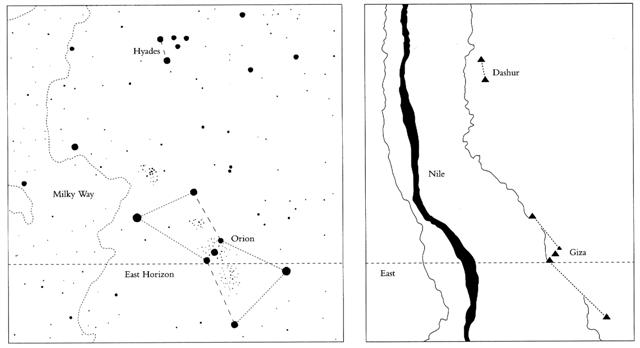
7-6. On Easter Island the first star ('point') of Orion viz. his 'foot' - Rigel - marked where a new year was beginning:
... In view of the almost universal prevalence of the Pleiades year throughout the Polynesian area it is surprising to find that in the South Island and certain parts of the North Island of New Zealand and in the neighboring Chatham Islands, the year began with the new Moon after the yearly morning rising, not of the Pleiades, but of the star Rigel in Orion ... According to my interpretations this place should have coincided with Ea6-28. And it ought to have coincided with the first new moon after Thuban had culminated at 21h:
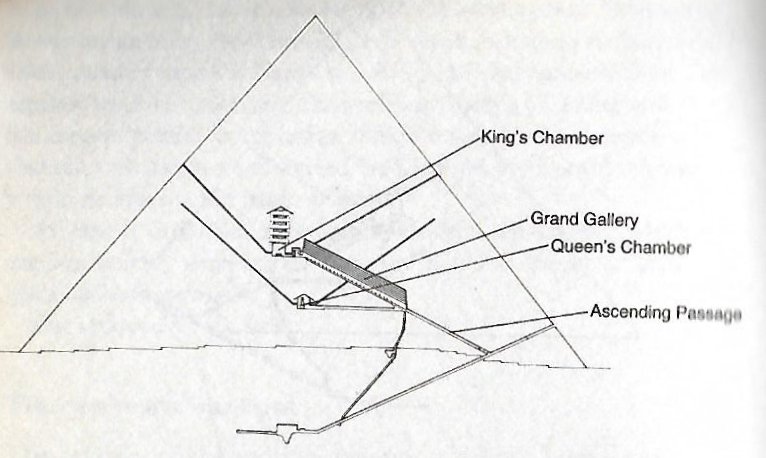
... The star could be seen, both by day and night, from the bottom of the central passage of the Great Pyramid of Cheops (Knum Khufu) at Ghizeh, in 30° of north latitude, as also from the similar points in five other like structures; and the same fact is asserted by Sir John Herschel as to the two pyramids at Abousseir ... ... For some reason, too, it had taken their fancy to place the Great Pyramid almost exactly on the 30th parallel at latitude 29º 58' 51". This, a former astronomer royal of Scotland once observed, was 'a sensible defalcation from 30º', but not necessarily in error: For if the original designer had wished that men should see with their body, rather than their mental eyes, the pole of the sky from the foot of the Great Pyramid, at an altitude before them of 30º, he would have had to take account of the refraction of the atmosphere, and that would have necessitated the building standing not at 30º but at 29º 58' 22' ...
140 → 20 weeks and 135 → 5 months each carrying 27 days. The distance from June 7 to January 29 could be measured as 394 - 158 = 236 nights (8 synodic lunar months) → 230 + 6 days ('for loading the canoe'). But the distance from June 17 to October 19 was 292 - 168 = 124 days (→ 360 - 236 = 364 - 240 = 366 - 242).
