The bird sequence ended with the Beehive,
i.e ε at the center of the
Cancer carapace, above the head of the Hydra:
|
Egyptian
jubilation |
 |
Phoenician
he |
 |
Greek
epsilon |
Ε (ε) |
|
Wikipedia points at the Egyptian
gesture with arms held high as a Sign of jubilation,
which may have been the origin (via Phoenician he)
of epsilon.

 |
The old one was mourned at the arrival of the new one.

|
he ruru
he taiko |
he kumara
he kiakia |
he tuvi |
|
Sula cyanops
... It should be pointed out that
the combined name ruru-taiko refers in
MAO. to a black petrel (Procellaria
parkinsoni). There are no cultural data
available for ruru, which seems to be derived
from PPN. *lulu 'owl'...
There are no cultural data available for ...
taiko (compare RAR. taiko 'black petrel',
MGV. tiaku 'petrel?, omen of death', but the
textual association of taiko and spirits
should be dept in mind ...

...
The transference of the name for
sweet potatoes, kumara, to a sea bird (Oestrelata
incerta or Oestrelata leucoptera)
presents a problem in taxonomy. In a short
recitation that accompanies the string game, the
next bird on the list, kiakia, the white
tern, is associated with the leaves of the sweet
potato ...
White tern. Leucanus albus royanus
...
... Grey tern, Tuvituvi (Procelsterna
caerulea skottsbergi) ...
Anous stolidus
unicolor
... The dark
brown tern with a round tail is called tuao
... I was told that tavi is a small,
lead-colored bird that lives on the little islets (motu)
off the coast. He is supposed to look like the
tuvi, the grey tern, and owes his name to his
call ... |
|
MAY 20 (140) |
21 (*61) |
22 |
23 |
24 (144 = 12 *
12) |
 |
 |
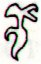 |
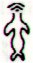 |
 |
|
Ga3-1 |
Ga3-2 |
Ga3-3 |
Ga3-4 |
Ga3-5
(64) |
|
AL TARF (The End)
= β Cancri
(124.3)
RAS ALGETHI (α
Herculis) |
χ Cancri (125.2),
BRIGHT FIRE
= λ Cancri
(125.4)
*84.0 = *125.4 - *41.4 |
AVIOR
= ε Carinae
(126.4), φ Cancri (126.8)
*85.0 = *126.4 - *41.4 |
ο Ursae Majoris
(127.4)
*86.0 = *127.4 - *41.4 |
Pushya-8
(Nourisher)
υ Cancri (128.1),
θ CANCRI
(128.2) |
|
July 23 (204) |
24 (*125) |
25 |
26 (187 + 20) |
27 (208) |
|
°July 19 (200) |
20 (*121) |
21 |
22 / 7 |
23 (204) |
|
26 (177 = 6 * 29½) |
'June 27 |
28 |
29 (*100) |
SIRIUS |
|
"June 12 |
13 (*84) |
14 (165 + 365) |
Te Maro 15 |
16 |
|
Day 365 + 166 = 531 = 18 * 29½ (Te
Maro 15).



|
|
... Makoi got up and began
to familiarize himself with the (new) land. (This
took place) on the fifteenth
day of the month of June ('Maro'). He
went toward the sheer face of the rocks (titi o
te opata), was astonished (aaa), came up
to the middle (of the outer rim of the crater), and
stood at the very edge. He looked down and saw the 'Pu
Mahore of Hau Maka' (on the
coast) and said, 'There it is, the hole of the
mahore fish of Hau Maka!' He turned his
face and looked toward the back (i.e., in the
direction of the crater). No sooner had he seen how
the dark abyss opened up (below him), when a
fragrant breeze came drifting by. Again Makoi
said, 'This is the dark abyss of Hau Maka'.
