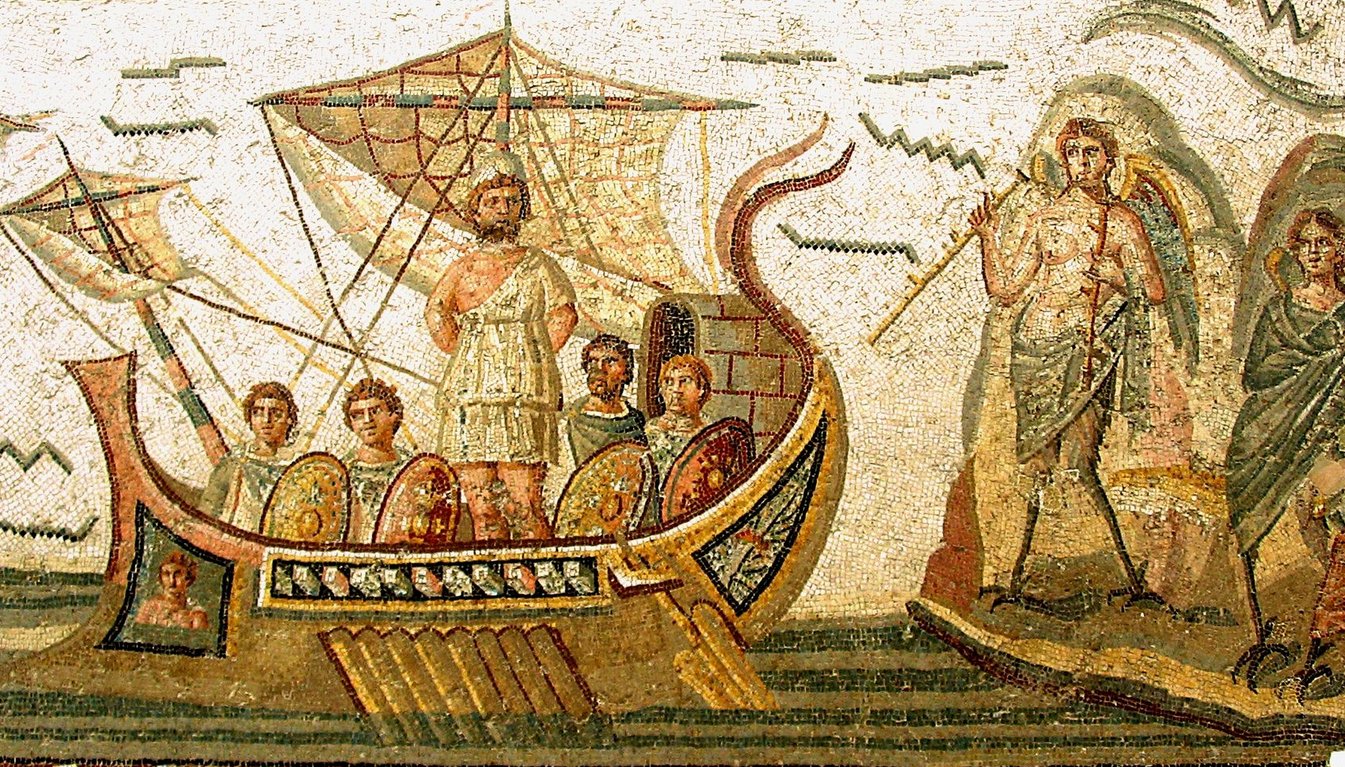
The nightside journey ended when the pointed nose
of the Sun ship was caught in a net. It began when the nose of
his ship had
been cut off:


... The little spring was
concealed by a succulent growth of strange plants, bearing
gigantic leaves and pendant clusters of long yellow fruit, which
she named bananas. The intervening space was filled with a
luxuriant growth of slender stems and twining vines, of which
she called the former sugar-cane and the latter yams; while all
around the house were growing little shrubs and esculent roots,
to each one of which she gave an appropriate name. Then
summoning her little boy, she bade him gather the breadfruit and
bananas, and, reserving the largest and best for the gods,
roasted the remainder in the hot coals, telling him that in the
future this should be his food. With the first mouthful, health
returned to the body of the child, and from that time he grew in
strength and stature until he attained to the fullness of
perfect manhood.
