The name Te Pei was probably chosen in order to
indicate empty and hard ('thirsty') river beds (rima
aueue) - they were the grooves which would lead fresh water downhill to the level of
the sea:
Pei. Grooves, still
visible on the steep slopes of some hills, anciently used as
toboggans. People used to slide down them seated on banana-tree
barks. This pastime, very popular, was called pei-âmo.
Vanaga. Like, as; pei ra, thus, like that; such, the same
as; pei na, thus, like that; pei ra ta matou,
proverb; pei ra hoki, likeness, similitude; pei ra tau,
system; pei ra hoki ta matou, usage. PS Sa.: pei,
thus. This is particuarly interesting as preserving one of the
primordial speech elements. It is a composite, pe as, and
i as demonstrative expressive of that which is within
sight; therefore the locution signifies clearly as-this.
Churchill. Mgv.: To juggle balls. Ta.: pei, id. Mq.:
pei, id. Peiaha, jaws, gills of fish. Ta.: peihaha,
peiha, gills. Ma.: piha, id. Peipei, to
approach. Churchill.
This idea agrees with the name given by Makoi for his
station number 50,
because pau means very little left; pei and
pau were similar in meaning:
Pau. 1. To run out
(food, water): ekó pau te kai, te vai, is said when there
is an abundance of food or water, and there is no fear of
running out. Puna pau, a small natural well near the
quarry where the 'hats' (pukao) were made; it was so
called because only a little water could be drawn from it every
day and it ran dry very soon. 2. Va'e pau, clubfoot.
Paupau: Curved. Vanaga. 1. Hakapau, to pierce (cf.
takapau, to thrust into). Pau.: pau, a cut, a
wound, bruised, black and blue. 2. Resin. Mq.: epau,
resin. Ta.: tepau, gum, pitch, resin. (Paupau)
Hakapaupau, grimace, ironry, to grin. 3. Paura
(powder), gunpowder. 4. Pau.: paupau, breathless. Ta.:
paupau, id. 5. Ta.: pau, consumed, expended. Sa.:
pau, to come to an end. Ma.: pau, finished. 6. Ta.:
pau, to wet one another. Mq.: pau, to moisten.
Churchill. Paua
or
pāua
is the Māori name given to three species of large edible
sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs which belong to the family
Haliotidae (genus Haliotis), known in the USA as
abalone, and in the UK as ormer shells ... Wikipedia
Thus there
was a Heap of Fuel (μ Cancri), but not yet any fire:
... He was moreover confronted with
identifications which no European, that is, no average rational
European, could admit. He felt himself humiliated, though not
disagreeably so, at finding that his informant regarded fire and
water as complementary, and not as opposites. The rays of light
and heat draw the water up, and also cause it to descend again
in the form of rain. That is all to the good. The movement
created by this coming and going is a good thing. By means of
the rays the Nummo draws out, and gives back the life-force.
This movement indeed makes life. The old man realized that he
was now at a critical point. If the Nazarene did not understand
this business of coming and going, he would not understand
anything else. He wanted to say that what made life was not so
much force as the movement of forces. He reverted to the idea of
a universal shuttle service. 'The rays drink up the little
waters of the earth, the shallow pools, making them rise, and
then descend again in rain.' Then, leaving aside the question of
water, he summed up his argument: 'To draw up and then return
what one had drawn - that is the life of the world'
...

... 'Yes, for he was a monstrous thing and
fashioned marvelously, nor was he like to any man that lives by
bread, but like a wooded peak of the towering hills, which
stands out apart and alone from others.' Odysseus, choosing
twelve men, the best of the company, left his ships at shore and
sallied to the vast cave. It was found stocked abundantly with
cheeses, flocks of lambs and kids penned apart, milk pails,
bowls of whey; and when the company had entered and was sitting
to wait, expecting hospitality, the owner came in, shepherding
his flocks. He bore a grievous weight of dry wood, which he cast
down with a din inside the cave, so that in fear all fled to
hide. Lifting a huge doorstone, such as two and twenty good
four-wheeled wains could not have raised from the ground, he set
this against the mouth of the cave, sat down, milked his ewes
and goats, and beneath each placed her young, after which he
kindled a fire and spied his guests
...