He turned around, walked on in utter amazement, and
arrived at the house. He spoke to Ira, 'Hey
you, my friends! How forgetful we (truly) are. This
place is adequate (? tau or 'beautiful'), the
dark abyss lies there peacefully!' Ira
replied, 'And what should that remind us of up
here?' All arose and climbed up. They went on and
arrived; they all had a good look (at the inside of
the crater). They returned home and sat down. Night
fell, and they went to sleep
... [E:19]
 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
NOV 19 (*243) |
20 (324) |
21 |
22 |
23 |
|
GREDI (Goat)
=
α
Capricorni
(307.2),
σ
Capricorni (307.5),
ALSHAT (The Sheep)
=
ν
Capricorni
(307.9) |
Al Sa’d al Dhabih-20 (Lucky One of the Slaughterers)
/
Ox / Herd Boy-9
(Buffalo)
DABIH
=
β
Capricorni
(308.0),
κ
Sagittarii (308.1),
SADIR (Hen's Breast)
=
γ
Cygni
(308.4),
PEACOCK
=
α
Pavonis
(308.7)
*267.0 = *308.4 - *41.4 |
OKUL = π Capricorni
(309.6),
BOS = ρ Capricorni
(309.9)
ARNEB (α Leporis)
MINTAKA (δ Orionis)
|
ο
Capricorni (310.2),
θ
Cephei (310.5)
HEKA (λ Orionis)
ALNILAM (ε Orionis)
|
ROTTEN MELON
= ε Delphini,
φ Pavonis (311.2), η Delphini (311.4), ζ Delphini, ρ
Pavonis (311.7)
PHAKT (α Columbae)
ALNILAK (ζ Orionis)
|
 |
|
Jan 22 |
23 (388) |
24 |
25 (*310) |
26 |
|
°Jan 18 (383) |
19 |
20 |
21 (*306) |
22 |
|
'Dec 27 (360) |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 (*284) |
|
"Dec 12 (*266) |
13 |
14 (348) |
14 |
16 |
|
he tu-ao |
he tuvi → he tavi |
|
|
|
The dark
brown tern with a round tail is called tuao
... Ao, the world.
...
I was told that tavi is a small, lead-colored
bird that lives on the little islets (motu)
off the coast. He is supposed to look like the
tuvi, the grey tern, and owes his name to his
call ... Grey tern, Tuvituvi (Procelsterna
caerulea skottsbergi) ...
Anous stolidus
unicolor
...
|
|
MAY 25 (5-25) |
26 (*266) |
27 |
28 (348) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
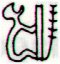
Ga3-6 |
Ga3-7 |
Ga3-8 |
Ga3-9
(68) |
|
Āshleshā-9
(Embrace) /
Willow-24 (Stag)
π¹ Ursa Majoris,
δ HYDRAE (129.6),
AL MINHAR
AL SHUJĀ
= σ
Hydrae,
MUSEIDA
= π²
Ursae Majoris
(129.9)
RAS ALHAGUE (α
Ophiuchi)
|
Al Nathrah-6
(Gap)
BEEHIVE
(Exhalation of Piled-up Corpses)
= ε Cancri,
η Pyxidis (130.4),
XESTUS
= ο Velorum
(130.5), ζ Pyxidis (130.7),
ASCELLUS
BOREALIS = γ Cancri,
β Pyxidis (130.9)
*89.0 = *130.4 - *41.4 |
Extended Net-26a
(Ox) /
Arkū-sha-nangaru-sha-shūtu-12
(Southeast Star in the Crab)
η Hydrae (131.0),
ASCELLUS
AUSTRALIS = δ Cancri
(131.4),
KOO SHE
(Bow and
Arrow)
= δ Velorum
(131.6), α Pyxidis (131.8), ε Hydrae (131.9)
*90.0 = *131.4 - *41.4 |
ι Cancri (132.0), ρ Hydrae (132.4)
*91.0 = *132.4 - *41.4 |
|
... He is bound to it with
willow thongs in the 'five-fold bond' which
joins wrists, neck, and ankles together
...