He became a mighty warrior in those days, and was
known throughout all the island, so that when he died, his name,
Mokuola, was given to the islet in the bay of Hilo
where his bones were buried; by which name it is called even to
the present time
...
|
Motu
1. To cut; to snap off: motu-á te hau,
the fishing line snapped off; to engrave, to inscribe
letters or pictures in stone or in wood, like the
motu mo rogorogo, inscriptions for recitation in
lines called kohau. 2. Islet; some names of
islets: Motu Motiro Hiva, Sala y Gómez; and
around the island: Motu Nui, Motu Iti, Motu Kaokao,
Motu Tapu, Motu Marotiri, Motu Kau, Motu Tavake, Motu
Tautara, Motu Ko Hepa Ko Maihori, Motu Hava. Motu
rau uri, southeast wind. Motu takarua, west
wind. Vanaga.
To break, to cut with a knife, to
sever, to rupture; rent, reef, shoal, rock; motu poto,
to cut short; aretare motu, an oratory; motu
kivakiva, an uncovered shoal; motumotu, to
cut up; tae motumotu, e ko motumotu,
indissoluble. P Pau.: motu, island; komutu,
to break. Mgv.: motu, an island, a rock, to cut,
to be broken. Mq.: motu, island, land, to break,
to cut up, to take to pieces. Ta.: motu, a low
island, to be broken, cut up. Motuava (motu
- ava 1), a hollowed rock. Motuhaua,
archipelago. Motupiri (motu - piri),
archipelago. Motuputuputu (motu -
putuputu), archipelago. Moturauri, south wind
T. Moturogorogo, to write T. Churchill.
H Moku 1. To be cut, severed,
amputated, broken in two, as a rope; broken loose, as a
stream after heavy rains, or as a bound person; to
punctuate. Moku ka pawa, dawn has broken. Kai
moku ka noho 'ana, relations separated by the sea.
Ho'o moku, to cut and divide; a cutting,
division, separation. 2. District, island, islet,
section, forest, grove, clump, severed portion,
fragment, cut, laceration, scene in a play. Cfr.
mokupuni, momoku. Moku lehua, lehua
forest. Ho'o moku, to place one over a moku,
district. 3. Ship, schooner, vessel, boat, said to be so
called because the first European ships suggested
islands. 4. A stage of pounded poi (such poi
sticks together as a mass and can be separated cleanly -
moku - from the pounding board). Wehewehe |
|
Ora
1. Healthy; to recover, to be saved (from
an illness or a danger): ku-ora-á, ina kai mate,
he recovered, he did not die; ku-ora-á te haoa,
the wound has healed; e-ora-no-á, he is still
alive; ora-hakaou mai, to come back to life;
ora ké, what a pleasant breeze! (lit: how healthy!).
2. Stick for spinning top (made from the shell of a
sandalwood nut) with which children make the top spin.
Vanaga.
1. December, January. Ora nui,
November, October. 2. To live, to exist, to draw breath,
to survive, to subsist, to be well, healthy, safe, to
refresh, a pause, rest, ease; e ko ora,
incurable; ora tuhai, previous existence; ora
iho, to resuscitate, to revive; ora nui,
vigorous; oraga, life, existence; oraga roaroa,
oraga roaroa ke, oraga ina kai mou,
immortality; oraga kore, lifeless; oraga mau,
oraga ihoiho, vivacious; oraora, oraora
no iti, to be better; hakaora, to draw
breath, to revive, to strengthen, healthy, to sanctify,
to animate, to save, to repose, to cure, to rest, to
comfort, to assuage; hakaora ina kai mou, to
immortalize; hakaoratagata, Messiah, Saviour. 3.
To give water to; kua ora te kevare, to water a
horse; hakaunu ora, to water. 4. To staunch, to
stop the flow of a liquid. 5. To make an escape;
hakaora, to discharge, to deliver, to set free. 6.
To be awake (probably ara); hakaora to
guard. 7. A zephyr, light wind; kona ora,
a breezy spot; ahau ora, agreeable breeze.
Churchill.
Ola, life, health, well-being,
living, livelihood, means of support, salvation; alive,
living; curable, spared, recovered, healed; to live; to
spare, save, heal, grant life, survive, thrive. Ola
loa, long life, longevity, Ola 'ana, life,
existence. Wehewehe.