As a kind of confirmation we should remember that the text on the Keiti tablet had been designed to carry 628 days ↔ Ea6-28 ↔ 2 * 314. ... In north Asia the common mode of reckoning is in half-year, which are not to be regarded as such but form each one separately the highest unit of time: our informants term them 'winter year' and 'summer year'. Among the Tunguses the former comprises 6½ months, the latter 5, but the year is said to have 13 months; in Kamchatka each contains six months, the winter year beginning in November, the summer year in May; the Gilyaks on the other hand give five months to summer and seven to winter. The Yeneseisk Ostiaks reckon and name only the seven winter months, and not the summer months. This mode of reckoning seems to be a peculiarity of the far north: the Icelanders reckoned in misseri, half-years, not in whole years, and the rune-staves divide the year into a summer and a winter half, beginning on April 14 and October 14 respectively. But in Germany too, when it was desired to denote the whole year, the combined phrase 'winter and summer' was employed, or else equivalent concrete expressions such as 'in bareness and in leaf', 'in straw and in grass' ... Let us therefore carefully trace the dates and the prominent stars from the '2nd coming' (manu kake rua) placed as glyph number 13 * 16 = 208 → 48 days after June 9:
The 'spear' pointing upwards was a threat to life and therefore the 'spear' oriented downwards should be the opposite. Vero. To throw, to hurl (a lance, a spear). This word was also used with the particle kua preposed: koía kua vero i te matá, he is the one who threw the obsidian [weapon]. Verovero, to throw, to hurl repeatedly, quickly (iterative of vero). Vanaga. 1. Arrow, dart, harpoon, lance, spear, nail, to lacerate, to transpierce (veo). P Mgv.: vero, to dart, to throw a lance, the tail; verovero, ray, beam, tentacle. Mq.: veó, dart, lance, harpoon, tail, horn. Ta.: vero, dart, lance. 2. To turn over face down. 3. Ta.: verovero, to twinkle like the stars. Ha.: welowelo, the light of a firebrand thrown into the air. 4. Mq.: veo, tenth month of the lunar year. Ha.: welo, a month (about April). Churchill. Sa.: velo, to cast a spear or dart, to spear. To.: velo, to dart. Fu.: velo, velosi, to lance. Uvea: velo, to cast; impulse, incitement. Niuē: velo, to throw a spear or dart. Ma.: wero, to stab, to pierce, to spear. Ta.: vero, to dart or throw a spear. Mg.: vero, to pierce, to lance. Mgv.: vero, to lance, to throw a spear. Mq.: veo, to lance, to throw a spear. Churchill 2.
... A vestige of the practice of putting the king to death at the end of a year's reign appears to have survived in the festival called Macahity, which used to be celebrated in Hawaii during the last month of the year. About a hundred years ago a Russian voyager described the custom as follows: 'The taboo Macahity is not unlike to our festival of Christmas. It continues a whole month, during which the people amuse themselves with dances, plays, and sham-fights of every kind. The king must open this festival wherever he is. On this occasion his majesty dresses himself in his richest cloak and helmet, and is paddled in a canoe along the shore, followed sometimes by many of his subjects. He embarks early, and must finish his excursion at sunrise. The strongest and most expert of the warriors is chosen to receive him on his landing. The warrior watches the canoe along the beach; and as soon as the king lands, and has thrown off his cloak, he darts his spear at him, from a distance of about thirty paces, and the king must either catch the spear in his hand, or suffer from it: there is no jesting in the business. Having caught it, he carries it under his arm, with the sharp end downwards, into the temple or heavoo. On his entrance, the assembled multitude begin their sham-fights, and immediately the air is obscured by clouds of spears, made for the occasion with blunted ends. Hamamea (the king) has been frequently advised to abolish this ridiculous ceremony, in which he risks his life every year; but to no effect. His answer always is, that he is as able to catch a spear as any one on the island is to throw it at him ...
