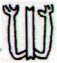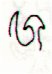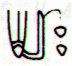Once again. If we should assume the creators of the text in Manuscript E
used the time-frame of Bharani to define dates, then day 288
should correspond to where the Sun reached Antares, viz. in
"October 15:
|
CLOSE TO THE
SUN: |
|
SEPT
20 |
21
(*184) |
EQUINOX |
23 |
24 |
25 (268) |
 |
 |
 |
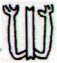 |
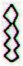 |
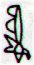 |
|
Ga7-14 |
Ga7-15 |
Ga7-16 (185) |
Ga7-17 |
Ga7-18 |
Ga7-19 |
|
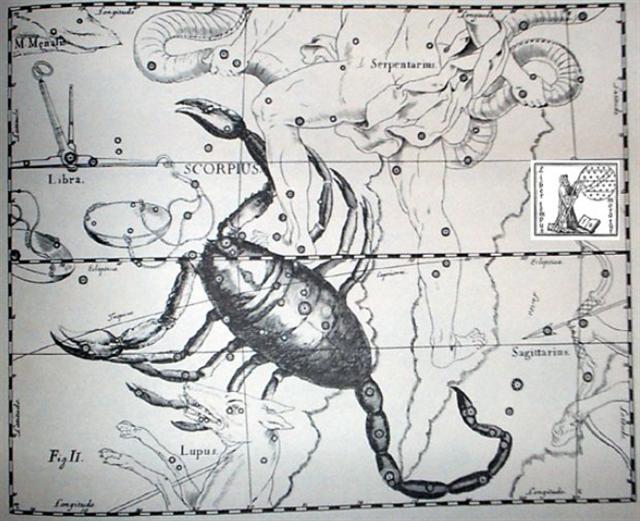
Heart-5 (Fox)
σ
Scorpii
(247.0),
HEJIAN
=
γ
Herculis (247.2),
ψ
Ophiuchi (247.7) |
ρ
Ophiuchi (248.1),
KAJAM (Club) =
ω
Herculis
(248.3),
χ
Ophiuchi (248.5),
SHE LOW (Market Tower) =
υ
Ophiuchi,
Tr.
Austr. (248.7), ζ Tr. Austr. (248.8) |
Al Kalb-16 (The Heart) /
Jyeshtha-18 (Eldest) /
ANA-MUA-1 (Entrance pillar)
ANTARES
= α Scorpii
(249.1),
MARFIK (Elbow) = λ Ophiuchi,
φ Ophiuchi (249.5), ω Ophiuchi (249.8) |
γ Apodis (250.1), σ Herculis (250.3), θ Tr.
Austr. (250.6), τ Scorpii (250.7) |
HAN = ζ Ophiuchi
(251.0) |
ζ
Herculis,
η
Tr. Austr.
(252.1), η Herculis, β Apodis (252.5) |
 |
|
Nov
23 |
24 |
25 |
26
(330) |
27 |
28 |
|
°Nov
19 |
20 |
21
(325) |
22
(*246) |
23 |
24 |
|
'Oct
27 (300) |
28 |
29
(*222) |
30 |
31 |
'Nov
1 |
|
"Oct
13 |
14 |
Tagaroa Uri
15 |
16 |
17
(290) |
18 |
|
DAY
247 |
248 |
249
(= 432 - 183) |
250 |
251 |
252 |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
MARCH 22 |
23 |
24 |
EQUINOX |
26
(*370) |
27
(86) |
|
Net-19 (Crow)
AIN (Eye) =
ε Tauri,
θ¹
Tauri,
θ²
Tauri (65.7) |
no
star listed (66) |