The explorers reach
Easter Island in a 'canoe' (vaka). The name of
their craft is given as Oraorangaru 'saved from
the billows' (Brown 1924:40) or Te Oraora-miro
'the living-wood' (ME:58). The Routledge reference 'Each
(man went) on a piece of wood' (RM:278) also seems to
refer to the name of the canoe. As far back as 1934, the
name was no longer understood. I favor the following
explanation: The difficulty in interpreting the name of
the canoe of the explorers arises from the name segment
oraora. To begin with, the compound form
oraora ngaru should be analyzed in comparison
with other Polynesian compounds, such as MAO.
pare-ngaru 'that which fends off the waves' (i.e.,
the hull of the boat), TAH. tere-'aru 'that which
moves through the waves' (i.e., riding the waves on a
board). There are several possible translations for
oraora as the reduplication of ora. Te
Oraora Miro can be translated as 'the pieces of
wood, tightly lashed together' (compare TAH. oraora
'to set close together, to fit parts of a canoe') and be
taken to refer to the method of construction of the
explorer canoe, while Oraora Ngaru means 'that
which parts the water like a wedge', or 'that which
saves (one) from the waves, that which is stronger than
the waves'. (Barthel 2) |
| Hiro
1. A deity invoked when praying for rain
(meaning uncertain). 2. To twine tree fibres (hauhau,
mahute) into strings or ropes.
Ohirohiro, waterspout
(more exactly pú ohirohiro), a column of water
which rises spinning on itself.
Vanaga. To spin, to twist. P Mgv.: hiro, iro,
to make a cord or line in the native manner by twisting
on the thigh. Mq.: fió, hió, to spin, to
twist, to twine. Ta.: hiro, to twist. This
differs essentially from the in-and-out movement
involved in hiri 2, for here the movement is that
of rolling on the axis of length, the result is that of
spinning. Starting with the coir fiber, the first
operation is to roll (hiro) by the palm of the
hand upon the thigh, which lies coveniently exposed in
the crosslegged sedentary posture, two or three threads
into a cord; next to plait (hiri) three or other
odd number of such cords into sennit. Hirohiro,
to mix, to blend, to dissolve, to infuse, to inject, to
season, to streak with several colors; hirohiro ei
paatai, to salt. Hirohiroa, to mingle;
hirohiroa ei vai, diluted with water. Churchill.
Ta.: Hiro, to exaggerate. Ha.:
hilohilo, to lengthen a speech by mentioning
little circumstances, to make nice oratorial language.
Churchill.
Whiro
'Steals-off-and-hides'; also [in addition to the name of
Mercury] the universal name for the 'dark of the Moon'
or the first day of the lunar month; also the deity of
sneak thieves and rascals.
Makemson. |
The nightside journey appeared to be very short
because from where you went to sleep in the evening and to the
following morning when you woke up, you would
usually not remember what had happened, what your dream soul (kuhane) had
done. You had been lying still and unconsious in the dark - like the dormant Mother Earth in winter.
The image of the night was used for the winter, and then also
for the journey from death to revival in general.
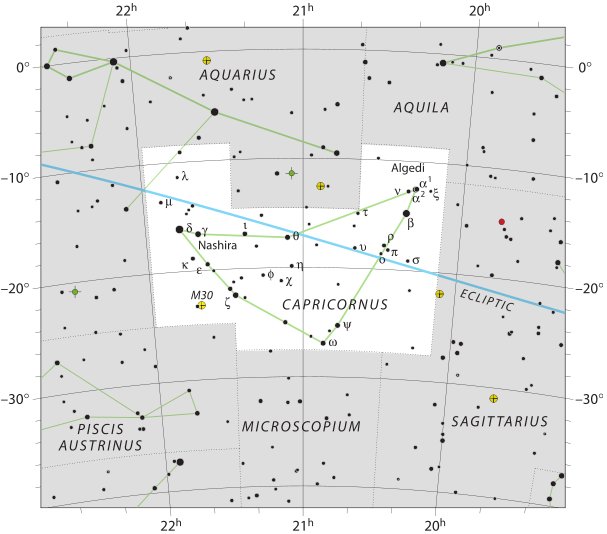
The Eagle carried the
immobilized ('dead') man safely across the waters of the night to
'dawn', and this journey was beginning at Sagittarius and could once upon a time
have ended at the tail of the
Goat (Deneb Algiedi) or at the Pleiades:


... At mid-summer,
at the end of a half-year reign, Hercules is made drunk with
mead and led into the middle of a circle of twelve stones
arranged around an oak, in front of which stands an altar-stone;
the oak has been lopped until it is T-shaped. He is bound to it
with willow thongs in the 'five-fold bond' which joins wrists,
neck, and ankles together, beaten by his comrades till he
faints, then flayed, blinded, castrated, impaled with a
mistletoe stake, and finally hacked into joints on the
altar-stone ...
