|
RIGEL
A hole going through must be balanced by another hole at the other side of course. Otherwise there would be no channel through.
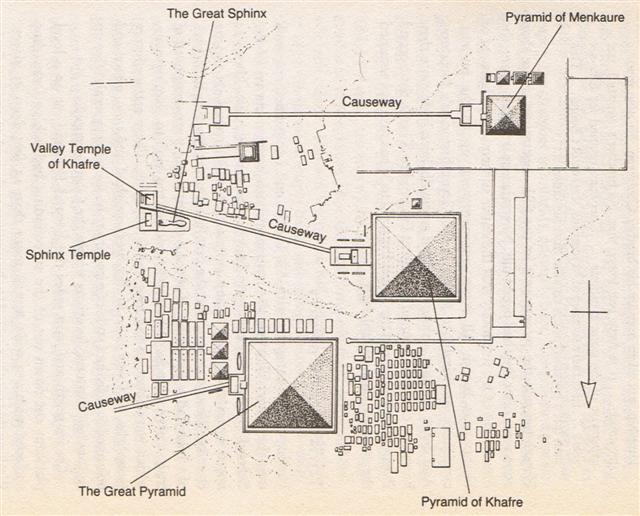
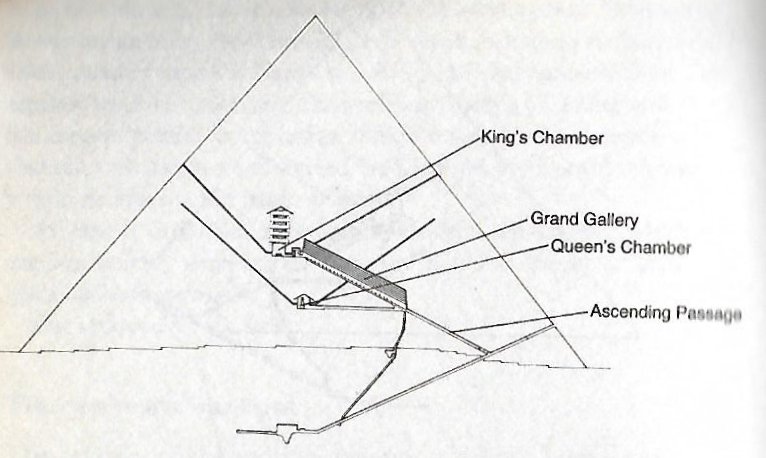
But in the C text, there seems to be also a one-sided hole (i.e. rather a pit than a hole) - a hole with no return. Which in a way means a hole (mata) with no origin (origo). Mata. 1. Tribe, people; te mata tûai-era-á, the ancient tribes. 2. Eye; mata ite, eyewitness. 3. Mesh: mata kupega. 4. Raw, uncooked, unripe, green, matamata, half-cooked, half-ripe. Kahi matamata, a tuna fish. Vanaga. 1. The eye; mata neranera, mata kevakeva, mata mamae, to be drowsy; mata keva, mataraparapa, matapo, blind; mata hakahira, squint eyed; mata pagaha, eye strain. 2. Face, expression, aspect, figure, mien, presence, visage, view; mata mine, mata hakataha, mata pupura, mata hakahiro, to consider. 3. Raw, green, unripe. 4. Drop of water. 5. Mesh; hakamata, to make a net. 6. Cutting, flint. 7. Point, spear, spike (a fish bone). 8. Chancre. Matamata, sound of water. Churchill. There is a wide range of significations in this stem. It will serve to express an opening as small as the mesh of a net or as large as a door of a house; it will serve to designate globular objects as large as the eye or as small as the bud on a twig or the drop of rain, and designating a pointed object it answers with equal facility for the sharpened tip of a lance or the acres of a headland; it describes as well the edge of a paddle or the source from which a thing originates. Churchill 2. Matá. Black obsidian spear points, all belonging to the Late Period which began ca 1680. Heyerdahl 3. Down through a channel into the King's Chamber in the great pyramid of the Creator God Khnum-Khufu a brilliant stream of light from the guiding star Thuban in Draco would arrive, but the Queen's Chamber had no such light source - it was a dark moon pit: ... The star [Thuban] could be seen, both by day and night, from the bottom of the central passage of the Great Pyramid of Cheops (Knum Khufu) at Ghizeh, in 30° of north latitude, as also from the similar points in five other like structures; and the same fact is asserted by Sir John Herschel as to the two pyramids at Abousseir ...
Hiro. 1. A deity invoked when praying for rain (meaning uncertain). 2. To twine tree fibres (hauhau, mahute) into strings or ropes. Ohirohiro, waterspout (more exactly pú ohirohiro), a column of water which rises spinning on itself. Vanaga. To spin, to twist. P Mgv.: hiro, iro, to make a cord or line in the native manner by twisting on the thigh. Mq.: fió, hió, to spin, to twist, to twine. Ta.: hiro, to twist. This differs essentially from the in-and-out movement involved in hiri 2, for here the movement is that of rolling on the axis of length, the result is that of spinning. Starting with the coir fiber, the first operation is to roll (hiro) by the palm of the hand upon the thigh, which lies coveniently exposed in the crosslegged sedentary posture, two or three threads into a cord; next to plait (hiri) three or other odd number of such cords into sennit. Hirohiro, to mix, to blend, to dissolve, to infuse, to inject, to season, to streak with several colors; hirohiro ei paatai, to salt. Hirohiroa, to mingle; hirohiroa ei vai, diluted with water. Churchill. Ta.: Hiro, to exaggerate. Ha.: hilohilo, to lengthen a speech by mentioning little circumstances, to make nice oratorial language. Churchill. Whiro 'Steals-off-and-hides'; also [in addition to the name of Mercury] the universal name for the 'dark of the Moon' or the first day of the lunar month; also the deity of sneak thieves and rascals. Makemson.
