On Easter Island the beginning was with the yam roots and this was
the first task of the Explorers too, viz. to
establish a yam plantation:
... After that, Ira spoke these words: 'This is the
diggning stick (? ko koko), Kuukuu. You shall work
the land for me and plant the yam roots [te uhi]!'
Makoi named the place Hanga Te Pau, 'the landing
site of Ira'. So that they would remember (? he
aringa, literally, 'as face'), the open side [ko
mua] of Hanga Te Pau was given this name. Ira
got up. They all climbed to the top of the hill.
They climbed up on the tenth day of the month of
June ('Maro') ... They made camp and constructed a
house [te hare]. Kuukuu got up, worked the
ground, and heaped up the earth for the yam roots [he
puke i te uhi] ... [E:18]
3 of the corners in the illustration above have Sun
symbols, but not the 4th (down in the southwest,
toga) where the Sun should be 'heaped-up'.

... Interestingly, since another
meaning of shi is 'death', the number 4 is
considered unlucky. For example, the
floor numbering in hotels
sometimes jumps mysteriously from 3 to 5; it is also
considered unlucky to give four of something as a
present ...

... The practice of turning down
the fingers, contrary to our practice, deserves
notice, as perhaps explaining why sometimes savages
are reported to be unable to count above four. The
European holds up one finger, which he counts, the
native counts those that are down and says 'four'.
Two fingers held up, the native counting those that
are down, calls 'three'; and so on until the white
man, holding up five fingers, gives the native none
turned down to count. The native is nonplussed, and
the enquirer reports that savages can not count
above four ...
... The king arose from his
sleeping mat and said to all the people: 'Let us go
to Orongo so that I can announce my death!'
The king climbed on the rock and gazed in the
direction of Hiva, the direction in which he
had travelled (across the ocean). The king said:
'Here I am and I am speaking for the last time.' The
people (mahingo) listened as he spoke. The
king called out to his guardian spirits (akuaku),
Kuihi and Kuaha, in a loud voice: 'Let
the voice of the rooster of Ariana (→
Arianrhod → Gemma, α
Cor. Bor. → St John's Day) crow softly.
The stem with many roots (i.e.,
the king) is entering!' The king fell down, and
Hotu A Matua died ...

The date given, "June 10, is significant, because
this was at the beginning of the month when the Sun
stood at his apex ('the top of the hill'):
... The month, which takes its
name from Juppiter the oak-god, begins on June 10th
and ends of July 7th. Midway comes St. John's Day,
June 24th, the day on which the oak-king was
sacrificially burned alive. The Celtic year was
divided into two halves with the second half
beginning in July, apparently after a seven-day
wake, or funeral feast, in the oak-king's honour
...
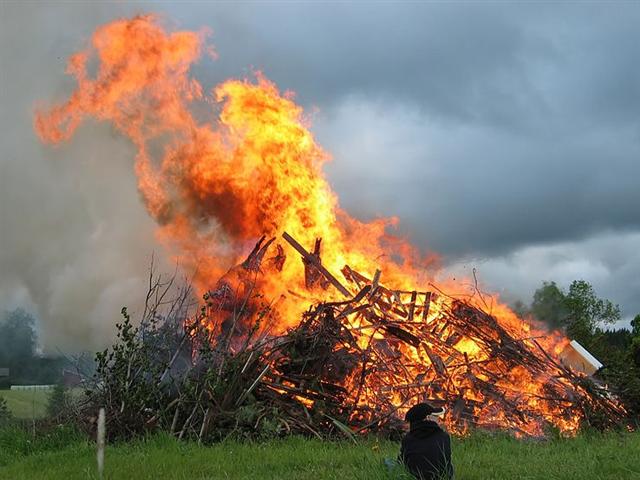

|
MAY
14 |
15
(500) |
16
(136) |
17 |
18 |
19 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga2-24 |
Ga2-25 |
Ga2-26 |
Ga2-27 → π |
Hanga
Te Pau |
Ga2-29 (59) |
|
φ Gemini (118.4)
*77.0 = *118.4 - *41.4 |
DRUS (Hard)
= χ Carinae
(119.9) |
ω Cancri
(120.2) |
8h (121.7)
χ Gemini (121.0),
NAOS
= ζ Puppis
(121.3) |
ρ
Puppis (122.0),
HEAP OF FUEL
= μ Cancri
(122.1),
ζ
Monocerotis (122.3), ψ
Cancri (122.6),
REGOR (Roger backwards) = γ Velorum
(122.7) |
TEGMINE = ζ Cancri
(123.3) |
.jpg) |
|
July
17 (*118) |
18 |
19
(200) |
20
(*121) |
21 |
22 /
7 |
|
°July 13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17
(*118) |
18 (199) |
|
'June
20 (*91) |
SOLSTICE |
'June
22 (173) |
23 |
ST
JOHN'S DAY |
25 (*96) |
|
"June
6 (*77) |
7 |
8 |
9
(160) |
TE
MARO 10 |
11 |
|
he ea.a Ira.he iri he oho ki runga
anake. i te
angahuru o te raa o te maro i iri
ai - Ira got
up. They all climbed to the top of the
hill. They
climbed up on the tenth day of the month
of June ('Maro’).
[E:18] |
|
CLOSE
TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
NOV
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17
(321) |
18 (*242) |
|
ι Sagittarii (301.2),
TEREBELLUM = ω Sagittarii,
ξ Aquilae (301.3),
ALSHAIN (Falcon) = β Aquilae
(301.6), φ Aquilae (301.8) |
ε Pavonis, θ Sagittarii (302.3), γ
Sagittae (302.5), μ Pavonis (302.7) |
τ Aquilae
(303.8) |
20h (304.4)
η Sagittae (304.2), δ Pavonis (304.4)
*263.0 = *304.4 - *41.4 |
SHANG WEI (Higher Guard) = κ Cephei
(305.2),
θ
Sagittae (305.4),
TSEEN FOO
(Heavenly Raft)
= θ Aquilae (Ant.)
(305.6), ξ Capricorni (305.8)
*264.0 = *305.4 - *41.4 |
TSO KE (Left Flag)
= ρ Aquilae
(306.3) |

