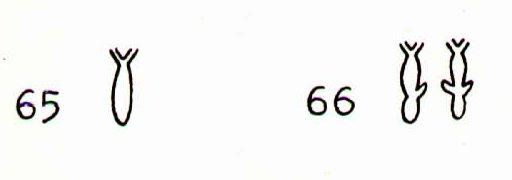Once again. The sow was connected with fertility
because she had so many piglets (children). According to
Nordic mythology she - by the name of Särimner
(Pork-eternal, Sär-imner) -
returned to be
devoured again each new year. But she was lame on one leg
for once upon a time someone had broken it in order
to get at the marrow.
Therefore, the correct place
for her ought to be at the winter solstice.

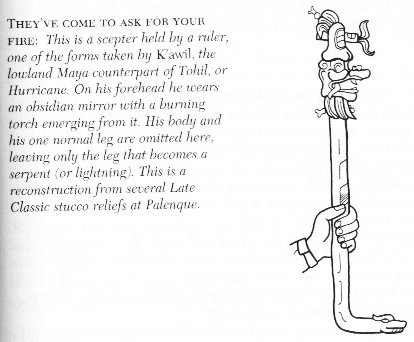
... They walked in crowds when
they arrived at Tulan, and there was no fire.
Only those with Tohil had it: this was the
tribe whose god was first to generate fire. How it
was generated is not clear. Their fire was already
burning when Jaguar Quitze and Jaguar
Night first saw it: 'Alas! Fire has not yet
become ours. We'll die from the cold', they said.
And then Tohil spoke: 'Do not grieve. You
will have your own even when the fire you're talking
about has been lost', Tohil told them.
'Aren't you a true god!
Our sustenance and our support! Our god!' they said
when they gave thanks for what Tohil had said.
'Very
well, in truth, I am your god: so be it. I am your
lord: so be it,' the penitents and sacrificers were
told by Tohil. And this was the warming of
the tribes. They were pleased by their fire.
After that a great downpour began, which cut short
the fire of the tribes. And hail fell thickly on all
the tribes, and their fires were put out by the
hail. Their fires didn't start up again. So then
Jaguar Quitze and Jaguar Night asked for
their fire again: 'Tohil, we'll be finished
off by the cold', they told Tohil. 'Well, do
not grive', said Tohil. Then he started a
fire. He pivoted inside his sandal ...
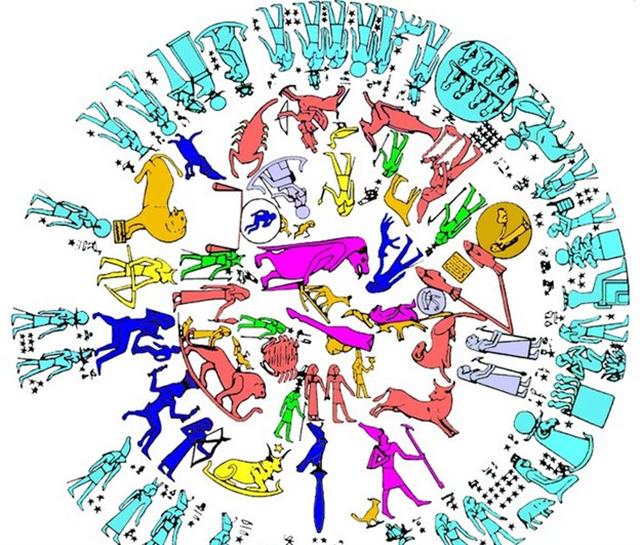
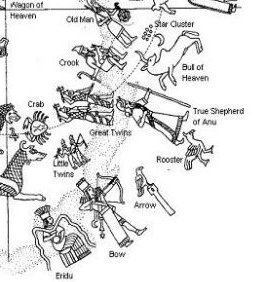
... Ishtar, scorned, goes up to
heaven in a rage, and extracts from Anu the promise
that he will send down the Bull of Heaven to avenge
her. The Bull descends, awesome to behold. With his
first snort he downs a hundred warriors. But the two
heroes tackle him. Enkidu takes hold of him by the
tail, so that Gilgamesh as espada can come in
between the horns for the kill. The artisans of the
town admire the size of those horns: 'thirty pounds
was their content of lapis lazuli'. (Lapis lazuli is
the color sacred to Styx, as we have seen. In Mexico
it is turquoise.) Ishtar appears on the walls of
Uruk and curses the two heroes who have shamed her,
but Enkidu tears out the right thigh of the Bull of
Heaven and flings it in her face, amidst brutal
taunts. It seems to be part of established procedure
in those circles. Susanowo did the same to the
sun-goddess Amaterasu, and so did Odin the Wild
Hunter to the man who stymied him ...
On
Easter Island, and at the time of rongorongo, the winter
solstice occurred when the Sun reached
ξ Orionis,
|
Egyptian djed |
 |
Phoenician
sāmekh |
 |
Greek
xi |
Ξ (ξ) |
|
... In rongorongo times
the last Greek lettered star
in Orion (ξ)
rose with the Sun in June 21. The letter
seems to have originated from the
Phoenician letter samekh (tent
peg, supporting prop), which in turn may
have been derived from the ancient
Egytian djed column ...
 |
corresponding to the time when the Full Moon was at μ Sagittarii - named the
Foal by the Copts (according to Allen).
|
Te Kioe Uri (*81
- *93) |
|
1
ngaoho |
1
naunau. |
1
uku koko |
1 nehenehe |
1
poporo. |
|
Nahe. Ta.:
Angiopteris erecta [maybe
evecta?: 'Mule's-foot
Fern']. Sa.: nase, the
giant fern. Churchill. Bishop
Jaussen: crustacé. Barthel. In
Jamaica the species
Angiopteris evecta
['Mule's-foot Fern'] is widely
naturalized and is registered as
an invasive species. The plant
was introduced by Captain Bligh
from Tahiti as a staple food for
slaves and cultivated in the
Castleton Gardens in 1860. From
there it was able to distribute
itself throughout the eastern
half of the island. Wikipedia.