The distance from the Talons of the Eagle, which
at the time of the Bull rose with the Sun in day 227 (»
π) - according to the network structure of our Gregorian calendar - to heliacal Deneb
Algiedi (the Tail of the Goat) was short, only *265 - *227 = 38 days:
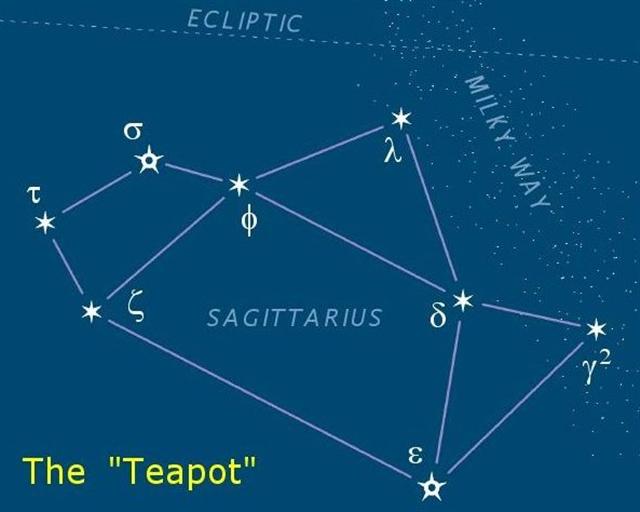
|
NOVEMBER 1 |
2
(306) |
3
(*227) |
4 |
5 |
31 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga8-22 |
Ga8-23 |
Ga8-24 (227) |
Ga8-25 |
Ga8-26 |
|
19h (289.2)
λ Aquilae (Ant.)
(289.1), γ Cor. Austr (289.3),
τ SAGITTARII
(289.4), ι Lyrae (289.5), δ Cor. Austr. (289.8) |
Al Baldah-19
AL BALDAH = π
Sagittarii,
ALPHEKKA MERIDIANA = α Cor.
Austr. (290.1), β
Cor. Austr. (290.2) |
ALADFAR (The Talons of the
Eagle) = η Lyrae
(291.1),
NODUS II = δ Draconis
(291.5), ψ Sagittarii (291.6), τ Draconis (291.7), θ Lyrae (291.8) |
ω Aquilae (292.1),
ρ Sagittarii
(292.6), υ Sagittarii
(292.7) |
π Draconis,
ARKAB PRIOR = β¹ Sagittarii
(293.0), ARKAB
POSTERIOR = β² Sagittarii,
ALRAMI (The Archer)
= α Sagittarii
(293.2), χ
Sagittarii
(293.6) |
| January 4 |
5 (*290) |
6 |
7 (372) |
8 |
|
°December 31 |
°January 1 |
2 |
3 (*288) |
4 |
|
'December 8 |
9 |
10 (*264) |
11 (345) |
12 |
|
"November 24 |
25 (329) |
26 (*250) |
27 |
28 |
|
DECEMBER 7 |
8 |
9 |
10 (*264) |
11 (345) |
12 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Gb2-6 |
Gb2-7 |
Gb2-8 |
Gb2-9 (264) |
Gb2-10 |
Gb2-11 (37) |
|
BUNDA (Foundation) /
KAKKAB
NAMMAΧ (Star of Mighty
Destiny) |
θ Piscis Austrini
(330.1), λ Oct. (330.7) |
|
Al Sa'd al Su'ud-22 /
Emptiness-11
TSIN = 36 Capricorni
(325.2),
ALPHIRK = β Cephei
(325.7),
SADALSUD = β
Aquarii,
ξ Gruis (325.9) |
no star listed (326) |
CASTRA = ε Capricorni
(327.2),
BUNDA
= ξ Aquarii
(327.5)
SIRIUS (α
Canis Majoris)
|
Mahar sha hi-na Shahū-26
(Western One in the Tail of
the Goat)
NASHIRA = γ Capricorni
(328.0), ν Oct. (328.3),
AZELFAFAGE
= π¹
Cygni,
κ Capricorni (328.7) |
Arkat sha hi-na Shahū-27
(Eastern One in the Tail
of the Goat)
ENIF = ε Pegasi, ERAKIS = μ
Cephei
(329.2),
46
CAPRICORNI, JIH
(the Sun) = κ Pegasi
(329.3), ι Piscis Austrini
(329.4), λ Capricorni
(329.6), ν Cephei (329.7),
DENEB
ALGIEDI
= δ Capricorni
(329.8) |
|
February 9 (40) |
10 |
11 (407) |
12 |
13 |
All Hearts' Day |
|
°February 5 |
6 |
7 |
8 (*324) |
9 (40) |
10 |
|
'January 13 (378) |
14 |
15 (*300) |
16 |
17 |
18 (383) |
|
"December 30
|
31 |
"January 1 |
2 |
3 (368) |
4 |