... They were
Ranginui, the Sky Father, and Papatuanuku,
the Earth Mother, both sealed together in a
close embrace. Crushed
between the weight of their bodies were their many
children, whose oppression deepened. They yearned to
be free; they fought their parents and each other to
break loose. Tuumatauenga, virile god of war,
thrust and shouted; Tangaroa of the oceans
whirled and surged; Tawhirirangimaatea,
Haumiatiketike and Rongomatane, of wild
foods and cultivated crops, tried their best but
were not successful; and Ruamoko, god of
earthquakes, yet to be born, struggled in the
confinement of his mother's womb ... Of them all,
Taane Mahuta [cfr Mahute, Boussonetia
papyrifera], the god of the forests, was the
most determined; he set his sturdy feet upon his
father's chest, and braced his upper back and
shoulders against the bosom of his mother. He
pushed; and they parted. So
the world, as the Maori understand it, came into
being ...
... A man had a daughter who
possessed a wonderful bow and arrow, with
which she was able to bring down everything she
wanted. But she was lazy and was constantly
sleeping. At this her father was angry and said: 'Do
not be always sleeping, but take thy bow and shoot
at the navel of the ocean, so that we may get fire.'
The navel of the ocean was a vast whirlpool in which
sticks for making fire by friction were drifting
about. At that time men were still without fire. Now
the maiden seized her bow, shot into the navel of
the ocean, and the material for fire-rubbing sprang
ashore. Then the old man was glad. He kindled a
large fire, and as he wanted to keep it to himself,
he built a house with a door which snapped up and
down like jaws and killed everybody that wanted to
get in. But the people knew
that he was in possession of fire, and the stag
determined to steal it for them. He took
resinous wood, split it and stuck the splinters in
his hair. Then he lashed two boats together, covered
them with planks, danced and sang on them, and so he
came to the old man's house. He sang: 'O, I go and
will fetch the fire.' The old man's daughter heard
him singing, and said to her father: 'O, let the
stranger come into the house; he sings and dances so
beautifully.' The stag landed and drew near the
door, singing and dancing, and at the same time
sprang to the door and made as if he wanted to enter
the house. Then the door snapped to, without however
touching him. But while it was again opening, he
sprang quickly into the house. Here he seated
himself at the fire, as if he wanted to dry himself,
and continued singing. At the same time he let his
head bend forward over the fire, so that he became
quite sooty, and at last the splinters in his hair
took fire. Then he sprang out, ran off and brought
the fire to the people ...
 |
|
July 28 |
29 (*130) |
30 |
31 (212) |
|
°July 24 |
25 |
26 (*127) |
27 (208) |
|
'July 1 |
2 |
3
(*104) |
4 (185) |
|
"June 17 |
18 |
19 (*90) |
20 (171 = 185 -
14) |
|
... When it
grew light, Makoi arose again. He went
off to further explore the area. He went along and
came to the 'dark rat'. He looked around and said:
'Here we are at the dark rat of Hau Maka'.
He gave it the name Te Kioe Uri A Hau Maka.
He went on and came to Te Piringa Aniva. When
he arrived there, he looked around and gave the name
Te Piringa Aniva. He went on and came to
Te Pei, looked around, and said, 'Here it is!'
So he gave the name Te Pei A Hau Maka. He
went on, all alone he went on, and came to Te Pou.
When he arrived there, he looked around and again
said, 'Here it is!' and gave the name Te Pou A
Hau Maka ... [E:20]
This should have happened in "June
16, because the events in "June 15 ended as follows:
... Makoi got up and began
to familiarize himself with the (new) land. (This
took place) on the fifteenth
day of the month of June ('Maro'). He
went toward the sheer face of the rocks (titi o
te opata), was astonished (aaa), came up
to the middle (of the outer rim of the crater), and
stood at the very edge. He looked down and saw the 'Pu
Mahore of Hau Maka' (on the
coast) and said, 'There it is, the hole of the
mahore fish of Hau Maka!' He turned his
face and looked toward the back (i.e., in the
direction of the crater). No sooner had he seen how
the dark abyss opened up (below him), when a
fragrant breeze came drifting by. Again Makoi
said, 'This is the dark abyss of Hau Maka'.