no
star listed (67) |
Rohini-4 (The Red One) /
Pidnu-sha-Shame-4 (Furrow of Heaven)
/
ANA-MURI-2 (Rear pillar - at the foot of which
was the place for tattooing)
ALDEBARAN
= α Tauri
(68.2),
THEEMIN = υ² Eridani
(68.5) |
no
star listed (69) |
no
star listed (70) |
 |
|
May 25 |
26 |
27
(*432) |
28
(148) |
29 |
30 |
|
°May
21 |
22 |
23
(*428) |
24
(144) |
25 |
26 |
|
'April 28 (*403) |
29 |
30
(*40) |
'May
1 |
2 |
3
(123) |
|
"April 14 (104) |
15 |
16
(*26) |
17
(*392) |
18 (108 + 365) |
19 |
|
DAY
65 (104 - 39) |
66 |
67
(= 4 * 108 - 365) |
68 |
69 |
70 |
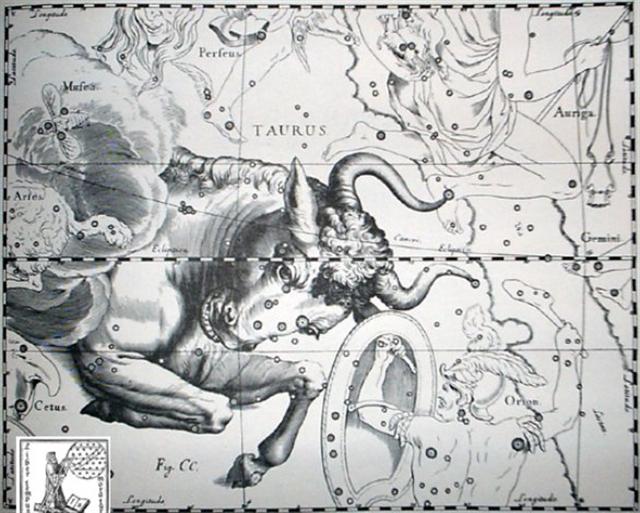
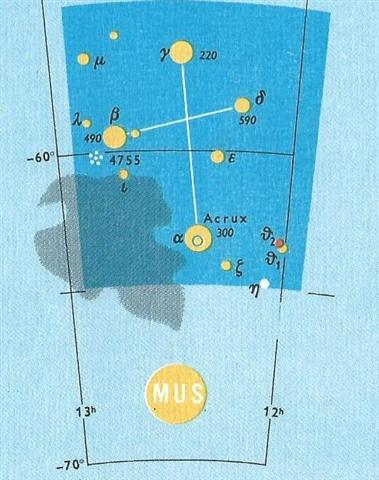
On Easter Island - far south of the equator - the
seasons were 'upside down' compared to those north of
the equator.
I have therefore suggested the C text was beginning where
Sirrah (the Navel of the Horse) was at the Full Moon,
i.e. where the summer half of the year could be regarded
to begin. This was where the Sun reached the Black Raven
(Corvus) - whose shadow could be perceived close to the
Southern Cross, below Mimosa (β
Crucis):
|
no glyph |
koia |
ki te
hoea |
ki te
henua |
te
rima te hau tea |
haga i
te mea ke |
ki te
henua - tagata honui |
|
Hoe. Hoe 1.
Paddle. Mgv.: hoe, ohe,
id. Mq., Ta.: hoe, id. 2. To
wheeze with fatigue (oeoe 2).
Arero oeoe, to stammer, to stutter;
Mgv. oe, to make a whistling
sound in breathing; ohe, a cry
from a person out of breath. Mq.: oe,
to wheeze with fatigue. 3. Blade, knife;
hoe hakaiu, clasp-knife,
jack-knife; hoe hakanemu,
clasp-knife; hoe pikopiko,
pruning knife. 4. Ta.: oheohe, a
plant. Ma.: kohekohe, id.
Churchill.T. Paddle. E hoe te heiva
= 'and to paddle (was their) pleasure'.