24 + 15 = 39:
Mauga, Maúga. 1. Last; aga maúga o te Ariki o Hotu Matu'a, King Hotu Matua's last work. 2. Hill, mountain. Mouga, moúga. Last; vânaga moúga o te Ariki O Hotu Matu'a, the last words of King Hotu Matu'a. Vanaga. Mauga kore, impalpable. Mouga. 1. Enough, that's all, at last. 2. Mountain, ridge of hills; mouga iti, hillock; tua mouga, mountain top; hiriga mouga; hillside, declivity, slope. P Pau.: mahuga, mountain. Mgv.: mou, maga, mountain. Mq.: mouna, mouka, peak or crest of a mountain. Ta.: maua, moua, mountain. 3. Extinction, end, interruption, solution; te mouga o te hiriga, end of a voyage; pagaha mouga kore, without consolation. 4. To get. Churchill. Toga. 1. Winter season. Two seasons used to be distinguished in ancient times: hora, summer, and toga, winter. 2. To lean against somehing; to hold something fast; support, post supporting the roof. 3. To throw something with a sudden movement. 4. To feed oneself, to eat enough; e-toga koe ana oho ki te aga, eat well first when you go to work. Vanaga. 1. Winter. P Pau., Mgv.: toga, south. Mq.: tuatoka, east wind. Ta.: toa, south. 2. Column, prop; togatoga, prop, stay. Togariki, northeast wind. Churchill. Wooden platform for a dead chief: ka tuu i te toga (Bb8-42), when the wooden platform has been erected. Barthel 2. The expressions Tonga, Kona, Toa (Sam., Haw., Tah.), to indicate the quarter of an island or of the wind, between the south and west, and Tokelau, Toerau, Koolau (Sam., Haw., Tah.), to indicate the opposite directions from north to east - expressions universal throughout Polynesia, and but little modified by subsequent local circumstances - point strongly to a former habitat in lands where the regular monsoons prevailed. Etymologically 'Tonga', 'Kona', contracted from 'To-anga' or 'Ko-ana', signifies 'the setting', seil. of the sun. 'Toke-lau', of which the other forms are merely dialectical variations, signifies 'the cold, chilly sea'. Fornander. Tuu. 1. To stand erect. 2. Mast, pillar, post. Van Tilburg. 1. To stand erect, mast, pillar, post; tuu noa, perpendicular; tanu ki te tuu, to set a post; hakatu tuu, to step a mast; tuu hakamate tagata, gallows; hakatuu, to erect, to establish, to inactivate, to form, immobile, to set up, to raise. P Mgv., Mq., Ta.: tu, to stand up. 2. To exist, to be. Mgv.: tu, life, being, existence. 3. To accost, to hail; tuu mai te vaka, to hail the canoe. Mgv.: tu, a cry, a shout. 4. To rejoin; tuua to be reunited. 5. Hakatuu, example, mode, fashion, model, method, measure, to number. PS Sa.: tu, custom, habit. Fu.: tuu, to follow the example of. 6. Hakatuu, to disapprove; hakatuu riri, to conciliate, to appease wrath. 7. Hakatuu, to presage, prognostic, test. 8. Hakatuu, to taste. 9. Hakatuu, to mark, index, emblem, seal, sign, symbol, trace, vestige, aim; hakatuu ta, signature; akatuu, symptom; hakatuua, spot, mark; hakatuhaga, mark; hakatuutuu, demarcation. Churchill. 1. To arrive: tu'u-mai. 2. Upright pole; to stand upright (also: tutu'u). 3. To guess correctly, to work out (the meaning of a word) correctly: ku-tu'u-á koe ki te vânaga, you have guessed correctly [the meaning of] the word. 4. To hit the mark, to connect (a blow). 5. Ku-tu'u pehé, is considered as... ; te poki to'o i te me'e hakarere i roto i te hare, ku-tu'u-á pehé poki ra'ura'u, a child who takes things that have been left in the house is considered as a petty thief. Tu'u aro, northwest and west side of the island. Tu'u haígoígo, back tattoo. Tu'u haviki, easily angered person.Tu'u-toga, eel-fishing using a line weighted with stones and a hook with bait, so that the line reaches vertically straight to the bottom of the sea. Tu'utu'u, to hit the mark time and again. Tu'utu'u îka, fish fin (except the tail fin, called hiku). Vanaga. ... To the Polynesian and to the Melanesian has come no concept of bare existence; he sees no need to say of himself 'I am', always 'I am doing', 'I am suffering'. It is hard for the stranger of alien culture to relinquish his nude idea of existence and to adopt the island idea; it is far more difficult to acquire the feeling of the language and to accomplish elegance in the diction under these unfamiliar conditions. Take for an illustrative example these two sentences from the Viti: Sa tiko na tamata e kila: there are (sit) men who know. Sa tu mai vale na yau: the goods are (stand) in the house. The use of tu for tiko and of tiko for tu would not produce incomprehensibility, but it would entail a loss of finish in diction, it would stamp the speaker as vulgar, as a white man ... Savage life is far too complex; it is only in rich civilization that we can rise to the simplicity of elemental concepts ... Churchill 2. These 3 (→ Ca10-10, Ca10-11, Ca10-12) should obviously be considered together, because there are no more similar 'hole' glyphs in the C text:
The Earth was a square in time-space. 10 * 10 + 11 * 11 + 12 * 12 = 100 + 121 + 144 = 365 → 13 * 13 + 14 * 14 = 169 + 196 = 365 → Ca10-13 + Ca10-14.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||







.jpg)