He turned around, walked on in utter amazement, and
arrived at the house. He spoke to Ira, 'Hey
you, my friends! How forgetful we (truly) are. This
place is adequate (? tau or 'beautiful'), the
dark abyss lies there peacefully!' Ira
replied, 'And what should that remind us of up
here?' All arose and climbed up. They went on and
arrived; they all had a good look (at the inside of
the crater). They returned home and sat down.
Night
fell, and they went to sleep
... [E:19]
He Tavi ("June 18)
was related to the call of
He Tuvi ("June 16).
In between it grew light (tu-ao) and here
Makoi had gone on his own to visit 4 kuhane
stations. |
... For some reason nothing was said about Te Manavai,
which in the journey of the kuhane came between Poko
Uri and Te Kioe Uri .
... The dream soul climbed up and reached
the rim of the crater. As soon as the dream soul looked into
the crater, she felt a gentle breeze coming toward her. She
named the place 'Poko Uri A Hau Maka O Hiva'. The
dream soul continued her search for a residence for King
Matua.
The
dream soul of Hau Maka reached (the smaller crater)
Manavai and named the place 'Te Manavai A Hau Maka
O Hiva'. The dream soul went on and reached Te Kioe
Uri. She named the place 'Te Kioe Uri A Hau Maka O
Hiva' ...
... Manavai Hollow where rainwater accumulates;
anciently, small, round gardens, preferably situated in low
shady spots, where the mahute tree was grown. Vanaga. 1.
Brain. 2. Valley, ravine, river, torrent, brook; manavai miro,
orchard, Mq.: manavai, valley,
brook. Ta.: anavai, river, brook. It scarcely
appears that these are fully coordinate. In Tahiti anavai
has a clear etymology, ana
meaning the bed of a stream. In Rapanui and in the
Marquesas mana most readily associates with maga,
as water in a forked bed. Churchill
...
However, Manuscript E seems to offer an explanation in the way
Makoi remembered how he documented the name: ... I wrote
(ta) Te Manavai A Hau Maka on the surface of a
banana leaf (kaka), and this is how I left it ...
There seems to have been a banana sequence
corresponding to the beginning of
side a on the G tablet; and Makoi
may have stated (ta as in tavi)
'this is my beginning', viz. at right ascension day *128 (= 2 *
64).
... He sat down [he noho] and rested [he hakaora].
There was no bride-donor (tumu) to live with (? kia ora).
He got up, the path went uphill, and he came (back) to the
house. It was dark when he reached the house. When he came to
the yam plantation of Kuukuu, he sat down.
Night was falling.
Ira asked Makoi the following question: 'How did you fare when
you wandered, when you went searching, when you found yourself
on the path of the dream soul of the father?' [E:20]
Makoi replied, 'There are indeed all those places. I did not
forget them at all (? kai viri kai viri) when I saw them
(text corrected, i-ui-nei). I alone saw no fewer than
four of my places, and I returned here only because night was
falling'. Then Ira spoke again: 'How
did you name them, last-born [hangupotu]?' Makoi replied,
'This is what happened, this is how I gave the names. I wrote (ta
[?]) 'Te Manavai A Hau Maka' on the surface of a banana leaf (kaka),
and this is how I left it'.
This is how Makoi remembered it.
No sooner had he said this, when Ira grew
angry and quarreled [he kakai] with Makoi.
He said the following (to him): 'You did not pay attention,
last-born, and you did not [tae] give the (full) name.
This is how it should be [Penei]: the Manavai of Hau Maka
of Hiva, in memory (mo aringa ora) of the father,
of his dream soul'. Makoi replied, 'In
Hiva the land belongs to him - the land here is mine, not his [tae
oona]!'
They stayed (there longer), on the
fifth day of the month of July ('Anakena'), they all got up,
went downhill [he turu], went on, and reached Hanga Te
Pau ... [E:21]
Once again they were at Hanga Te Pau.
|
he te verovero |
he ka araara |
he kukuru toua |
he makohe |
he kena |
he tavake |
|
Tou.