... I
remember from somewhere in
Heyerdahl's books that he
considered it significant that
neke-neke was a special
word in the vocabulary of Easter
Island, it meant 'walking
without legs, walking by moving
the weight this side and that
slowly advancing forward'. He
had discovered the word when he
asked how the statues had been
moved - they walked (neke-neke)
was the answer ...

 |
|
APRIL 11 |
12 |
4-13 → 14 * 29½ |
4-14→ *41.4 (104)
|
15 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-21 |
Ga1-22 |
Ga1-23 |
Ga1-24 |
Ga1-25 |
|
ο Aurigae (85.8), γ Leporis
(85.9)
YANG
MUN (α Lupi)
|
μ
Columbae,
SAIPH
(Sword) =
κ
Orionis
(86.5),
τ
Aurigae,
ζ
Leporis (86.6) |
υ Aurigae (87.1), ν Aurigae
(87.2),
WEZN (Weight) = β Columbae,
δ Leporis (87.7),
TZE (Son) = λ Columbae
(87.9) |
Ardra-6 (The Moist One) /
ANA-VARU-8 (Pillar to sit by)
χ¹
Orionis,
ξ
Aurigae (88.1),
BETELGEUZE
=
α
Orionis
(88.3),
ξ
Columbae (88.5),
σ
Columbae (88.7) |
η
Leporis (89.0),
PRAJA-PĀTI (Lord of Created
Beings) =
δ
Aurigae,
MENKALINAN (Shoulder of the
Rein-holder) = β Aurigae,
MAHASHIM (Wrist) = θ Aurigae,
and
γ
Columbae (89.3),
π
Aurigae (89.4),
η
Columbae (89.7)
*48.0 = *89.4 - *41.4 |
|
June 14 (165) |
15 |
16 |
17 (168) |
18 |
|
°June 10 (161) |
11 |
12 |
13 (164) |
14 |
|
'May 18 (*58) |
19 |
20 |
21 (141) |
22 |
|
"May 4
(*44) |
5 (136 = 125 + 12) |
Vaitu Potu 6 |
7 (127) |
8 |
|
24 = 165 - 141 |
25 = 501 - 365 - 111 |
26 |
127 -
100 |
28 |
|
ALCYONE (*56) |
31 |
BETELGEUZE (*88) |
52 |
AL MINHAR AL ASAD (*141) |
10 |
REGULUS (*152)
|
|
May 16 (501 = 80 + 56) |
June 17 (168 = 80 + 88) |
Aug 9 (221 = 80 + *141) |
Aug 20 (232 = 91 + *141) |
|
'April 19 (474 = 136 -
27) |
'May 21 (141 = 168 - 27) |
'July 13 (194 = 221 -
27) |
'July 24 (205 = 232 -
27) |
|
"April 5 (460 = 136 -
41) |
"May 7 (127 = 168 - 41) |
"June 29 (180 = 221 -
41) |
"July 10 (191 = 232 -
41) |
|
MARCH 13 (437 = 136 -
64) |
APRIL 14 (104 = 168 -
64) |
JUNE 6 (157 = 221 - 64) |
JUNE 6 (157 = 221 - 64) |
|
501 - 141 = 360 = 80 +
*280 |
168 - 141 = 27 = 393 =
80 + *313 = 80 - 53 |
221 - 141 = 80 → *0 |
232 - 141 = 91 = 80 +
*11 |
|

...
The earliest depiction that has
been linked to the constellation
of Orion is a prehistoric
(Aurignacian) mammoth ivory
carving found in a cave in the
Ach valley in Germany in 1979.
Archaeologists have estimated it
to have been fashioned
approximately 32,000 to 38,000
years ago ... The artist cut,
smoothed and carved one side (A)
and finely notched the other
side (B) and the edges.
Side A contains the
half-relief of an anthropoidal
figure, either human or a
human-feline hybrid, known as
the 'adorant' because its arms
are raised as if in an act of
worship.
|
Egyptian
jubilation |
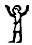 |
Phoenician
he |
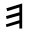 |
Greek
epsilon |
Ε (ε) |
|
Wikipedia points at
the Egyptian gesture
with arms held high
as a Sign of
jubilation, which
may have been the
origin (via
Phoenician he)
of epsilon.

 |
On side B together with
the four edges is a series of
notches that are clearly set in
an intentional pattern. The
edges contain a total of 39
notches in groups of 6, 13, 7
and 13. A further 49 notches on
side B are arranged in
four vertical lines of 13, 10,
12 and 13 respectively plus a
further notch that could be in
either of the middle two lines
... The grouping of the notches
on the plate suggests a
time-related sequence. The total
number of notches (88) not only
coincides with the number of
days in 3 lunations (88.5) but
also approximately with the
number of days when the star
Betelgeuse (α Ori) disappeared
from view each year between its
heliacal set (about 14 days
before the spring equinox around
33,000 BP) and its heliacal rise
(approximately 19 days before
the summer solstice).