Henry. Hoea, instrument for
tattooing. Barthel. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ca1-1 |
Ca1-2 |
Ca1-3 |
Ca1-4 |
Ca1-5 |
Ca1-6 |
|
CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
|
Sept 20 (263) |
21 |
Equinox |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
|
ALCHITA
= α Corvi,
MA WEI (Tail of the Horse) = δ Centauri
(183.1),
MINKAR = ε Corvi
(183.7), ρ Centauri (183.9) |
PÁLIDA (Pale) = δ Crucis
(184.6),
MEGREZ (Root of the Tail) =
δ
Ursae Majoris
(184.9) |
Hasta-13 (Hand) /
Chariot-28 (Worm)
GIENAH (Wing) =
γ
Corvi
(185.1),
ε
Muscae (185.2),
ζ
Crucis (185.4),
ZANIAH (Corner) = η Virginis
(185.9)
*144.0 = *185.4 - *41.4 |
CHANG SHA
(Long Sand-bank) = ζ Corvi
(186.3) |
INTROMETIDA (Inserted) =
ε
Crucis
(187.4),
ACRUX =
α
Crucis
(187.5)
*146.0 = *187.4 - *41.4 |
γ
Com. Berenicis (188.0),
σ
Centauri (188.1),
ALGORAB =
δ
Corvi
(188.5),
GACRUX = γ Crucis
(188.7) |
γ
Muscae (189.0),
AVIS SATYRA (Bird of the
Satyrs) =
η
Corvi
(189.3),
ASTERION (Starry) =
β
Canum Ven.
(189.5),
KRAZ = β Corvi,
κ Draconis (189.7) |

... Raven gazed up and down the beach.
It was pretty, but lifeless. There was
no one about to upset, or play tricks
upon. Raven sighed. He crossed his wings
behind him and strutted up and down the
sand, his shiny head cocked, his sharp
eyes and ears alert for any unusual
sight or sound. The mountains and the
sea, the sky now ablaze with the sun by
day and the moon and stars he had placed
there, it was all pretty, but lifeless.
Finally Raven cried out to the empty sky
with a loud exasperated cry. And before
the echoes of his cry faded from the
shore, he heard a muffled squeak. He
looked up and down the beach for its
source and saw nothing. He strutted back
and and forth, once, twice, three times
and still saw nothing. Then he spied a
flash of white in the sand. There, half
buried in the sand was a giant
clamshell. As his shadow fell upon it,
he heard another muffled squeak. Peering
down into the opening between the halves
of the shell, he saw it was full of tiny
creatures, cowering in fear at his
shadow ... |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
March 21 (80)
Al Fargh al Thāni-25 (Rear Spout)
0h (365.25)
CAPH (Hand) =
β
Cassiopeiae,
SIRRAH
(Navel of the Horse) =
α
Andromedae
(0.5),
ε
Phoenicis,
γ³
Oct.
(0.8) |
22
Uttara Bhādrapadā-27 (2nd of the Blessed
Feet) /
Wall-14 (Porcupine)
ο Oct. (1.3),
ALGENIB PEGASI = γ Pegasi
(1.8) |
23
χ Pegasi (2.1), θ Andromedae (2.7) |
24
σ Andromedae (3.0), ι Ceti (3.3), ζ
Tucanae (3.5), ρ Andromedae, π Tucanae
(3.7) |
Julian
equinox
no star listed (4) |
26 (85 = 185 - 100)
ANKAA = α Phoenicis,
κ Phoenicis (5.0)
ALPHARD (α
Hydrae)
|
27
λ Phoenicis (6.3), β Tucanae (6.4)
*148.0
+ *183.0 = *331.0 = *6.4 - *41.4 +
*366.0 |
 |
When the Explorers left their homeland in Vaitu Nui
25 this date should then be translated into
"April 25 and Te Maro 1 - when they reached
Easter Island - should be "June 1.
| E vae ra - ka
oho - ki te henua - kua huki |
ku kikiu - te
henua |
32 |
|
Huki. 1. Pole attached to
the poop from which the
fishing-net is suspended: huki kupega. 2. Digging stick. 3. To
set vertically, to stand (vt.). 4.
Huki á te mahina, said of the new moon when
both its horns have become visible. Vanaga. 1.
To post up, to publish. 2. To cut the throat (uki).
Mq.: Small sticks which close up the ridge of a
house. Ha.: hui, the small uniting sticks
in a thatched house. Churchill. Standing
upright. Barthel. M. Spit for roasting. Te
Huki, a constellation. Makemson. Hukihuki.
1. Colic. 2. To transpierce, a pricking. 3. To
sink to the bottom. Churchill.