|
Te Pei (66-78) |
Te Pou (79-91) |
|
MAY 14 |
15 (365 + 135) |
16 (136) |
17 |
18 (*58 = 2 * 29) |
19 |
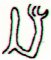 |
 |
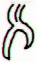 |
 |
 |
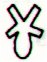 |
|
Ga2-24→
22 * 4 |
Ga2-25 |
Ga2-26
(8 * 7) |
Ga2-27 →
π |
50 Hanga Te Pau |
Ga2-29
(59) |
|
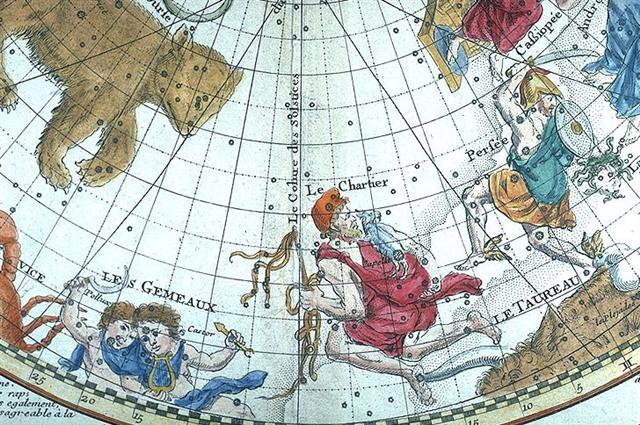
φ Gemini (118.4)
*77.0 = *118.4 - *41.4 |
DRUS
(Hard)
= χ Carinae
(119.9) |
ω
Cancri
(120.2) |
8h (121.7)
χ Gemini (121.0),
NAOS
= ζ Puppis
(121.3) |
ρ
Puppis (122.0),
HEAP OF
FUEL
= μ Cancri
(122.1),
ζ
Monocerotis (122.3), ψ
Cancri (122.6),
REGOR (Roger backwards) = γ Velorum
(122.7) |
TEGMINE = ζ Cancri
(123.3) |
.jpg) |
|
July 17 |
18 |
19 (200) |
20 (*121) |
21 |
22 / 7 |
|
°July
13 |
14 |
15 (196) |
16 |
17 (*118
= 4 * 29˝) |
18 |
|
20 (*91 = *88 +
*3) |
SOLSTICE |
'June 22 (173) |
23 |
ST JOHN'S DAY |
25 (*96) |
|
"June 6 (314
/ 2) |
7 |
8 (159 + 12) |
9 |
Te Maro 10
(173) |
11 (162) |
|
he ea.a Ira.he iri he oho ki runga anake.
i te angahuru o te raa o te
maro i iri ai - Ira got
up. They all climbed to the top of the hill.
They climbed up on the tenth day
of the month of June ('Maro’).
[E:18]
... The addition of 10 (lost days
in 1582 AD) + 2 (day difference since then) = 12
will explain that when Hotu A Matua arrived
to Easter Island the day number was not 288
("October 15) but 300 (Tangaroa Uri 15) ... |
|
57 |
58 |
200 - 141 = 59 |
60 |
61 = 173 - 112 |
62 = 162 - 100 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
NOV 13 |
14 |
15 |
16
(*240) |
17 |
18 (322) |
|
ι Sagittarii (301.2),
TEREBELLUM = ω Sagittarii,
ξ Aquilae (301.3),
ALSHAIN (Falcon) = β Aquilae
(301.6), φ Aquilae (301.8) |
ε Pavonis, θ Sagittarii (302.3), γ Sagittae (302.5),
μ Pavonis (302.7) |
τ Aquilae
(303.8) |
20h (304.4)
η Sagittae (304.2), δ Pavonis (304.4)
*263.0 = *304.4 - *41.4 |
SHANG WEI (Higher Guard) = κ Cephei
(305.2),
θ
Sagittae (305.4),
TSEEN FOO
(Heavenly Raft)
= θ Aquilae (Ant.)
(305.6), ξ Capricorni (305.8)
*264.0 = *305.4 - *41.4 |
TSO KE (Left Flag) = ρ Aquilae (306.3) |

... In late September or early
October 130, Hadrian and his entourage, among them
Antinous, assembled at Heliopolis to set sail
upstream as part of a flotilla along the River Nile.