In my glyph type dictionary this 'butterfly' has been named takaure rather than pepe: The word taka-ure is more adequate, because according to Manuscript E the kuhane saw a place on Easter Island which she named the Bay of Flies (Haga Takaure). This place came just before the dream soul went up to the Place Aloft (Poike). Takaure. Fly; horse-fly. Vanaga. A fly; takaure iti, mosquito; takaure marere ke, swarm. Churchill. Taka, takataka. Circle; to form circles, to gather, to get together (of people). Vanaga. 1. A dredge. P Mgv.: akataka, to fish all day or all night with the line, to throw the fishing line here and there. This can only apply to some sort of net used in fishing. We find in Samoa ta'ā a small fishing line, Tonga taka the short line attached to fish hooks, Futuna taka-taka a fishing party of women in the reef pools (net), Maori takā the thread by which the fishhook is fastened to the line, Hawaii kaa in the same sense, Marquesas takako a badly spun thread, Mangareva takara a thread for fastening the bait on the hook. 2. Ruddy. 3. Wheel, arch; takataka, ball, spherical, round, circle, oval, to roll in a circle, wheel, circular piece of wood, around; miro takataka, bush; haga takataka, to disjoin; hakatakataka, to round, to concentrate. P Pau.: fakatakataka, to whirl around. Mq.: taka, to gird. Ta.: taa, circular piece which connects the frame of a house. Churchill. Takai, a curl, to tie; takaikai, to lace up; takaitakai, to coil. P Pau.: takai, a ball, to tie. Mgv.: takai, a circle, ring, hoop, to go around a thing. Mq.: takai, to voyage around. Ta.: taai, to make into a ball, to attach. Churchill. ... There is a couple residing in one place named Kui [Tui] and Fakataka.[Haka-taka] After the couple stay together for a while Fakataka is pregnant. So they go away because they wish to go to another place - they go. The canoe goes and goes, the wind roars, the sea churns, the canoe sinks. Kui expires while Fakataka swims. Fakataka swims and swims, reaching another land. She goes there and stays on the upraised reef in the freshwater pools on the reef, and there delivers her child, a boy child. She gives him the name Taetagaloa. When the baby is born a golden plover flies over and alights upon the reef. (Kua fanau lā te pepe kae lele mai te tuli oi tū mai i te papa). And so the woman thus names various parts of the child beginning with the name 'the plover' (tuli): neck (tuliulu), elbow (tulilima), knee (tulivae) ... Tui. 1. To sew mats, to make strings. E-tahi tuitui reipá i Te Pei, ekó rava'a e-varu kaukau; i-garo ai i Hiva, i te kaiga, a necklace of mother-of-pearl is on te Pei, few will find it (lit: eight groups of people); it has remained in Hiva, in our homeland. 2. The three stars of Orion's Belt. Vanaga. Ure. 1. Generation; ure matá, warlike, bellicose generation (matá, obsidian, used in making weapons). 2. Offspring; brother; colleague i toou ure ka tata-mai, your colleague has turned up. 3. Friendship, friendly relationship; ku-ké-á te ure, they have become enemies (lit.: friendship has changed). 4. Penis (this definition is found in Englert's 1938 dictionary, but not in La Tierra de Hotu Matu'a). Ure tahiri, to gush, to spurt, to flow; e-ure tahiri-á te toto, blood is flowing in gushes. Ure tiatia moana, whirlwind which descend quickly and violently onto the ocean; whirlpool, eddy. Vanaga. Penis; kiri ure, prepuce, foreskin. P Pau., Mgv., Ta.: ure, penis. Ureure, spiral. Ta.: aureure, id. Urei, to show the teeth. Mgv.: urei, to uncover the eye by rolling back the lids. Churchill. Pau.: Ureuretiamoana, waterspout. Ta.: ureuretumoana, id. Churchill. H. Ule 1. Penis. For imaginative compounds see 'a'awa 1, 'aweule, ulehala, ulehole, ulepa'a, ulepuaa, ule'ulu. Kū ka ule, he'e ka laho, the penis is upright, the scrotum runs away (refers to breadfruit: when the blossom (pōule) appears erect, there will soon be fruit). 2. Tenon for a mortise; pointed end of a post which enters the crotch of a rafter (also called ma'i kāne). Ho'o ule, to form a tenon or post for the crotch of a rafter. 3. To hang. Wehewehe. ... From a religious point of view, the high regard for flies, whose increase or reduction causes a similar increase or reduction in the size of the human population, is interesting, even more so because swarms of flies are often a real nuisance on Easter Island, something most visitors have commented on in vivid language. The explanation seems to be that there is a parallel relationship between flies and human souls, in this case, the souls of the unborn. There is a widespread belief throughout Polynesia that insects are the embodiment of numinous beings, such as gods or the spirits of the dead, and this concept extends into Southeast Asia, where insects are seen as the embodiment of the soul ... ... Then King Matua said to Hotu, 'You must not forget [he mee o rehu] the flies [te takaure] when you take along (all the things that are necessary) and sail off. If you forget the flies [ana rehu i a koe te takaure], the multitude (piere) of the people will disappear [he ngaro]. When you reach the land [ana tomo ki runga.ki tou kainga] to which you are travelling [ena koe ka oho], it will be over quickly (?) for the multitude of the people. When the flies die [ana moko te ihu o te takaure], the human population dies too [he moko tokoa te ihu o tou piere tangata].' [E:57]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





.jpg)



.jpg)