HUI¹,
v. Haw., to unite together, to mix, to
add one to another, to assemble, meet; s.
cluster, collection of things; huihui, a
bunch, cluster; huiuna (for huiana),
a seam in a garment; la-hui, collection
of people, a nation. Sa. sui, to dilute,
to add ingredients to a thing; sui, to
sew, to thread beads; susui, to mend,
repair; susuia, to fasten the ridge-pole
of a house. Tong., hui, mingle, mix,
join; fufui, a flock of birds. N. Zeal.,
hui, huhui, to gather, mix, unite;
ra-hui, a company; ka-hui, a herd,
a flock. Tah., hui, a collection of
persons, a company; hui-hui manu, flock
of birds; hui-tara-wa, Orion's belt.
Marqu., huhui, a bundle of taro. Sanskr.,
yu, to bind, join, mix; yuj, to
join; yuga, a yoke, a pair, a couple;
yûti, mixing; yûtha, flock of birds
or beasts. Greek, ζευγνυμι,
to join, put to, yoke up, bind, fasten;
ζευγος, a
yoke of beasts, pair, couple; ζυγον,
the yoke; ζωνη,
belt, girdle. Lat., jugum,
a yoke; jugo,
bind up, tie together; jungo,
bind, join, unite. Goth., juk,
a yoke. A.-Sax., geok,
id. Scand., ok,
id. Armen., zugel,
attach together, yoke up; zoygkh,
a couple, a pair. Pers., yûgh,
a yoke. Irish, ughaim,
harness. Welsh, jow,
yoke. Lett., jûgs,
yoke. Anc. Slav., jgo,
yoke. Bohem., gho,
id. Lith., jungas,
id. A singular coincidence of application, if it
has no nearer connection, by the Polynesian and
the Latin of this word to similar purposes,
occurs in the huhui
and hui-tarawa
of the former and
jugulæ
of the latter. In Hawaiian huhui
designates a constellation generally, but
especially that of the Pleiades; in Tahitian
hui-tarawa,
lit. the transverse or horizontal cluster,
designates the stars generally called Orion's
belt, and in Latin jugulæ
represents the very same stars in the
constellation Orion. HUI²,
v. Haw., to ache, be in pain; s.
bodily pain; niho-hui, the toothache;
hui, huihui, cold, chilly, as morning
air or cold water; hukeki, hukiki,
cold, shivering on account of wet. N. Zeal.,
huka, cold. Tah., hui, hui-hui,
to throb as an artery, twitchings in the flesh.
Sanskr., çuch¹,
to be afflicted, grieve; çuch²,
to be wet, fetid; çuch,
s., sorrow, grief; quære suçîma,
cold? To this Sanskr. çuch
Benfey refers the
Goth. hiufau,
to mourn, lament, and the O. H. Germ.
huvo, an owl.
(Fornander) |
 |
 |
|
Cb3-1 (50) |
Cb3-2 (392 + 51 = 443) |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
5h
(76.1)
ε
Leporis (76.0),
CURSA
= β
Eridani
(76.4), λ Eridani (76.7)
*35.0 = *76.4 - *41.4 |
μ
Aurigae, μ Leporis (77.6) |
|
June
5 (156 = 115 + 41) |
6 |
|
'May 9 (129 = 115 + 14) |
10 |
|
Vaitu Nui 25 (115 = 230 / 2) |
26 |
|
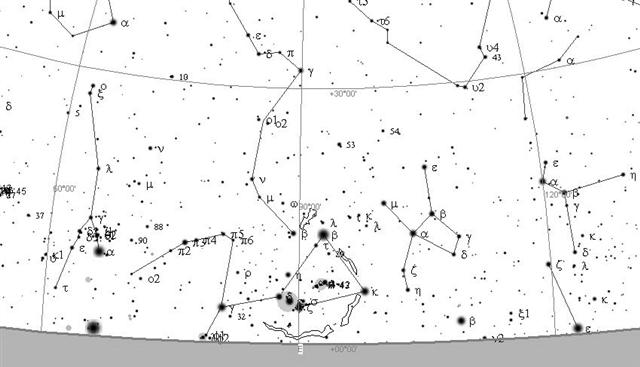
... In view
of the almost universal prevalence of the
Pleiades year throughout the Polynesian area it
is surprising to find that in the South Island
and certain parts of the North Island of New
Zealand and in the neighboring Chatham Islands,
the year began with the new Moon after the
yearly morning rising, not of the Pleiades, but
of the star Rigel in Orion ...
 |
| manu pao i te
hau tea - kua tu |
manu rere ki
te hau tea - kua tu |
manu rere ki
te hau tea |
kiore - henua |
|
Pao. To cut off, to throw a lance.