The retinue included officials, the Prefect, army
and naval commanders, as well as literary and
scholarly figures. Possibly also joining them was
Lucius Ceionius Commodus, a young aristocrat whom
Antinous might have deemed a rival to Hadrian's
affections. On their journey up the Nile, they
stopped at Hermopolis Magna, the primary shrine to
the god Thoth. It was shortly after this, in October
[in the year A.D.] 130 - around the time of the
festival of Osiris - that Antinous fell into the
river and died, probably from drowning. Hadrian
publicly announced his death, with gossip soon
spreading throughout the Empire that Antinous had
been intentionally killed. The nature of Antinous's
death remains a mystery to this day, and it is
possible that Hadrian himself never knew; however,
various hypotheses have been put forward. One
possibility is that he was murdered by a conspiracy
at court. However, Lambert asserted that this was
unlikely because it lacked any supporting historical
evidence, and because Antinous himself seemingly
exerted little influence over Hadrian, thus meaning
that an assassination served little purpose. Another
suggestion is that Antinous had died during a
voluntary castration as part of an attempt to retain
his youth and thus his sexual appeal to Hadrian.
However, this is improbable because Hadrian deemed
both castration and circumcision to be abominations
and as Antinous was aged between 18 and 20 at the
time of death, any such operation would have been
ineffective. A third possibility is that the death
was accidental, perhaps if Antinous was intoxicated.
However, in the surviving evidence Hadrian does not
describe the death as being an accident; Lambert
thought that this was suspicious. Another
possibility is that Antinous represented a voluntary
human sacrifice. Our earliest surviving evidence for
this comes from the writings of Dio Cassius, 80
years after the event, although it would later be
repeated in many subsequent sources. In the second
century Roman Empire, a belief that the death of one
could rejuvenate the health of another was
widespread, and Hadrian had been ill for many years;
in this scenario, Antinous could have sacrificed
himself in the belief that Hadrian would have
recovered. Alternately, in Egyptian tradition it was
held that sacrifices of boys to the Nile,
particularly at the time of the October Osiris
festival, would ensure that the River would flood to
its full capacity and thus fertilize the valley;
this was made all the more urgent as the Nile's
floods had been insufficient for full agricultural
production in both 129 and 130. In this situation,
Hadrian might not have revealed the cause of
Antinous's death because he did not wish to appear
either physically or politically weak. Conversely,
opposing this possibility is the fact that Hadrian
disliked human sacrifice and had strengthened laws
against it in the Empire ... |
|
Jan 16 |
17 |
18 (383) |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
°Jan 12 |
13 (378) |
14 |
15
(*300) |
16 |
17 |
|
20 (354) |
SOLSTICE |
22 |
'Dec 23 |
CHRISTMAS EVE |
25 (*279) |
|
"Dec 6
(340) |
7 |
8 (354) |
9 |
Ko Koró 10 (356) |
11 (*265) |
|
*160 |
*161 |
*162 |
*304 - *141 |
*164 |
*265 - *100 |
Also the name Te Manavai for the 3rd kuhane
station (on the mainland) now rings true:
Manavai. Hollow where rainwater accumulates;
anciently, small, round gardens, preferably situated in low
shady spots, where the mahute tree was grown. Vanaga.
1. Brain. 2. Valley, ravine, river, torrent, brook;
manavai miro, orchard, Mq.: manavai, valley,
brook. Ta.: anavai, river, brook. It scarcely appears
that these are fully coordinate. In Tahiti anavai has
a clear etymology, ana meaning the bed of a stream.
In Rapanui and in the Marquesas mana most readily
associates with maga, as water in a forked bed.
Churchill.
Mahute.
A tree (Boussonetia papyrifera) formerly more
abundant on the island, the fibres of which were used for
clothing (see nua and hami). Vanaga. The tree
Broussonetia papyrifera, indispensible for all types
of fasteners (lines, twine, ropes, and rigging).
Barthel 2. Maute, paper mulberry (mahute G). P
Mgv.: eute, ute, id. Mq.: ute, id.