Conversely, the nine-month
period when Orion was visible in
the sky approximately matched
the duration of human pregnancy,
and the timing of the heliacal
rise in early summer would have
facilitated a ‘rule of thumb’
whereby, by timing conception
close to the reappearance of the
constellation, it could be
ensured that a birth would take
place after the severe winter
half-year, but leaving enough
time for sufficient nutrition of
the baby before the beginning of
the next winter. There is a
resemblance between the
anthropoid on side A and the
constellation Orion. None of
these factors is convincing when
taken in isolation, because of
the high probability that
apparently significant
structural and numerical
coincidences might have arisen
fortuitously. However, taken
together they suggest that the
anthropoid represented an
asterism equivalent to today’s
constellation of Orion, and that
the ivory plate as a whole
related to a system of time
reckoning linked to the moon and
to human pregnancy. If so, then
ethnographic comparisons would
suggest that the
Geißenklösterle culture
related their ‘anthropoid’
asterism to perceived cycles of
cosmic power and fertility ... |
|
Te Kioe Uri
(*81 - *93) |
Te
Piringa Aniva (*94 - *106) |
|
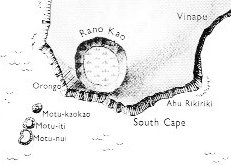
... The
cult place of Vinapu
is located between the fifth
and sixth segment of the
dream voyage of Hau Maka.
These segments, named 'Te
Kioe Uri' (inland from
Vinapu) and 'Te
Piringa Aniva' (near
Hanga Pau Kura) flank
Vinapu from both the
west and the east. The
decoded meaning of the names
'the dark rat' (i.e., the
island king as the recipient
of gifts) and 'the gathering
place of the island
population' (for the purpose
of presenting the island
king with gifts) links them
with the month 'Maro',
which is June. Thus the last
month of the Easter Island
year is twice connected with
Vinapu. Also, June is
the month of summer solstice
[a mistake: south of the
equator it is winter
solstice], which again
points to the possibility
that the Vinapu
complex was used for
astronomical purposes
...
 |
|
1
kavakava atua |
1
kohe. |
1 nehenehe |
1
pua |
1
harahara |
1
hua taru. |
1
makere |
|
Makere and Hata. were cock-roaches,
and then followed Tuere Heu. and Tureme.
.jpg)
Hata.
1. Table, bureau. P Pau.:
afata, a chest, box.
Mgv.: avata, a box,
case, trunk, coffin. Mq.:
fata, hata, a
piece of wood with several
branches serving as a rack,
space, to ramify, to branch;
fataá, hataá,
stage, step, shelf. Ta.:
fata, scaffold, altar.
2. Hakahata, to
disjoint; hakahatahata,
to loosen, to stretch. P
Pau.: vata, an
interval, interstice. Mgv.:
kohata, the space
between two boards, to be
badly joined; akakohata,
to leave a space between two
bodies badly joined;
hakahata, to be large,
broad, wide, spacious, far
off. Mq.: hatahata,
fatafata, having
chinks, not tightly closed,
disjointed. Ta.: fatafata,
open. 3. Hatahata,
calm, loose, prolix, vast.
Mgv.: hatahara,
broad, wide, spacious, at
one's ease. Ta.: fatafata,
free from care. Mq.:
hatahata, empty, open.
4. Hatahata, tube,
pipe, funnel. Churchill.
Sa.: fata, a raised
house in which to store
yams, a shelf, a handbarrow,
a bier, a litter, an altar,
to carry on a litter;
fatāmanu,
a scaffold. To.:
fata,
a loft, a bier, a
handbarrow, to carry on a
bier; fataki,
a platform. Fu.:
fata,
a barrow, a loft;
fatataki,
two sticks or canes attached
to each other at each side
of a house post to serve as
a shelf. Niuē:
fata,
a cage, a handbarrow, a
shelf, a stage, (sometimes)
the upper story of a house.
Uvea: fata,
a barrow, a bier. Fotuna:
fata,
a stage. Ta.: fata,
an altar, a scaffold, a
piece of wood put up to hang
baskets of food on;
afata,
a chest, a box, a coop, a
raft, a scaffold. Pau.:
fata,
a heap; afata,
a box, a chest. Ma.:
whata,
a platform or raised
storehouse for food, an
altar, to elevate, to
support. Moriori:
whata,
a raft. Mq.: fata,
hata,
hataá,
shelves. Rapanui:
hata,
a table. Ha.: haka,
a ladder, an artificial
henroost; alahaka,
a ladder. Mg.: ata,
a shelf; atamoa,
a ladder; atarau,
an altar. Mgv.:
avata,
a coffer, a box. Vi.:
vata,
a loft, a shelf;
tāvata,
a bier. The Samoan
fata
is a pair of light timbers
pointed at the ends and tied
across the center posts of
the house, one in front, the
other behind the line of
posts; rolls of mats and
bales of sennit may be laid
across these timbers;
baskets or reserved victuals
may be hung on the ends. The
litter and the barrow are