Churchill.
Paopao, spade, shovel, rubbish, to
lacerate, to have a quarrel with. Churchill.
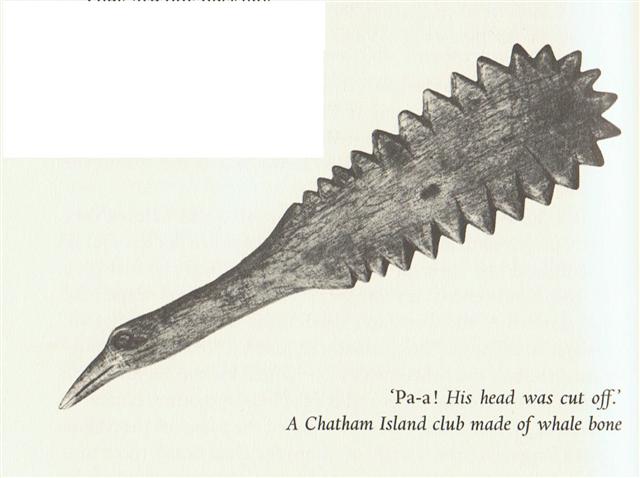

There are 27 teeth around the
tail of the bird above. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Cb4-13 → 14 * 29½ |
Cb4-14 (477 = 392 + 85) |
Cb4-15 |
Cb4-16 (87 = 3 * 29) |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
| no
star listed (110) |
ALUDRA (Virgin) = η Canis Majoris
(111.1),
PROPUS = ι Gemini (111.4),
GOMEISA (Water-eyed) = β Canis Minoris
(111.6)
*70.0 = *111.4 - *41.4 |
ρ Gemini (?) (112.1),
Eskimo Nebula = NGC2392 Gemini
(112.2)
ANTARES (α Scorpii)
|
Al Dhirā'-5 (Forearm) /
Punarvasu-7 /
Mash-mashu-Mahrū-10 (Western One of the Twins)
CASTOR
= α Gemini
*113.4 = *41.4 + *72.0 |
|
July
9 (10 * 19) |
10
|
11
|
12
(193 = 152 + 41) |
|
'June 12 (190 - 27) |
13
(164) |
14 |
15 |
|
"May
29 (190 - 41) |
30
(150) |
31 |
Te Maro 1
(8 * 19) |
|
... The jaguar learned from
the grasshopper that the toad and the rabbit had
stolen its fire while it was out hunting, and
that they had taken it across the river. While
the jaguar was weeping at this, an anteater came
along, and the jaguar suggested that they should
have an excretory competition. The anteater,
however, appropriated the excrement containing
raw meat and made the jaguar believe that its
own excretions consisted entirely of ants. In
order to even things out, the jaguar invited the
anteater to a juggling contest, using their eyes
removed from the sockets: the anteater's eyes
fell back into place, but the jaguar's remained
hanging at the top of a tree, and so it became
blind. At the request of the anteater, the
macuco bird made the jaguar new eyes out of
water, and these allowed it to see in the dark.
Since that time the jaguar only goes out at
night. Having lost fire, it eats meat raw. It
never attacks the macuco ...'
 |
Therefore their sea journey appears to have had a duration of 152 ("June 1) - 115
("April 25) = 37 days. However, we should consider
Te Maro 1 as a day when they were safe, had 'descended', made
'land-fall'. Thus their
voyage across the waters
measured 36 (= 432 / 12) days.
|
115 |
35 |
151 |
|
"April 25 |
"May 31 |
|
Vaitu nui 25 |
Vaitu potu 31 |
Vaituru (vai-turu
1), water conduit.