|
NAKSHATRA DATES: |
|
JUNE 7 (*78) |
8 |
9 |
10 (161) |
11 |
12 |
|
The Knot (Ukdah) |
Rishu A.-13 (Head
of the Lion)
ψ Leonis (146.4),
RAS ELASET AUSTRALIS
= ε Leonis
(146.6) |
VATHORZ PRIOR = υ Carinae
(147.9) |
|
Star-25 /
ANA-HEU-HEU-PO-5
(Pillar where debates were
held)
ALPHARD = α Hydrae
(142.3), ω Leonis (142.6),
τ¹
Hydrae
(142.7) |
Al Tarf-7
ψ Velorum (143.3),
ALTERF
(The End)
= λ Leonis, τ² Hydrae
(143.4), ξ Leonis (143.5) |
A Hydrae
(144.1)
VEGA (α Lyrae)
|
UKDAH
= ι Hydrae
(145.4), κ Hydrae (145.5),
SUBRA = ο Leonis
(145.8) |
|
August 10 |
11 |
12 |
13 (*145) |
14 |
15 (227) |
|
°August 6 |
7 |
8 (220) |
9 |
10 |
11 (*143) |
|
'July 14 |
15 |
16 |
17 (*118) |
18 |
19 (200) |
|
SIRIUS |
"July 1 |
2 |
3 (*104) |
4 |
5 (186) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga3-19 (78) |
Ga3-20 |
Ga3-21 |
Ga3-22 |
Ga3-23 |
Ga3-24 |
The journey over the sea
by the Explorers took 37 days, which
was the distance from "April 25
(115) at heliacal Cursa - as if
indicating where the river Eridanus was
beginning - to heliacal Castor in
"June 1 (Maro 1). At the time
of the Bull the corresponding dates
would have been APRIL 2 (92)
respectively MAY 9 (129).
However, the
nakshatra side (the night side) - i.e. looking at the
position of the Full Moon - ought to have given a better measure
for the true length of their canoe journey. 37 + 183 = 220 (»
π). In the womb
of the headless Rogo figure in "December 1 (*255) a
perfect little Sun 'was cooking':
.jpg)
|
NOVEMBER 6 |
7 (*231) |
8 |
9 |
10 (314) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Gb1-1
(23 * 10) |
Gb1-2 |
Gb1-3
|
Gb1-4 |
Gb1-5
(314 - 80) |
|
DENEB
OKAB (Eagle's Tail)
= δ Aquilae (Ant.)
(294.0),
α
VULPECULAE (Little Fox)
(294.9) |
ν
Aquilae (Ant.) (295.0),
ALBIREO
= β Cygni
(295.5) |
ALSAFI
(Fire Tripods)
= σ Draconis
(296.0), μ Aquilae (296.3), ι Aquilae (Ant.)
(296.8), κ Aquilae (Ant.) (296.9) |
ε
Sagittae (297.1), σ Aquilae (Ant.) (297.4),
SHAM (Arrow)
= α Sagittae
(297.8) |
β
Sagittae (298.0), χ Aquilae (298.3), ψ Aquilae
(298.8) |
|
January 9 |
10
(*295) |
11 |
12 |
13 (378) |
|
°January
5 |
6 (*291) |
7 |
8 |
9 (374) |
|
Lucia |
'December 14 (*268) |
15 |
16 (350) |
17 |
|
"November 29 |
30
(*254) |
"December 1 |
2 (336) |
3 |
|
NAKSHATRA DATES |
|
Side a
according to the heliacal Gregorian calendar SIRIUS
was at °June 30 when NUNKI was close to the Full
Moon (cfr Ga2-11).