two light poles with small
slats lashed across at
intervals. The Marquesan
fata
is a stout stem of a sapling
with the stumps of several
branches, a hat tree in
shape, though found among a
barehead folk. These
illustrations are sufficient
to show what is the common
element in all these
fata
identifications, light
cross-pieces spaced at
intervals. With this for a
primal signifaction it is
easy to see how a ladder, a
raft, a henroost, an altar
come under the same stem for
designation. Perhaps Samoan
fatafata
the breast obtains the name
by reason of the ribs; it
would be convincing were it
not that the plumpness of
most Samoans leaves the ribs
a matter of anatomical
inference. Churchill 2. |
|
APRIL 16 (*26) |
17 (472) |
18
(*393) |
19 |
20 (*30) |
21 (111) |
22 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-26 |
Ga1-27 |
Ga1-28 |
Ga1-29 |
Ga1-30 |
Ga2-1 |
Ga2-2 |
|
μ Orionis (90.3), χ² Orionis
(90.5) |
6h (91.3 = 273.4 - 182.1)
ν
Orionis
(91.4),
θ
Columbae (91.5),
π
Columbae (91.6)
*50.0 = *91.4 - *41.4 =
*232.0 - *172.0 |
ξ Orionis
(92.5) |
Al Han'ah-4 (Brand) /
Maru-sha-pu-u-mash-mashu-7
(Front of the Mouth of the
Twins)
TEJAT PRIOR
=
η
Gemini
(93.4),
γ
Monocerotis (93.5),
κ
Aurigae (93.6),
κ
Columbae (93.8)
*52.0 = *93.4 - *41.4 |
FURUD
= ζ Canis Majoris
(94.9) |
Well-22 (Tapir) /
Arkū-sha-pu-u-mash-mashu-8
(Back of the Mouth of the
Twins)
δ
Columbae (95.2),
TEJAT POSTERIOR
=
μ
Gemini,
MIRZAM (The Roarer) = β
Canis Majoris
(95.4),
CANOPUS
(Canopy) =
α
Carinae
(95.6),
ε
Monocerotis (95.7),
ψ1
Aurigae (95.9)
*54.0 = *95.4 - *41.4 |
no star listed (96) |
|
... The
Pythagoreans make Phaeton
fall into Eridanus, burning
part of its water, and
glowing still at the time
when the Argonauts passed
by. Ovid stated that since
the fall the Nile hides its
sources. Rigveda 9.73.3 says
that the Great Varuna has
hidden the ocean. The
Mahabharata tells in its own
style why the 'heavenly
Ganga' had to be brought
down. At the end of the
Golden Age (Krita Yuga)
a class of Asura who
had fought against the
'gods' hid themselves in the
ocean where the gods could
not reach them, and planned
to overthrow the government.
So the gods implored
Agastya (Canopus, alpha
Carinae = Eridu) for help.
The great Rishi did as he
was bidden, drank up the
water of the ocean, and thus
laid bare the enemies, who
were then slain by the gods.
But now, there was no ocean
anymore! Implored by the
gods to fill the sea again,
the Holy One replied: 'That
water in sooth hath been
digested by me. Some other
expedient, therefore, must
be thought of by you, if ye
desire to make endeavour to
fill the ocean ...
 |
|
June 19 (170) |
20 (513 / 3) |
SOLSTICE |
22 (*93) |
23 (174) |
ST JOHN'S DAY |
25 |
|
°June
15 (*86) |
16 |
17 (168) |
18 |
19 |
20 (*91) |
SOLSTICE |
|
'May 23 (*63) |
24 (12 * 12) |
25 (145) |
26 |
27 |
28 (*68) |
29 |
|
9 (*49 = 7 * 7) |
"May 10 (130) |
Vaitu Potu 11 |
12 (*52) |
12 (*418) |
14 (*54) |
15 (500) |
|
29 = 170 - 141 |
130 - 100 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 = *55 - *20 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
OCT 16 |
17 (290) |
18
(*394 - *183) |
19 (475 - 183) |
20 |
21 (*214) |
22 (295) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga8-6 (31 + 178) |
Ga8-7 (210) |
Ga8-8 |
Ga8-9 |
Ga8-10 |
Ga8-11 (214) |
Ga8-12 |
|
Winnowing Basket-7 (Leopard)
18h (273.4)
*232.0 = *273.4 - *41.4
NASH
(Point) =
γ
Sagittarii
(273.7),
θ
Arae (273.8) |
ZHŌNGSHĀN =
ο
Herculis
(274.0),
π
Pavonis (274.6) |
ι Pavonis (275.1),
POLIS = μ Sagittarii
(275.9)
MENKAR (α Ceti) |
η Sagittarii (276.9) |
Purva Ashadha-20 (Elephant
Tusk, Fan, Winnowing Basket) |
KAUS BOREALIS = λ Sagittarii
(279.3) |
|
KAUS MEDIUS
=
δ
Sagittarii,
κ
Lyrae (277.5),
TUNG HAE (Heavenly Eastern
Sea) =
η
Serpentis
(277.7),
SHAOU PIH (Minor Minister) =
φ
Draconis
(277.8),
KWEI SHE =
χ
Draconis
(277.9 |
φ
Oct. (278.1),
KAUS AUSTRALIS =
ε
Sagittarii
(278.3),
ξ
Pavonis (278.4),
AL ATHFAR (The Talons of
the Falling Eagle)
=
μ
Lyrae
(278.6)
*237.0 = *278.4 - *41.4 |

... As has already been
mentioned, the Delphians
worshipped Dionysus once a
year as the new-born child,
Liknites, 'the Child
in the Harvest Basket',
which was a shovel-shaped
basket of rush and osier
used as a harvest basket, a
cradle, a manger, and a
winnowing-fan for tossing
the grain up into the air
against the wind, to
separate it from the chaff.
The worship of the Divine
Child was established in
Minoan Crete, its most
famous early home in Europe.