Vaitupu, spring water. To.:
vaitubu,
well water ...Turu
1. To fall in drops, to flow, to leak, to descend, a
drop; turu ki tai, to take refuge at sea;
hakaturu, to cause to descend, to lower, to take
soundings; hakaturuturu, to heave and pitch
...
The
number of glyphs on side a of the C tablet is 396 (= 432
- 36) and the number encoded in the tresses of
Pachamama is also 11 * 36.
|
Counting in the tresses of
Pachamama from right to left: |
|
1 |
26 |
78 |
1 |
29 |
90 |
|
2 |
26 |
2 |
30 |
|
3 |
26 |
3 |
31 |
|
4 |
25 |
104 |
4 |
34 |
124 |
|
5 |
26 |
5 |
31 |
|
6 |
27 |
6 |
30 |
|
7 |
26 |
7 |
29 |
|
Total = 396 = 182 + 214 = 11 * 36 |
Maro: A sort of small banner or pennant of bird
feathers tied to a stick. Maroa: 1. To stand up,
to stand. 2. Fathom (measure). See kumi.
Vanaga. Maro: 1. June. 2. Dish-cloth T P Mgv.:
maro, a small girdle or breech clout. Ta.: maro,
girdle. Maroa: 1. A fathom; maroa hahaga,
to measure. Mq.: maó, a fathom. 2. Upright, stand
up, get up, stop, halt. Mq.: maó, to get up, to
stand up. Churchill. Pau.: Maro, hard, rough,
stubborn. Mgv.: maro, hard, obdurate, tough. Ta.:
mârô, obstinate, headstrong. Sa.: mālō,
strong. Ma.: maro,
hard, stubborn. Churchill.
Ta.: Maro,
dry, desiccated. Mq.: mao,
thirst, desiccated. Fu.: malo,
dry. Ha.: malo,
maloo, id.
Churchill. Mgv.:
Maroro, the
flying fish. (Ta.: marara,
id.) Mq.: maoo,
id. Sa.: malolo,
id. Ma.: maroro,
id. Churchill. MALO ¹, s. Haw., a
strip of kapa or cloth tied around the loins of men to
hide the sexual organs. Polynesian, ubique, malo,
maro, id., ceinture, girdle-cloth, breech-cloth.
Sanskr., mal, mall, to hold; malla,
a cup; maltaka, a leaf to wrap up something, a
cup; malâ-mallaka, a piece of cloth worn over the
privities. Greek, μηρνομαι; Dor., μαρνομαι,
to draw up, furl, wind round. No etymon in Liddell and
Scott. MALO ², v. Haw., to dry up, as
water in pools or rivers, be dry, as land, in opposition
to water, to wither, as vegetables drying up; maloo,
id., dry barren. Ta., maro, dry, not wet;
marohi, dry, withered. A later application of this
word in a derivative sense is probably the Sam. malo,
to be hard, be strong; malosi, strong; the Marqu.
mao, firm, solid; N. Zeal., maroke, dry;
Rarot., Mang., maro, dry and hard, as
land.Sanskr., mŗi,
to die; maru,
a desert, a mountain; marut,
the deities of wind; marka,
a body; markara,
a barren woman; mart-ya,
a mortar, the earth; mîra,
ocean. For the argument by which A. Pictet connects
maru and
mira with
mŗi, see
'Orig. Ind.Eur', i. 110-111. It is doubtless correct.
But in that case 'to die' could hardly have been the
primary sense or conception of mŗi.
To the early Aryans the desert, the maru,
which approached their abodes on the west, must have
presented itself primarily under the aspect of 'dry,
arid, sterile, barren', a sense still retained in the
Polynesian maro.
Hence the sense of 'to wither, to die', is a secondary
one. Again, those ancient Aryans called the deity of the
wind the Marut;
and if that word, as it probably does, refers itself to
the root or stem mŗi,
the primary sense of that word was certainly not 'to
die', for the winds are not necessarily 'killing', but
they are 'drying', and that is probably the original
sense of their name. Lat., morior,
mors, &c.
Sax., mor,
Eng., moor,
equivalent to the Sanskr. maru.
(Fornander)

|