I maybe should change the night sky stars (and dates) reflecting the heliacal 'plumb line' in Auriga (at Cb3-14). 180║ corresponds to 365╝ / 2 = 182.625 days and 89.3 + 182.625 = 271.925:
But the results do not at first appear very encouraging. Rukbalgethi Genubi is θ Herculis. Etamin is γ Draconis, and τ Ophiuchi (272.9) was rising a day before 18h (273.9). The glyph Signs are different in kind from those at the beginning of side a in the G text, but possibly the front pointed wing of manu rere can be understood as an inversion of the pointed front part in Ga1-1, because the left arm of hanau in Cb3-14 is pointed and designed similar to the left arm of tagata in Ga1-2:
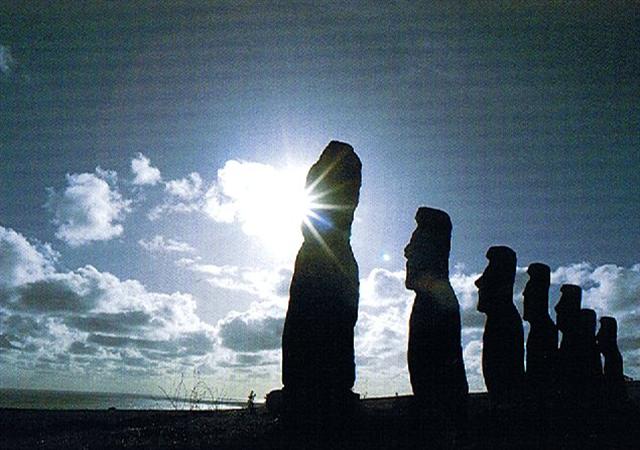
In June 18 the northern summer solstice was approaching and Sun had only 'one wing', i.e. beyond June 21 he would begin to move towards the south in order to leave his northern domain. Possibly this explains the curious cut-off (koti) 'string curve' in front of the eyeless manu rere (in Cb3-13). St Lucia offered her 2 eyes but Sun had only 1 eye to offer. ... On the late afternoon of the June solstice, towards sunset, we reached Ahu Akivi near the centre of the western side of Easter Island. This is an inland site, 3 kilometers from the coast. Like Ahu Nau Nau at Anakena, it has seven Moai, but in this case none of them have topknots and, uniquely, all face west towards the sea - which is clearly visible from the high point on which they stand. There is a curious tradition concerning these grizzled, otherworldly statues, solemn and powerful, with their blank, aloof eye-sockets gazing out over the limitless ocean. Like most of the other Moai of Easter Island the local belief is that they died, long ago, at the time when mana - magic - supposedly fled from the island never to return. However, in common with only a very few of the other Moai, it is believed that these particular statues still have the power, twice a year, to transform themselves into aringa ora - literally 'living faces' - a concept startlingly similar to the ancient Egyptian notion that statues became 'living images' (sheshep ankh) after undergoing the ceremony of the 'opening of the mouth and the eyes'. Statues at Angkor were likewise considered to be lifeless until their eyes had been symbolically 'opened'. The great stone Moai of Easter Island were at one time equipped with beautiful inlaid eyes of white coral and red scoria. In a number of cases - though not at Ahu Akivi - sufficient fragments have been found to make restoration possible, showing that the figures originally gazed up at an angle towards the sky. It is therefore easy to guess why this island was once called Mata-Ki-Te-Rangi, 'Eyes Looking at Heaven'. On a moonlit night its hundreds of 'living' statues scanning the stars with glowing coral eyes would have seemed like mythic astronomers peering into the cosmos. And in the heat of the day those same eyes would have tracked the path of the sun, which the ancient Egyptians called the 'Path of Horus' or the 'Path of Ra'. This was also the 'path' pursued by the Akhu Shemsu Hor, the 'Followers of Horus', for whom the exclamation Ankh'Hor - 'the god Horus Lives' - would have been an everyday usage. The principal astronomical alignments of the great temple of Angkor Wat in Cambodia are towards sunrise on the December solstice and sunrise on the March equinox - respectively midwinter and the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere. The two moments in the year when Easter Island traditions say that the Moai of Ahu Akivi come alive and are 'particularly meaningful' are the June solstice and the September equinox - respectively midwinter and the beginning of spring in these southern latitudes. Rigorous archaeoastronomical studies by William Mulloy, William Liller, Edmundo Edwards, Malcolm Clark and others have confirmed that the east fašade of Ahu Akivi does have a very definite equinoctial orientation and, indeed, that 'the complex was designed to mark the time of the equinoxes' ...
If the 7 Moai at Ahu Akivi were exceptional in receiving eyes (coming 'alive') at the equinoxes (while all the rest of the stone statues on the island anciently always were looking with their watchful eyes towards the interior), then there could have been an exceptional manu rere (Ra) who lost his single 'eye' at the June winter solstice. Furthermore, the curved string in front in Cb3-13 can be contrasted with the very straight string of a plumb line. Such lines were used in the night in order to find stars, but in daytime the Sun was pinpointed by using a straight wooden rod.
Possibly side a of the Mamari tablet could correspond to daytime observations, because Metoro found a 'tree' (rakau) in June:
However at Ca4-1 there could be straight lines reaching out in the night sky towards the stars in Auriga:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||