In 1903, on the site of the
temple of Dictaean Zeues -
the Zeus who was yearly born
in Rhea's cave at Dicte near
Cnossos, where Pythagoras
spent 'thrice nine hallowed
days' [27] of his initiation
- was found a Greek hymn
which seems to preserve the
original Minoan formula in
which the gypsum-powdered,
sword-dancing Curetes, or
tutors, saluted the Child at
his birthday feast. In it he
is hailed as 'the Cronian
one' who comes yearly to
Dicte mounted on a sow and
escorted by a spirit-throng,
and begged for peace and
plenty as a reward for their
joyful leaps ... |
|
Dec 19 (*273) |
20 (354) |
SOLSTICE |
22 |
23 (174 + 183) |
X-MAS EVE |
25
(359) |
|
°Dec 15 (*269) |
16 (350) |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 (354) |
21 |
|
'Nov 22 (*246) |
23 |
24 (328) |
25 |
26 (*250) |
27 |
28 (332) |
|
"Nov 8 |
9 |
10 (314) |
11 |
12 (*236) |
13 |
14 |
|
*273 - *141 |
*133 |
*134 |
*135 |
*236 - *100 |
*137 |
*138 |
The 'walking' ('Marching') giant fern nehenehe
(nahe, neke-neke) was named
twice in the list of 'things', having moved 4 right
ascension days ahead from Betelgeuze
to the 'tent pillar' at
ξ Orionis (the
solstice), the Club of Orion.

|
he huru o te me'e
[E:69]
Huru. Custom,
tradition, behaviour,
manners, situation, circumstances; poki huru hare,
child who stays inside (to keep a fair
complexion); te huru o te tagata
rivariva, a fine person's behaviour;
pehé te huru o Hiva? what is the
situation on the mainland? Huruhuru,
plumage, feathers (the short
feathers, not the tail feathers),
fleece of sheep. Vanaga. Samoa: sulu,
a torch; to light by a torch;
sulusulu, to carry a torch;
susulu, to shine (used of the
heavenly bodies and of fire). Futuna:
susulu, the brightness of the moon.
Tonga: huluaki, huluia,
huluhulu, to light, to enlighten;
fakahuhulu, to shine; iuhulu,
a torch or flambeau, to light with a
torch. Niuē: hulu, a torch;
huhulu, to shine (as the moon).
Maori: huru, the glow of the sun
before rising, the glow of fire.
Churchill 2. |
|
1 |
he |
ngaatu |
a Oti. |
|
1 |
tavari |
|
1 |
riku |
|
1 |
ngaoho |
|
1 |
naunau. |
|
1 |
uku koko |
|
1 |
nehenehe |
|
1 |
poporo. |
|
1 |
kavakava atua |
|
1 |
kohe. |
|
1 |
nehenehe [sic!] |
|
1 |
pua |
|
1 |
harahara |
|
1 |
hua taru. |
|
1 |
makere |
|
1 |
hata. |
|
1 |
tuere heu. |
|
1 |
tureme |
The last of these 'things', Tureme,
was when the Full Moon reached the
right ascension line at Vega, the
ancient star at the north pole.
There was no final dot at Tureme
which possibly meant we should
continue to read for one more right
ascension day:
The glyph type beginning at "May 15
(365 + 155 = 500 days),
... A sidelight
falls upon the notions connected
with the stag by Horapollo's
statement concerning the Egyptian
writing of 'A long space of time: A
Stag's horns grow out each year. A
picture of them means a long space
of time.'

Chairemon
(hieroglyph no. 15, quoted by
Tzetzes) made it shorter: 'eniautos:
elaphos'. Louis Keimer,
stressing the absence of stags in
Egypt, pointed to the Oryx (Capra
Nubiana) as the appropriate
'ersatz', whose head was, indeed,
used for writing the word rnp
= year, eventually in 'the Lord of
the Year', a well-known title of
Ptah. Rare as this modus of writing
the word seems to have been - the
Wörterbuch der Aegyptischen Sprache
(eds. Erman and Grapow), vol. 2, pp.
429-33, does not even mention this
variant - it is worth considering
(as in every subject dealt with by
Keimer), the more so as Chairemon
continues his list by offering as
number 16: 'eniautos: phoinix',
i.e., a different span of time, the
much-discussed 'Phoenix-period' (ca.
500 years) ...
... Gronw Pebyr,
who figures as the lord of Penllyn -
'Lord of the Lake' - which was also
the title of Tegid Voel, Cerridwen's
husband, is really Llew's twin and
tanist ... Gronw reigns during the
second half of the year, after
Llew's sacrificial murder; and the
weary stag whom he kills and flays
outside Llew's castle stands for
Llew himself (a 'stag of seven
fights'). This constant shift in
symbolic values makes the allegory
difficult for the prose-minded
reader to follow, but to the poet
who remembers the fate of the
pastoral Hercules the sense is
clear: after despatching Llew with
the dart hurled at him from Bryn
Kyvergyr, Gronw flays him, cuts him
to pieces and distributes the pieces
among his merry-men. The clue is
given in the phrase 'baiting his
dogs'. Math had similarly made a
stag of his rival Gilvaethwy,
earlier in the story. It seems
likely that Llew's mediaeval
successor, Red Robin Hood, was also
once worshipped as a stag. His
presence at the Abbot's Bromley Horn
Dance would be difficult to account
for otherwise, and stag's horn moss
is sometimes called Robin Hood's
Hatband. In May, the stag puts on
his red summer coat. Llew visits the
Castle of Arianrhod in a coracle of
weed and sedge. The coracle is the
same old harvest basket in which
nearly every antique Sun-god makes
his New Year voyage; and the virgin
princess, his mother, is always
waiting to greet him on the bank ...
was toga:
|
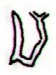 |
|
toga |
Toga. 1. Winter season. Two
seasons used to be distinguished in
ancient times: hora, summer,
and toga, winter. 2. To lean
against somehing; to hold something
fast; support, post supporting the
roof. 3. To throw something with a
sudden movement. 4. To feed oneself,
to eat enough; e-toga koe ana oho
ki te aga, eat well first when
you go to work. Vanaga. 1. Winter. P
Pau., Mgv.: toga, south. Mq.:
tuatoka, east wind. Ta.:
toa, south. 2. Column, prop;
togatoga, prop, stay.