In ancient times, a tou was someone who
had recovered from an epidemic, but whose
illness meant that someone else in the family
had to die. The tou were regarded as
portents of evil. Toutou, lush; fertile
(land). Toûa: Egg yolk; the colour
yellow; soft, fibrous part of tree bark; toûa
mahute, mahute fibres. Vanaga. Toua:
Wrath, anger, rage, revenge, battle, combat,
debate, dispute, dissension, uprising, revolt,
quarrel, fight, hostility (taua); toua
rae, to provoke, rae toua, to open
hostilities, toua kakai, to rebuke,
tuki toua, to stir up dissension; totoua,
hostility; hakatoua, fighter, warrior. P
Mgv.: toua, war, battle. Mq.: toua,
war, dispute, quarrel. The form with o is
found only in these three languages, taua
is found in the general migration, Rapanui is
the only speech which has both. Toutou,
fertile (tautau); hakatoutou, to
fertilize. Mq.: taútaú, fertile.
Toùvae, to run; hakauruuru toùvae,
id.
Churchill.


 |
|
MAY 14 |
(500 = 365 +
135 ) |
16 (136) |
17 |
18 |
19 |
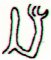 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga2-24 (54) |
Ga2-25 → 225 |
Ga2-26 |
Ga2-27 → π |
Hanga Te Pau |
Ga2-29 (59) |
|
φ
Gemini (118.4)
*77.0 = *118.4 - *41.4 |
DRUS (Hard)
= χ Carinae
(119.9) |
ω
Cancri
(120.2) |
8h
(121.7)
χ Gemini (121.0),
NAOS
= ζ Puppis
(121.3) |
ρ
Puppis (122.0),
HEAP OF FUEL
= μ Cancri
(122.1),
ζ
Monocerotis (122.3), ψ
Cancri (122.6),
REGOR (Roger backwards)
= γ Velorum
(122.7) |
TEGMINE = ζ Cancri
(123.3) |
.jpg) |
|
July 17
(*118) |
18 |
19 (200) |
20 (*121) |
21 |
22 / 7 |
|
°July 13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 (*118) |
18 (199) |
|
'June 20
(*91) |
SOLSTICE |
'June 22
(173) |
23 |
ST JOHN'S DAY |
25 (*96) |
|
"June 6 (*77) |
7 |
8 |
9 (160) |
TE MARO 10 |
11 |
|
he ea.a Ira.he iri he oho ki runga anake.
i te angahuru o te raa o
te maro i iri ai - Ira got
up. They all climbed to the top of the hill.
They climbed up on the
tenth day of the month of June ('Maro’).
[E:18] |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
NOV 13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 (321) |
18 (*242) |
|
ι Sagittarii (301.2),
TEREBELLUM
= ω Sagittarii,
ξ Aquilae (301.3),
ALSHAIN (Falcon)
= β Aquilae
(301.6), φ Aquilae (301.8) |
ε Pavonis, θ Sagittarii (302.3), γ Sagittae
(302.5), μ Pavonis (302.7) |
τ Aquilae (303.8) |
20h
(304.4)
η Sagittae (304.2), δ Pavonis (304.4)
*263.0 = *304.4 - *41.4 |
SHANG WEI (Higher Guard)
= κ Cephei
(305.2),
θ
Sagittae (305.4),
TSEEN FOO
(Heavenly Raft)
= θ Aquilae (Ant.)