Ta.: aute, Hibiscus
rosa-sinensis. Pau.: aute, id. Mahutehute
(mahute - tutu 1) bast cloth in the last stage
of preparation (maute). Churchill.
|
Nga Kope Ririva Tutuu Vai |
- |
|
365 |
A Te Taanga |
|
Te Pu Mahore |
1 |
- 13 |
- 378 |
A Hau Maka O Hiva
|
|
Te Poko Uri |
2 |
14 - 26 |
- 391 |
A
Hau Maka I
[Sic!]
Hiva |
|
Te Manavai |
3 |
- 39 |
- 404 |
A Hau Maka O Hiva |
|
Te Kioe Uri |
4 |
- 52 |
- 417 |
|
Te Piringa Aniva |
5 |
- 65 |
- 430 |
|
Te Pei |
6 |
- 78 |
- 443 |
|
Te Pou |
7 |
79 - 91 |
- 456 |
|
Hua Reva |
8 |
- 104 |
- 469 |
|
Akahanga |
9 |
- 117 |
- 482 |
|
Hatinga Te Kohe |
10 |
- 130 |
- 495 |
|
Roto Iri Are |
11 |
- 143 |
- 508 |
|
Tama He Ika Kino He Ihu Roroa |
12 |
- 156 |
- 521 |
- |
|
One Tea
|
13 |
-
169 |
-
534 |
A Hau Maka O Hiva |
|
Hanga Takaure |
14 |
-
182 |
-
547 |
|
Poike |
15 |
-
195 |
-
560 |
|
Pua Katiki |
16 |
-
208 |
-
573 |
|
Maunga Teatea |
17 |
- 221 |
- 586 |
|
Mahatua |
18 |
-
234 |
-
599 |
|
Taharoa |
19 |
-
247 |
-
612 |
|
Hanga Hoonu |
20 |
-
260 |
-
625 |
|
Rangi Meamea |
21 |
-
273 |
-
638 |
|
Peke Tau O Hiti |
22 |
-
286 |
-
651 |
|
Maunga Hau Epa |
23 |
-
299 |
-
664 |
|
Oromanga |
24 |
-
312 |
-
677 |
|
Hanga Moria One |
25 |
-
325 |
-
690 |
|
Papa O Pea |
26 |
-
338 |
-
703 |
|
Ahu Akapu |
27 |
- 351 |
- 716 |
|
Te Pito O Te Kainga
|
28 |
-
364 |
-
729 |
Reading the G text we will find right ascension day
number *39 (at the time of Bharani) to be at Elnath, and the
peculiar name Thirst-slaking Camels can now be perceived as
at
least reasonable - here, in a dry deserted place, there was an oasis with fresh
drinking water.
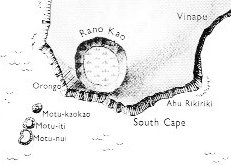
... On the south-western tip of Easter
Island, at Orongo, up near the ragged edge of the
Rano Kau crater, are four small holes very precisely
pecked through the bedrock just beside a large Ahu.
Since Orongo is know to have been an important ritual
centre, these holes attracted the attention of the Norwegian
Archaeological Expedition which visited the island in
1955-56. They were studied by Dr Edwin Ferdon. After making
detailed observations at the solstices and the equinoxes he
concluded: 'it can definitely be stated that the complex of
four holes constituted a sun-observation device'. As well as
one Ahu, Orongo also formerly had one Moai,
a unique specimen, carved out of basalt, that was removed to
the British Museum in 1868.
.jpg)
"... the divine progenitor of all important genealogies,
whose image was venerated at Orongo ..." (Van Tilburg)
Perched on a headland with a
precipitous drop to the ocean on one side and the gigantic,
reed-filled crater of Rano Kau on the other, the main
remaining feature of the site is a conglomeration of 54
squat oval houses with massively thick walls of horizontal
stone slabs and domed corbel-vaulted ceilings ...
.jpg)
|
Te Manavai |
Te Kioe Uri |
|
1 he kape |
1 he hauhau |
1 he mahute |
|
Kape.