Togariki, northeast wind.
Churchill. Wooden platform
for a dead chief: ka tuu i te
toga (Bb8-42), when the wooden
platform has been erected. Barthel
2. The expressions Tonga,
Kona, Toa (Sam., Haw.,
Tah.), to indicate the quarter of an
island or of the wind, between the
south and west, and Tokelau,
Toerau, Koolau (Sam.,
Haw., Tah.), to indicate the
opposite directions from north to
east - expressions universal
throughout Polynesia, and but little
modified by subsequent local
circumstances - point strongly to a
former habitat in lands where the
regular monsoons prevailed.
Etymologically 'Tonga', 'Kona',
contracted from 'To-anga' or
'Ko-ana', signifies 'the
setting', seil. of the sun. 'Toke-lau',
of which the other forms are merely
dialectical variations, signifies
'the cold, chilly sea'. Fornander.
And probably the reason the creators
of Manuscript E here introduced a
list of sugarcane species was toga ↔ toa:
Toa.1. Moa toa, cock.
P Pau., Mgv., Mq., Ta.: toa,
brave. Mq.: toa, male. (But
Mgv.: toa, female.) 2.
Sugarcane. T Pau., Mgv., Mq., Ta.:
to, id. (To., Niuē: to,
id. Sa., Fu.: tolo, id.) This
form occurs only in Rapanui. In New
Zealand, where the plant does not
grow, the name is applied to any
similar haulm. Churchill. Mgv.:
Toa, ironwood. Ta.: toa,
id. Mq.: toa, id. Sa.: toa,
id. Ha.: koa, id. Churchill.
Ta.: Toa, a gout of blood.
Sa.: to'a, to coagulate.
Toatoa, a bad smell of the sea.
Sa.: to'ato'a, to smell bad.
Churchill. T. Warrior, the tree
aito (Casuarina). Henry.
T. Toa, rock , coral.
Churchill.
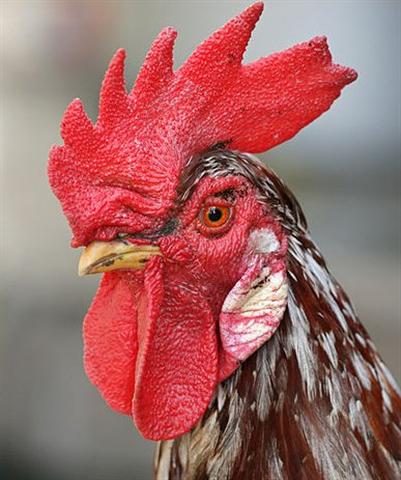
For close to the True Sherpherd of
Anu (Orion) was a Rooster
(Moa Toa), which we can find
also in the Dendera ceiling.

|
Te Piringa Aniva
(*94 - *106) |
|
1 makere |
1 hata. |
1
tuere heu. |
1 tureme
1 he rangi koro vao. |
2 he tua mamari
manu. |
3 he tua manu auau |
|
...
Then Teke said to
Oti, 'Go to the
sugarcane plantation
[ka oho ki roto
ki te toa] and
carefully break off
[ka hahati]
pieces of cane. Not
one variety shall be
left (i.e., shall be
omitted) when the
pieces of sugarcane
are taken along.'
Teke and Oti went
with their
assistants, entered
into the sugarcane
plantation, and
broke off pieces
everywhere. Teke
said the names [he
nape i te ingoa]
of all the different
varieties of
sugarcane. [E:69-70]
|
he
toa
(sugarcane) |
|
1 |
he |
rangi
koro
vao. |
a
Teke.
a
Oti. |
|
2 |
tua
mamari
manu. |
|
3 |
tua
manu
auau |
|
4 |
ruma. |
|
5 |
tuitui
koviro. |
|
6 |
vitiviti. |
|
7 |
marikuru. |
...
Toa
'Canne
à
sucre
en
fleur'
(blooming
sugar
cane)
is
the
explanation
given
by
Bishop
Jaussen
(according
to
Barthel):
Die
in
den
Metorogesängen
oft
vorkommende
Benennung
der
Zeichen
65
bzw.
66
als
toa
wurde
von
Jaussen
auf
das
Zuckerrohr
bezogen;
eine
Auffassung,
die
keine
Stütze
in
den
Tafeltexten
findet.
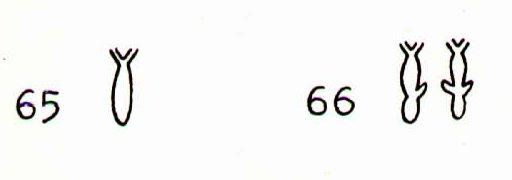
Berücksichtigt
man
aber,
daß
die
Metorogesänge
phonetisch
nicht
immer
ganz
exakt
niedergeschrieben
wurden,
so
findet
man
eine
sinnvolle
Lösung,
wenn
man
zwischen
tôa
und
to'a
underscheidet:
Das
erste
Wort
bedeutet
Zuckerrohr,
das
zweite
dagegen
Feind,
Mörder.
Englert
1948,
503:
'caña
de
azucar'
bzw.