Side
b
at
the time of Julius Caesar SIRIUS was at 'June 30
when ROTTEN MELON was close to the Full Moon (cfr
Gb1-18). |
MAY 8 (493) |
9 (*49) |
10 (130) |
11 |
|
Ghost-23
(?)
ρ Gemini (?) (112.1),
Eskimo Nebula = NGC2392 Gemini
(112.2)
ANTARES (α
Scorpii)
|
Al
Dhirā'-5 /
Punarvasu-7 /
Mash-mashu-Mahrū-10
(Western One of the Twins)
CASTOR
(Beaver)
= α Gemini
(113.4) |
ANA-TAHUA-VAHINE-O-TOA-TE-MANAVA-7
(Pillar
for elocution)
υ Gemini (114.0),
MARKAB PUPPIS = κ Puppis
(114.7), ο Gemini (114.8),
PROCYON
= α Canis Minoris
(114.9) |
α
MONOCEROTIS
(115.4), σ Gemini (115.7) |
|
July 11 |
12 (193) |
13 |
14
(*480) |
|
°July 7
(188) |
8 |
9 |
10
(*111) |
|
'June 14 |
15 (166) |
16 |
17 (*88) |
|
"May 31
(121) |
Maro 1 (*72) - E:17 |
"June 2 |
3 (*64) |
|
i te raa po rae o
te.maro.i tomo ai
te ihu o te
vaka.o Ira |
|
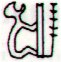
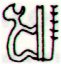
Ihu
1. Nose; ihu more,
snub nose, snub-nosed person. 2. Ihuihu
cape, reef; ihuihu - many reefs, dangerous
for boats. 3. Ihu moko, to die out (a family
of which remains only one male without sons);
koro hakamao te mate o te mahigo, he-toe e-tahi
tagata nó, ina aana hakaara, koîa te me'e e-kî-nei:
ku-moko-á te ihu o te mahigo, when the members
of family have died and there remains only one man
who has no offspring, we say: ku-moko-á te ihu o
te mahigo. To disappear (of a tradition, a
custom), me'e ihu moko o te tagata o te kaiga
nei, he êi, the êi is a custom no longer
in use among the people of this island. 4. Eldest
child; first-born; term used alone or in conjunction
with atariki. Vanaga.
1. Nose, snout, cape
T (iju G). Po ihuihu, prow of a canoe.
P Pau.: ihu, nose. Mgv.: ihu, nose;
mataihu, cape, promontory. Mq., Ta.: ihu,
nose, beak, bowsprit. Ihupagaha, ihupiro,
to rap on the nose, to snuffle. 2. Mgv.: One who
dives deep. Ta.: ihu, to dive. Churchill.
Sa.: isu, nose, snout, bill. Fu., Fakaafo,
Aniwa, Manahiki: isu, the nose. Nuguria;
kaisu, id. Fotuna: eisu, id. Moiki:
ishu, id. To., Niuē,
Uvea, Ma., Ta., Ha., Mq., Mgv., Pau., Rapanui,
Tongareva, Nukuoro: ihu,
id. Rarotonga: putaiu,
id. Vaté: tus,
id. Viti: uthu,
nose. Rotumā: isu,
id. ... usu
and ngusu
... serve as transition forms, usu
pointing to
isu the nose in
Polynesia and ngusu
to ngutu
the mouth, which is very near, nearer yet when we
bear in mind that ngutu
the mouth is snout as well and that isu
the nose is snout too ...
Churchill 2. |
In other words, the journey of the Explorers
could have ended where Castor had gone to the Full Moon,
when the Sun had reached the Fire Tripods in Draco - in
"December 1 (*255).
... In China,
every year about the beginning of April, certain officials
called Sz'hüen used of old to go about the country
armed with wooden clappers. Their business was to summon the
people and command them to put out every fire. This was the
beginning of the season called Han-shih-tsieh, or
'eating of cold food'. For three days all household fires
remained extinct as a preparation for the solemn renewal of
the fire, which took place on the fifth or sixth day after
the winter solstice [Sic!]. The ceremony was performed with
great pomp by the same officials who procured the new fire
from heaven by reflecting the sun's rays either from a metal
mirror or from a crystal on dry moss. Fire thus obtained is
called by the Chinese heavenly fire and its use is enjoined
in sacrifices: whereas fire elicited by the friction of wood
is termed by them earthly fire, and its use is prescribed
for cooking and other domestic purposes
...