'Bitter-taro' (Alocasia macrorrhiza). In
1957 kape was still cultivated in much
the same way as dry taro. It is a type of food
to be eaten during times of famine. According to
Fuentes (1960:856), the tubers had to be kept in
the earth-oven for 15 (sic) days in order
to eliminate some of the poisonous components.
Barthel 2. Arum, yam. Churchill. Bitterness by
doing it with Bad-taste produced the kape
(mangeongeo ki ai ki roto he rakerake ka pu
te kape).
... In June 10 (161) was the first day beyond
*80, i.e. the first day beyond the Star in the
Bull towards the north, and at the time of
rongorongo this could evidently have been the
place for He Mahute ...
... Teke said to Oti, 'Go and take the hauhau
tree, the paper mulberry tree, rushes, tavari
plants, uku koko grass, riku ferns, ngaoho
plants, the toromiro tree, hiki kioe plants (Cyperus
vegetus), the sandalwood tree, harahara
plants, pua nakonako plants, nehenehe ferns, hua
taru grass, poporo plants, bottle gourds (ipu
ngutu), kohe plants, kavakava atua ferns,
fragrant tuere heu grass, tureme grass (Dichelachne
sciurea), matie grass, and the two kinds of
cockroaches makere and hata.' Oti
and all his assistants went and took the hauhau
tree with them. All kinds of things [te huru
o te mee] (i.e., plants) and insects [?]
were taken along ... [E:69] |
|
APRIL 5 |
6 (96 = 80 +
16) |
7 (81 + 16) |
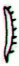 |
 |
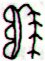 |
|
Ga1-15 |
Ga1-16 |
Ga1-17 |
|
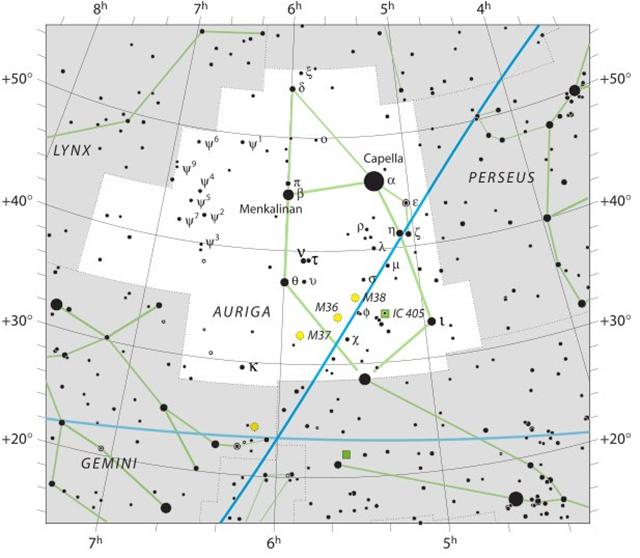
λ Aurigae (79.0), λ Leporis (79.6), ρ Aurigae
(79.7)
ARCTURUS (α Bootis) |
Shur-narkabti-sha-iltanu-5 (Star in the Bull
towards the north)
σ
Aurigae (80.4),
BELLATRIX (Female Warrior)
= γ Orionis,
SAIF AL JABBAR (Sword of the Giant)
= η Orionis
(80.7),
ELNATH
(The Butting One)
=
β
Tauri = γ Aurigae
(80.9)
*39.0 = *80.4 - *41.4 |
ψ
Orionis (81.1),
NIHAL (Thirst-slaking Camels)
= β Leporis
(81.7) |
 |
|
June 8 |
9 (*80) |
10 (161) |
|
... The
month, which takes its name from Juppiter the
oak-god, begins on June 10th and ends of July
7th. Midway comes St. John's Day, June 24th, the
day on which the oak-king was sacrificially
burned alive. The Celtic year was divided into
two halves with the second half beginning in
July, apparently after a seven-day wake, or
funeral feast, in the oak-king's honour
... |
|
°June 4 |
5
(156) |
6
(*77) |
|
'May
12 |
13 |
14
(*54 = 161 - 107) |
|
"April 28 (4 * 29˝) |
Vaitu Nui 29
(*39) |
30 (120 = 161
- 41) |
|
118 - 100 =
18 |
19 = 131 -
112 |
161 - 141 |
|

.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)