'enemigo;
asesino'.
Ferner:
he
to'a
o te
îka,
el
que
ha
dado
muerte
a
una
persona'
...
|
 |
 |
|
toa |
rau hei |
... There are
12 Chinese types of year:
|
Rat |
Ox |
Tiger |
Rabbit |
Dragon |
Snake |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
Horse |
Goat |
Monkey |
Rooster |
Dog |
Pig |
|
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
The first day
of each Chinese year will always
fall sometime between January 21
and February 21, inclusive. The
traditional Chinese calendar is
lunisolar, like the
Hebrew calendar but unlike the
Western (Gregorian) solar
calendar or the Islamic lunar
calendar
...
|
|
APRIL 22 |
23 |
24 |
(*35 = 115 - 80) |
26 |
27 |
(118 = 4 * 29½) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga2-2 |
Ga2-3 |
Ga2-4 |
Ga2-5 (35) |
Ga2-6 |
Ga2-7 |
Ga2-8 |
|
CLOSE TO THE
SUN: |
|
no star listed (96) |
β Monocerotis, ν
Gemini (97.0) |
no star listed (98) |
ν Puppis (99.2), ψ3
Aurigae (99.4), ψ2
Aurigae (99.5)
*58.0 = *99.4 -
*41.4
GEMMA (α Cor. Bor.) |
ψ4 Aurigae (100.5),
MEBSUTA
(Outstretched) = ε
Gemini
(100.7) |
SIRIUS
= α Canis Majoris
(101.2), ψ5 Aurigae
(101.4), ν Gemini
(101.6), ψ6 Aurigae
(101.7)
*60.0 = *101.4 -
*41.4 |
τ
Puppis (102.2),
ψ7
Aurigae (102.4)
*61.0 = *102.4 -
*41.4 |
|
... In other words,
the ancient Druidic
religion based on
the oak-cult will be
swept away by
Christianity and the
door - the god Llyr
- will languish
forgotten in the
Castle of Arianrhod,
the Corona
Borealis. This
helps us to
understand the
relationship at Rome
of Janus and the
White Goddess Cardea
who is ... the
Goddess of Hinges
who came to Rome
from Alba Longa. She
was the hinge on
which the year swung
- the ancient Latin,
not the Etruscan
year - and her
importance as such
is recorded in the
Latin adjective
cardinalis -
as we say in English
'of cardinal
importance - which
was also applied to
the four main winds;
for winds were
considered as under
the sole direction
of the Great Goddess
until Classical
times ... |
|
June 25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 (180) |
30 (*101) |
July 1 |
|
SOLSTICE |
°June 22 |
23 |
ST JOHN'S DAY |
25 (*96) |
26 (6 * 29½) |
27 |
|
'May 29 |
30 |
31 |
'June 1 (*72) |
2 |
3 (154) |
4 |
|
"May 15 (500) |
16 (136) |
17 |
Vaitu Potu
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 (*61) |
|
35 |
36 = 136 - 100 |
37 |
38 |
39 = 180 - 141 |
40 |
41 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
OCT 22 (295) |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 (300) |
28 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga8-12 |
Ga8-13 (216) |
Ga8-14 |
Ga8-15 |
Ga8-16 |
Ga8-17 (220) |
Ga8-18 |
|
KAUS BOREALIS = λ
Sagittarii
(279.3) |
ν
Pavonis (280.4),
κ
Cor. Austr.
(280.9)
*239.0 = *280.4 -
*41.4 |
Abhijit-22
(Victorious)
θ
Cor. Austr.
(281.0),
VEGA
= α Lyrae
(281.8) |
no star listed (282) |
ζ
Pavonis (283.4),
λ
Cor. Austr. (283.6),
DOUBLE DOUBLE =
ε
Lyrae
(283.7),
ζ
Lyrae (283.8)
*242.0 = *283.4 -
*41.4 |
South Dipper-8
(Unicorn)
Φ
Sagittarii
(284.0),
μ
Cor. Austr. (284.6),
η
Cor. Austr.,
θ
Pavonis (284.8) |
SHELIAK
(Tortoise) =
β
Lyrae,
ν
Lyrae (285.1),
ο
Draconis (285.5).
λ
Pavonis (285.7)
ATLAS (27 Tauri)
|
|
Dec 25 |
Dec 26 (360) |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 (364) |
31 |
|
SOLSTICE |
°Dec 22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 (360) |
27 |
|
'Nov 28 |
29 (360 - 27) |
30 (*254) |
'Dec 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
"Nov 14 |
15 (360 - 41) |
16 (320) |
17 |
18 (*242) |
19 |
20 (*244) |
|
*138 |
*139 |
*240 - *100 |
*282 - *141 |
*142 |
*143 |
*144 |
|
... 'Tell us a
story!' said the
March Hare. 'Yes,
please do!' pleaded
Alice. 'And be quick
about it', added the
Hatter, 'or you'll
be asleep again
before it's done.'
'Once upon a time
there were three
little sisters', the
Dormouse began in a
great hurry: 'and
their names were
Elsie, Lacie, and
Tillie; and they
lived at the bottom
of a well — '
 |
... The
king arose from his sleeping
mat and said to all the
people: 'Let us go to
Orongo so that I can
announce my death!' The king
climbed on the rock and
gazed in the direction of
Hiva, the direction in
which he had travelled
(across the ocean). The king
said: 'Here I am and I am
speaking for the last time.'
The
people (mahingo)
listened as he spoke. The
king called out to his
guardian spirits (akuaku),
Kuihi and Kuaha,
in a loud voice: 'Let the
voice of the rooster of
Ariana (→
Arianrhod →
Gemma, α Cor.