(305.6), ξ Capricorni (305.8)
*264.0 = *305.4 - *41.4 |
TSO
KE (Left Flag)
= ρ Aquilae
(306.3) |

... In late September or
early October 130, Hadrian and his entourage,
among them Antinous, assembled at Heliopolis to
set sail upstream as part of a flotilla along
the River Nile. The retinue included officials,
the Prefect, army and naval commanders, as well
as literary and scholarly figures. Possibly also
joining them was Lucius Ceionius Commodus, a
young aristocrat whom Antinous might have deemed
a rival to Hadrian's affections. On their
journey up the Nile, they stopped at Hermopolis
Magna, the primary shrine to the god Thoth. It
was shortly after this, in October [in the year
A.D.] 130 - around the time of the festival of
Osiris - that Antinous fell into the river and
died, probably from drowning. Hadrian publicly
announced his death, with gossip soon spreading
throughout the Empire that Antinous had been
intentionally killed. The nature of Antinous's
death remains a mystery to this day, and it is
possible that Hadrian himself never knew;
however, various hypotheses have been put
forward. One possibility is that he was murdered
by a conspiracy at court. However, Lambert
asserted that this was unlikely because it
lacked any supporting historical evidence, and
because Antinous himself seemingly exerted
little influence over Hadrian, thus meaning that
an assassination served little purpose. Another
suggestion is that Antinous had died during a
voluntary castration as part of an attempt to
retain his youth and thus his sexual appeal to
Hadrian. However, this is improbable because
Hadrian deemed both castration and circumcision
to be abominations and as Antinous was aged
between 18 and 20 at the time of death, any such
operation would have been ineffective. A third
possibility is that the death was accidental,
perhaps if Antinous was intoxicated. However, in
the surviving evidence Hadrian does not describe
the death as being an accident; Lambert thought
that this was suspicious. Another possibility is
that Antinous represented a voluntary human
sacrifice. Our earliest surviving evidence for
this comes from the writings of Dio Cassius, 80
years after the event, although it would later
be repeated in many subsequent sources. In the
second century Roman Empire, a belief that the
death of one could rejuvenate the health of
another was widespread, and Hadrian had been ill
for many years; in this scenario, Antinous could
have sacrificed himself in the belief that
Hadrian would have recovered. Alternately, in
Egyptian tradition it was held that sacrifices
of boys to the Nile, particularly at the time of
the October Osiris festival, would ensure that
the River would flood to its full capacity and
thus fertilize the valley; this was made all the
more urgent as the Nile's floods had been
insufficient for full agricultural production in
both 129 and 130. In this situation, Hadrian
might not have revealed the cause of Antinous's
death because he did not wish to appear either
physically or politically weak. Conversely,
opposing this possibility is the fact that
Hadrian disliked human sacrifice and had
strengthened laws against it in the Empire ... |
|
Jan 16 |
17 |
18 (383) |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
°Jan 12 |
13 (378 →
Saturn) |
14 |
15 (*300) |
16 |
17 |
|
'Dec 20 (354) |
SOLSTICE |
22 |
23 |
CHRISTMAS EVE |
25 (*279) |
|
"Dec 6 (340)
|
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 (*265) |
|
... The evening of 23 June, St. John's Eve, is
the eve of celebration before the Feast Day of
Saint John the Baptist. The Gospel of Luke (Luke
1:36, 56-57) states that John was born about six
months before Jesus; therefore, the feast of
John the Baptist was fixed on 24 June, six
months before Christmas Eve ... |

|
Hanga Te Pau |
24 |
Hanga Te Pau |
|
he kena |
186 + 41 =
227 (π) |
|
"June 10 (161) |
Te Ana-kena 5 (186) |
|
*122 |
*147 |
Ana. 1. Cave. 2. If. 3. Verbal prefix: he-ra'e
ana-unu au i te raau, first I drank the medicine.
Vanaga. 1. Cave, grotto, hole in the rock. 2. In order that,
if. 3. Particle (na 5); garo atu ana,
formerly; mee koe ana te ariki, the Lord be with
thee. PS Sa.: na, an intensive postpositive particle.
Anake, unique. T Pau.: anake, unique, to be
alone. Mgv.: anake, alone, single, only, solely. Mq.:
anake, anaé, id. Ta.: anae, all, each,
alone, unique. Anakena, July. Ananake, common,
together, entire, entirely, at once, all, general,
unanimous, universal, without distinction, whole, a company;
piri mai te tagata ananake, public; kite aro o te
mautagata ananake, public; mea ananake,
impartial; koona ananake, everywhere. Churchill.
Splendor; a name applied in the Society Islands to ten
conspicious stars which served as pillars of the sky. Ana
appears to be related to the Tuamotuan ngana-ia, 'the
heavens'. Henry translates ana as aster, star.
