katiki |
|
Maunga Teatea |
|
Mahatua |
|
Taharoa |
|
Hanga Hoonu |
|
Rangi Meamea |
|
Peke Tau O Hiti |
|
Maunga Hau Epa |
|
Oromanga |
|
Hanga Moria One |
|
Papa O Pea |
|
Ahu Akapu |
|
Te
Pito O Te Kainga |
| ihe tamaiti |
kotia - te
hokohuki |
kava haati |
kiore |
te hokohuki |
kua tu te rau
hei |
te moko - te
hokohuki |
|
Tia. (Tiha G) .To sew. T Mgv.:
tia, to prick, to pierce, to stick in.
Churchill. Ta.: tia, the lower belly.
Mq.: tia-kopu, pubes. Ma.: tia,
the lower abdomen. Tiahonu, to piece
together. Mq.: tuhonu, to mend, to patch.
Ma.: tuhonu, to join. Churchill. Mq.:
tiaha, drinking cup. Ha.: kiaha, a
cup, a mug. Tikao, to dig out, to
disembowel. Ma.: tikaro, to dig out of a
hole. Churchill. KIA. s. Haw.,
pillar or inner post of a house supporting the
roof, any kind of pillar or post, a mast of a
vessel; kia-aina, a supporter of the land, a
governor of a province. Marqu., tia, id.
Sam., ti'a, the stick used in
tanga-tia, a man's head (abusively);
tia-pula, taro-tops cut off for planting.
Sunda, tihang. Mal., tiang, a
pillar. Greek, κιων,
a pillar, support of the roof, the identical
sense of the Polynesian usage of the word.
Liddell and Scott give no etymology or
connections of κιων.
(Fornander) |
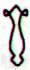 |
 |
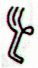 |
 |
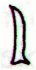 |
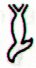 |
 |
|
Cb6-5 (146 + 366) |
Cb6-6 (11 * 11) |
Cb6-7 (392 + 122) |
Cb6-8 |
Cb6-9 |
Cb6-10 |
Cb6-11 |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
Rishu A.-13 (Head of the Lion)
ψ Leonis (146.4),
RAS ELASET AUSTRALIS = ε Leonis
(146.6)
*105.0 = *146.4 - *41.4 |
VATHORZ PRIOR =
υ
Carinae
(147.9) |
υ¹
Hydrae (148.4),
RAS ELASET BOREALIS (Northern Head of the Lion)
=
μ
Leonis
(148.7)
*107.0 = *148.4 - *41.4 |
TSEEN KE (Heaven's Record) =
φ
Velorum
(149.9) |
ν Leonis (150.1), π Leonis (150.6) |
υ² Hydrae (151.8) |
Al Jabhah-8 (Forehead) /
Maghā-10 (Bountiful) /
Sharru-14 (King)
10h (152.2)
AL JABHAH = η Leonis
(152.4),
REGULUS
(Little KIng) =
α
Leonis
(152.7)
*111.0 = *152.4 - *41.4 |
 |
|
Aug
14 |
15
(227) |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
|
'July 18 |
19
(200) |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
|
"July 4 |
TE ANAKENA 5
(186) |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
TE ANAKENA 10
(191) |
|
Arkat sha hi-na Shahū-27 (Eastern One in the
Tail of the Goat)
ENIF (The Nose) =
ε
Pegasi, ERAKIS =
μ
Cephei
(329.2),
46 CAPRICORNI,
JIH (the Sun) =
κ
Pegasi
(329.3),
ι
Piscis Austrini (329.4),
λ
Capricorni (329.6),
ν
Cephei (329.7),
DENEB ALGIEDI
=
δ
Capricorni
(329.8)
*288.0 = *329.4 - *41.4 |
θ
Piscis Austrini (330.1),
λ
Oct.
(330.7) |
KUH (Weeping) =
μ
Capricorni
(331.4),
γ
Gruis (331.5)
*290.0 = *331.4 - *41.4 |
no star listed (332) |
η Piscis Austrini (333.4)
*292.0 = *333.4 - *41.4 |
22h (334.8)
KAE UH (Roof) = ο Aquarii
(334.0),
AL KURHAH (White Spot) = ξ Cephei
(334.4),
SADALMELIK
(Lucky King) = α Aquarii,
AL DHANAB (The Tail) = λ Gruis
(334.6), ι Aquarii, ν Pegasi (334.7)
*293.0 = *334.4 - *41.4 |
ι Pegasi (335.0),
ALNAIR (The Bright One) = α Gruis
(335.1), μ Piscis Austrini, υ Piscis Austrini
(335.3),
WOO (Pestle) = π Pegasi
(335.7),
BAHAM = θ Pegasi,
τ Piscis Austrini (335.8) |
|
July 4 is the
185th day of the year (186th in leap years) in
the Gregorian calendar. There are 180 days
remaining until the end of the year. The
Aphelion, the point in the year when the Earth
is farthest from the Sun, occurs around this
date ...
1776 (= 4 *
444) A.D. was a leap year and therefore July 4
was not day 185 but day 186.


... Ira grew angry and quarreled
[he kakai] with Makoi. He said the
following (to him): 'You did not pay attention,
last-born, and you did not [tae] give the
(full) name. This is how it should be [Penei]:
the Manavai of Hau Maka of Hiva, in memory (mo
aringa ora) of the father, of his
dream soul'. Makoi replied, 'In Hiva the land
belongs to him - the land here is mine, not his
[tae oona]!' (E:21) |
|