Bor. → St John's Day)
crow softly.
The stem
with many roots (i.e., the
king) is entering!' The king
fell down, and Hotu A
Matua died. Then all the
people began to lament with
loud voices. The royal
child, Tuu Maheke,
picked up the litter and
lifted (the dead) unto it.
Tuu Maheke put his
hand to the right side of
the litter, and together the
four children of Matua
picked up the litter and
carried it. He and his
people formed a line and
went to Akahanga to
bury (the dead) in Hare O
Ava. For when he was
still in full possession of
his vital forces, A Matua
had instructed Tuu Maheke,
the royal child, that he
wished to be buried in
Hare O Ava. They picked
him up, went on their way,
and came to Akahanga.
They buried him in Hare O
Ava.
They dug
a grave, dug it very deep,
and lined it with stones (he
paenga). When that was
done, they lowered the dead
into the grave. Tuu
Maheke took it upon
himself to cover the area
where the head lay. Tuu
Maheke said, 'Don't
cover the head with coarse
soil (oone hiohio)'.
They finished the burial and
sat down. Night came,
midnight came, and Tuu
Maheke said to his
brother, the last-born: 'You
go and sleep. It is up to me
to watch over the father.'
(He said) the same to the
second, the third, and the
last. When all had left,
when all the brothers were
asleep, Tuu Maheke
came and cut off the head of
Hotu A Matua.
Then he covered everything
with soil. He hid (the
head), took it, and went up.
When he was inland, he put
(the head) down at Te
Avaava Maea. Another day
dawned, and the men saw a
dense swarm of flies pour
forth and spread out like a
whirlwind (ure tiatia
moana) until it
disappeared into the sky.
Tuu Maheke understood.
He went up and took the
head, which was already
stinking in the hole in
which it had been hidden. He
took it and washed it with
fresh water. When it was
clean, he took it and hid it
anew. Another day came, and
again Tuu Maheke came
and saw that it was
completely dried out (pakapaka).
He took it, went away, and
washed it with fresh water
until (the head) was
completely clean. Then he
took it and painted it
yellow (he pua hai pua
renga) and wound a strip
of barkcloth (nua)
around it. He took it and
hid it in the hole of a
stone that was exactly the
size of the head. He put it
there, closed up the stone
(from the outside), and left
it there. There it stayed.
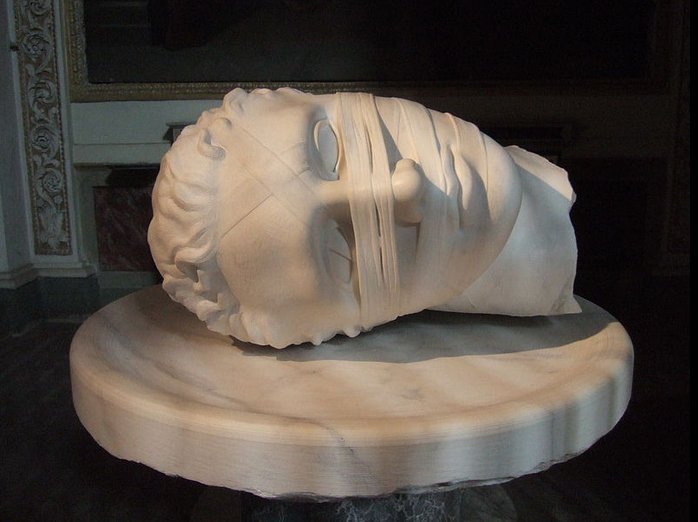

The death of king
Hotu was,
however, not told in
Manuscript E, it
came from other
sources (The
Eighth Island,
p. 218).
The close connection between
Orion and the Rooster suggests
the interpretation that the King
here was equivalent to the
World Tree at the time when it
was in bloom, i.e. when the King
became St John:
...
With the male Leo
turning into a female (Virgo)

there had to be
an opposite transformation half a
year later. This phenomenon could be
the central theme in the Olmec view
of the King (World Tree)

... I already
knew that the ceiba tree was the
model for the sacred World Tree of
the Maya, but I had never seen one
in flower when I knew what I was
looking at. I was really excited
because normally you can't see the
blossoms even if you're there when
the tree is in blossom. The fully
mature trees are hundreds of feet
high. and the blossoms are very
small. 'It's a ceiba', I chirped and
began looking for a branch low
enough to see one of the blossoms up
close. Joyce Livingstone, a retired
teacher, did the logical thing. She
bent over, picked up a fallen
branch, and held it out for me to
see. I was too excited and full of
myself to listen. She tapped my arm
more insistently and still I didn't
hear her. Finally, in frustration,
she grabbed my wrist and raised her
voice. 'Will you look at these?' she
said, waving the branch, and finally
I did. What I saw stunned me, for in
her hand lay a perfect replica of
the earflares worn by the Classic
Maya kings. Suddenly I understood
the full symbolism of so many of the
things I had been studying for
years. The kings dressed themselves
as the Wakah-Chan tree,
although at the time I didn't know
it was also the Milky Way ...
holding a Serpent
divided in the center and then
evidently stitched together again [Faka-taka].

...
Midsummer is the flowering
season of the oak, which is
the tree of endurance and
triumph, and like the ash is
said to 'court the lightning
flash'. Its roots are believed
to extend as deep underground as
its branches rise in the air -
Virgil mentions this - which
makes it emblematic of a god
whose law runs both in Heaven
and in the Underworld ...
|










.jpg)