The Tahitian conception of the sky as resting on ten star
pillars is unique and is doubtless connected with their
cosmos of ten heavens. The Hawaiians placed a pillar (kukulu)
at the four corners of the earth after Egyptian fashion;
while the Maori and Moriori considered a single great
central pillar as sufficient to hold up the heavens. It may
be recalled that the Moriori Sky-propper built up a single
pillar by placing ten posts one on top of the other.
Makemson .
Kena. A sea bird, with a white breast and black
wings, considered a symbol of good luck and noble attitudes.
Vanaga. Mgv.: kena, a white seabird. Mq.: kena,
a large bird. Churchill. Mq.: kena, burning, very
hot. Ha.: ena, red-hot, to burn as a fire. Churchill.
|
JUNE 7 (*78) |
8 |
9 |
10 (161) |
11 |
12 |
|
... The
month, which takes its name from Juppiter the
oak-god, begins on June 10th and ends of July
7th. Midway comes St. John's Day, June 24th, the
day on which the oak-king was sacrificially
burned alive. The Celtic year was divided into
two halves with the second half beginning in
July, apparently after a seven-day wake, or
funeral feast, in the oak-king's honour
... |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga3-19 (78 = 158 - 80) |
Ga3-20 |
Ga3-21 |
Ga3-22 |
Ga3-23 |
Ga3-24 |
|
The Knot (Ukdah) |
5 Imix 9 Kumk'u
Rishu A.-13 (Head of the Lion)
ψ Leonis (146.4),
RAS
ELASET AUSTRALIS
= ε Leonis
(146.6)
*105.0 = *146.4 - *41.4 |
VATHORZ PRIOR = υ Carinae
(147.9) |
|
Star-25 (Horse) /
ANA-HEU-HEU-PO-5 (Pillar where debates were
held)
ALPHARD
(The Horse) =
α
Hydrae
(142.3),
ω
Leonis (142.6),
τ¹
Hydrae (142.7) |
Al Tarf-7 (The End)
ψ
Velorum (143.3),
ALTERF = λ Leonis,
τ²
Hydrae (143.4),
ξ
Leonis (143.5)
*102.0 = *143.4 - *41.4 |
A Hydrae
(144.1)
VEGA (α Lyrae) |
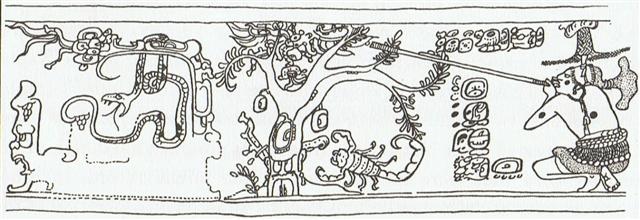
Creation of our present world
UKDAH (Knot)
= ι Hydrae
(145.4), κ Hydrae (145.5),
SUBRA = ο Leonis
(145.8)
*104.0 = *145.4 - *41.4 (= *288 - *184) |
|
Itzam-Yeh
defeated |
28 May (148),
3149 BC |
|
1st 3-stone
place |
21 May (141),
3114 BC |
|
Creation of
our present world |
13 August
(225), 3114 BC |
|
Och ta chan (Hun-Nal-Ye
'entered or became the sky') |
5 February
(36), 3112 BC |
|
21 May, 3114
BC - 5 February, 3112 BC =
542 |
|
542 'happens
to be' the sum of 365 days
and 6 * 29½ nights. |
|
|
Aug 10 |
11 |
12 |
13 (225) |
14 (*146) |
15 (227 → π) |
|
°Aug 6 |
7 |
8 (220) |
9 (*141) |
10 |
11 |
|
'July 14 |
15 |
16 |
17 (*118) |
18 |
19 (200) |
|
SIRIUS |
"July 1 |
2 |
3 (*104) |
4 (185) |
Te
Anakena 5 |
|
81 (= 158 -
77) |
82 |
83 |
84 |
85 = 185 -
100 |
86 = 227 -
141 |
|
... Makoi
replied, 'In Hiva the land belongs to him - the
land here is mine, not his [tae oona]!'