... In late September
or early October 130, Hadrian and his
entourage, among them Antinous,
assembled at Heliopolis to set sail
upstream as part of a flotilla along the
River Nile. The retinue included
officials, the Prefect, army and naval
commanders, as well as literary and
scholarly figures. Possibly also joining
them was Lucius Ceionius Commodus, a
young aristocrat whom Antinous might
have deemed a rival to Hadrian's
affections. On their journey up the
Nile, they stopped at Hermopolis Magna,
the primary shrine to the god Thoth. It
was shortly after this, in October [in
the year A.D.] 130 - around the time of
the festival of Osiris - that Antinous
fell into the river and died, probably
from drowning. Hadrian publicly
announced his death, with gossip soon
spreading throughout the Empire that
Antinous had been intentionally killed.
The nature of Antinous's death remains a
mystery to this day, and it is possible
that Hadrian himself never knew;
however, various hypotheses have been
put forward. One possibility is that he
was murdered by a conspiracy at court.
However, Lambert asserted that this was
unlikely because it lacked any
supporting historical evidence, and
because Antinous himself seemingly
exerted little influence over Hadrian,
thus meaning that an assassination
served little purpose. Another
suggestion is that Antinous had died
during a voluntary castration as part of
an attempt to retain his youth and thus
his sexual appeal to Hadrian. However,
this is improbable because Hadrian
deemed both castration and circumcision
to be abominations and as Antinous was
aged between 18 and 20 at the time of
death, any such operation would have
been ineffective. A third possibility is
that the death was accidental, perhaps
if Antinous was intoxicated. However, in
the surviving evidence Hadrian does not
describe the death as being an accident;
Lambert thought that this was
suspicious. Another possibility is that
Antinous represented a voluntary human
sacrifice. Our earliest surviving
evidence for this comes from the
writings of Dio Cassius, 80 years after
the event, although it would later be
repeated in many subsequent sources. In
the second century Roman Empire, a
belief that the death of one could
rejuvenate the health of another was
widespread, and Hadrian had been ill for
many years; in this scenario, Antinous
could have sacrificed himself in the
belief that Hadrian would have
recovered. Alternately, in Egyptian
tradition it was held that sacrifices of
boys to the Nile, particularly at the
time of the October Osiris festival,
would ensure that the River would flood
to its full capacity and thus fertilize
the valley; this was made all the more
urgent as the Nile's floods had been
insufficient for full agricultural
production in both 129 and 130. In this
situation, Hadrian might not have
revealed the cause of Antinous's death
because he did not wish to appear either
physically or politically weak.
Conversely, opposing this possibility is
the fact that Hadrian disliked human
sacrifice and had strengthened laws
against it in the Empire ... |
|
Jan
16 |
17 |
18 (383) |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
°Jan
12 |
13
(378 → Saturn) |
14 |
15
(*300) |
16 |
17 |
|
'Dec
20 (354) |
SOLSTICE |
22 |
23 |
CHRISTMAS EVE |
25 (*279) |
|
"Dec
6 (340) |
7 |
8 |
9 |
Ko
Koró 10 |
11 (*265) |
|
... The evening of 23 June, St. John's
Eve, is the eve of celebration before
the Feast Day of Saint John the Baptist.
The Gospel of Luke (Luke 1:36, 56-57)
states that John was born about six
months before Jesus; therefore, the
feast of John the Baptist was fixed on
24 June, six months before Christmas Eve
... |
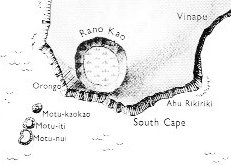
The geography of Easter Island has the 'Hill'
Rano Kau down in the southwest (toga).
314 / 2 = 157 = "June 6 had moved ahead to July 17
(*118) at the time of rongorongo.
|
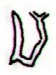
|
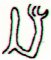 |
|
toga |
Ga2-24 |
|





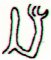
.jpg)