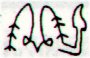Also the 9th Chinese station refers to the star Dabih (β Capricorni), but there appears to be no association to a lucky time:
However, I suspect there is a tradition going back to ancient Babylonia:
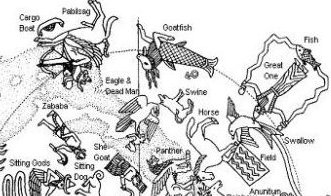
Eagle & Dead Man shows how a 'dead man' is uplifted in the claws of an eagle and how the eagle follows the Milky Way. In Gardiner's Sign List we can see a hieroglyph with a bound man:
Implicitly these bound hands at the backside means there are no digits visible - even his toes are at his back. He has nothing to count with and he cannot be counted with. He is completely harmless. In ancient Egypt they did everything backwards (upside down), and someone who was bound with his arms at the back was the opposite of a lucky man, i.e. in the Babylonian map above it probably was not an unlucky man. When Ulu died he was not unlucky, because he knew he would save the life of his son Mokuola. But in ancient Egypt they turned this story perversely upside down, letting the young one die instead of the old one: "In late September or early October 130, Hadrian and his entourage, among them Antinous, assembled at Heliopolis to set sail upstream as part of a flotilla along the River Nile. The retinue included officials, the Prefect, army and naval commanders, as well as literary and scholarly figures. Possibly also joining them was Lucius Ceionius Commodus, a young aristocrat whom Antinous might have deemed a rival to Hadrian's affections. On their journey up the Nile, they stopped at Hermopolis Magna, the primary shrine to the god Thoth. It was shortly after this, in October [in the year A.D.] 130 - around the time of the festival of Osiris - that Antinous fell into the river and died, probably from drowning. Hadrian publicly announced his death, with gossip soon spreading throughout the Empire that Antinous had been intentionally killed. The nature of Antinous's death remains a mystery to this day, and it is possible that Hadrian himself never knew; however, various hypotheses have been put forward. One possibility is that he was murdered by a conspiracy at court. However, Lambert asserted that this was unlikely because it lacked any supporting historical evidence, and because Antinous himself seemingly exerted little influence over Hadrian, thus meaning that an assassination served little purpose. Another suggestion is that Antinous had died during a voluntary castration as part of an attempt to retain his youth and thus his sexual appeal to Hadrian. However, this is improbable because Hadrian deemed both castration and circumcision to be abominations and as Antinous was aged between 18 and 20 at the time of death, any such operation would have been ineffective. A third possibility is that the death was accidental, perhaps if Antinous was intoxicated. However, in the surviving evidence Hadrian does not describe the death as being an accident; Lambert thought that this was suspicious. Another possibility is that Antinous represented a voluntary human sacrifice. Our earliest surviving evidence for this comes from the writings of Dio Cassius, 80 years after the event, although it would later be repeated in many subsequent sources. In the second century Roman Empire, a belief that the death of one could rejuvenate the health of another was widespread, and Hadrian had been ill for many years; in this scenario, Antinous could have sacrificed himself in the belief that Hadrian would have recovered. Alternately, in Egyptian tradition it was held that sacrifices of boys to the Nile, particularly at the time of the October Osiris festival, would ensure that the River would flood to its full capacity and this fertilize the valley; this was made all the more urgent as the Nile's floods had been insufficient for full agricultural production in both 129 and 130. In this situation, Hadrian might not have revealed the cause of Antinous's death because he did not wish to appear either physically or politically weak. Conversely, opposing this possibility is the fact that Hadrian disliked human sacrifice and had strengthened laws against it in the Empire." (Wikipedia)
I think we should connect the death of Castor with the Arrow constellation and with the inseparable pair Eagle & Dead Man (with the Eagle probably alluding to the old ruler):
The reversed (huri) figure in Cb11-20 has no hands and neither toes.
|