They stayed (there longer).
On the fifth day of
the month of July (Anakena), they all got
up, went downhill, went on, and reached Hanga
Te Pau. They took their provisions with
them, carrying them on their shoulders, went on,
and reached Te Pou. They made camp and
slept in Te Pou on the tenth of the month
of July (Anakena). Then they all got up,
carried their provision on their shoulders, went
straight ahead, and followed the path of the
dream soul of Hau Maka. They came to
Hua Reva and said, This is Hua Reva A Hau
Maka!... [E:21-22] |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
DEC 7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 (345) |
12 (*266) |
|
Al Sa'd al Su'ud-22 (Luckiest of the Lucky) /
Emptiness-11 (Rat)
TSIN =
36 Capricorni
(325.2),
ALPHIRK (The Flock) =
β
Cephei
(325.7),
SADALSUD
=
β
Aquarii,
ξ
Gruis (325.9) |
no star listed (326) |
CASTRA
= ε Capricorni
(327.2),
BUNDA
= ξ Aquarii
(327.5)
SIRIUS (α Canis Majoris) |
Mahar sha hi-na Shahū-26 (Western One in the
Tail of the Goat)
NASHIRA
=
γ
Capricorni
(328.0),
ν
Oct. (328.3), AZELFAFAGE
=
π¹
Cygni,
κ
Capricorni (328.7) |
Arkat sha hi-na Shahū-27 (Eastern One in the
Tail of the Goat)
ENIF
(The Nose)
=
ε
Pegasi,
ERAKIS
=
μ
Cephei
(329.2),
46 CAPRICORNI,
JIH
(the Sun)
=
κ
Pegasi
(329.3),
ι
Piscis Austrini (329.4),
λ
Capricorni (329.6),
ν
Cephei (329.7),
DENEB ALGIEDI
=
δ
Capricorni
(329.8)
*288.0 = *329.4 - *41.4 |
θ Piscis Austrini
(330.1), λ Octantis (330.7) |
|
Febr 9 (40) |
10 |
11 |
12 (408) |
13 (*329) |
All Hearts'
Day |
|
°Febr 5 (36) |
6 |
7 |
8 (*324) |
9 |
10 (41) |
|
'Jan 13 (378) |
14 |
15 (*300) |
16 |
17 |
18 (383) |
|
"Dec 30 |
31 (*285) |
"Jan 1 (366) |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
*184 = *325 -
*141 |
*185 = *285 -
*100 |
*(83 + 183 -
80) |
*187 |
*188 |
*189 |
... On February 9 the Chorti Ah
K'in, 'diviners', begin the agricultural year. Both
the 260-day cycle and the solar year are used in setting
dates for religious and agricultural ceremonies,
especially when those rituals fall at the same time in
both calendars. The ceremony begins when the diviners go
to a sacred spring where they choose five stones with
the proper shape and color. These stones will mark the
five positions of the sacred cosmogram created by the
ritual. When the stones are brought back to the
ceremonial house, two diviners start the ritual by
placing the stones on a table in a careful pattern that
reproduces the schematic of the universe. At the same
time, helpers under the table replace last year's
diagram with the new one. They believe that by placing
the cosmic diagram under the base of God at the center
of the world they demonstrate that God dominates the
universe. The priests place the stones in a very
particular order. First the stone that corresponds to
the sun in the eastern, sunrise position of summer
solstice is set down; then the stone corresponding to
the western, sunset position of the same solstice. This
is followed by stones representing the western, sunset
position of the winter solstice, then its eastern,
sunrise position. Together these four stones form a
square. They sit at the four corners of the square just
as we saw in the Creation story from the Classic period
and in the Popol Vuh. Finally, the center stone is
placed to form the ancient five-point sign modern
researchers called the quincunx
...

|




















.jpg)