Like archaic
China and certain Amero-Indian societies, Europe, until
quite recently, celebrated a rite involving the
extinguishing and renewal of domestic fires, preceded by
fasting and the use of the instruments of darkness. This
series of events took place just before Easter, so that the
'darkness' which prevailed in the church during the service
of the same name (Tenebrae), could symbolize both the
extinguishing of domestic fires and the darkness which
covered the earth at the moment of Christ's death. In all
Catholic countries it was customary to extinguish the lights
in the churches on Easter Eve and then make a new fire
sometimes with flint or with the help of a burning-glass.
Frazer brings together numerous instances which show that
this fire was used to give every house new fire. He quotes a
sixteenth-century Latin poem in a contemporary English
translation, from which I take the following significant
lines:
On Easter Eve the
fire all is quencht in every place, // And fresh againe from
out the flint is fecht with solemne grace.
Then Clappers
cease, and belles are set againe at libertée, // And
herewithall the hungrie times of fasting ended bée
...

... Indeed, at
the rituals of the installation, the chief is invested with
the 'rule' or 'authority' (lewaa) over the land, but
the land itself is not conveyed to him. The soil (qele)
is specifically identified with the indigenous 'owners' (i
taukei), a bond that cannot be abrogated. Hence the
widespread assertion
that
traditionally (or before the Lands Commission) the chiefly
clan was landless, except for what it had received in
provisional title from the native owners, i.e., as marriage
portion from the original people or by bequest as their
sister's son ... The ruling chief has no corner on the means
of production. Accordingly, he cannot compel his native
subjects to servile tasks, such as providing or cooking his
daily food, which are obligations rather of his own
household, his own line, or of conquered people (nona
tamata ga, qali kaisi sara). Yet even more dramatic
conditions are imposed on the sovereignity at the time of
the ruler's accession.
Hocart observes
that the Fijian chief is ritually reborn on this occasion;
that is, as a domestic god. If so, someone must have killed
him as a dangerous outsider. He is indeed killed by the
indigenous people at the very moment of his consecration, by
the offering of kava that conveys the land to his
authority (lewaa). Grown from the leprous body of a
sacrificed child of the native people, the kava the
chief drinks poisons him ... Sacred product of the people's
agriculture, the installation kava is brought forth
in Lau by a representative of the native owners (mataqali
Taqalevu), who proceeds to separate the main root in
no ordinary way but by the violent thrusts of a sharp
implement (probably, in the old time, a spear). Thus killed,
the root (child of the land) is then passed to young men
(warriors) of royal descent who, under the direction of a
priest of the land, prepare and serve the ruler's cup
... the tuu yaqona or cupbearer on this occasion
should be a vasu i taukei e loma ni koro, 'sister´s
son of the native owners in the center of the village'
... Traditionally, remark, the kava root was chewed
to make the infusion: The sacrificed child of the people is
cannibalized by the young chiefs.
The water of the
kava, however, has a different symbolic provenance.
The classic Cakaudrove kava chant, performed
at the Lau installation rites, refers to it as sacred
rain water from the heavens ... This male and chiefly water
(semen) in the womb of a kava bowl whose feet are
called 'breasts' (sucu), and from the front of which,
tied to the upper part of an inverted triangle, a sacred
cord stretches out toward the chief ... The cord is
decorated with small white cowries, not only a sign of
chieftainship but by name, buli leka, a continuation
of the metaphor of birth - buli, 'to form', refers in
Fijian procreation theory to the conceptual acception of the
male in the body of the woman. The sacrificed child of the
people will thus give birth to the chief. But only after the
chief, ferocious outside cannibal who consumes the
cannibalized victim, has himself been sacrificed by it. For
when the ruler drinks the sacred offering, he is in the
state of intoxication Fijians call 'dead from' (mateni)
or 'dead from kava' (mate ni yaqona), to
recover from which is explicitly 'to live' (bula). This
accounts for the second cup the chief is alone accorded, the
cup of fresh water. The god is immediately revived, brought
again to life - in a transformed state
...

|













.jpg)







