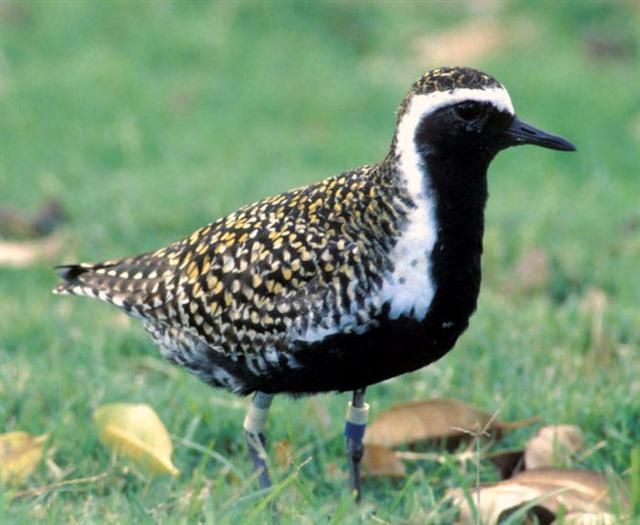
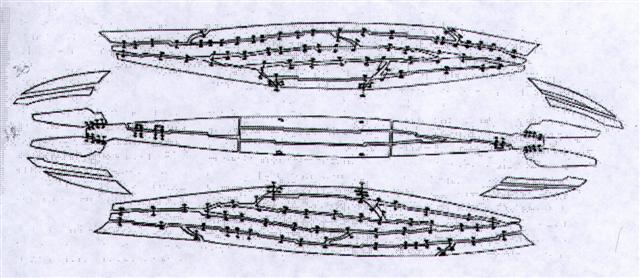
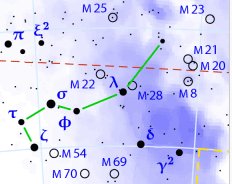
238. The 'fire-wood sticks' emerging from the whirlpool (the navel of the sea) could have originated from the remnants of the 'Old Ship'.
... And then she looked in her hand, she inspected it right away, but the bone's saliva wasn't in her hand. It is just a sign I have given you, my saliva, my spittle. This, my head, has nothing on it - just bone, nothing of meat. It's just the same with the head of a great lord: it's just the flesh that makes his face look good. And when he dies, people get frightened by his bones. After that, his son is like his saliva, his spittle, in his being, whether it be the son of a lord or the son of a craftsman, an orator. The father does not disappear, but goes on being fulfilled. Neither dimmed nor destroyed is the face of a lord, a warrior, craftsman, an orator. Rather, he will leave his daughters and sons. So it is that I have done likewise through you. Now go up there on the face of the earth; you will not die. Keep the word. So be it, said the head of One and Seven Hunaphu - they were of one mind when they did it ... Day 1 and day 2 of the Creation could have been causally connected and linked through the 'navel string' of the 'Milky Way':
... There is a couple residing in one place named Kui [Tui] and Fakataka [= create a cycle]. After the couple stay together for a while Fakataka is pregnant. So they go away because they wish to go to another place - they go. The canoe goes and goes, the wind roars, the sea churns, the canoe sinks. Kui expires while Fakataka swims.
Fakataka swims and swims, reaching another land. She goes there and stays on the upraised reef in the freshwater pools on the reef, and there delivers her child, a boy child. She gives him the name Taetagaloa [= Not-Tangaroa]. When the baby is born a golden plover flies over and alights upon the reef. (Kua fanau lā te pepe kae lele mai te tuli oi tū mai i te papa). And so the woman thus names various parts of the child beginning with the name 'the plover' (tuli): neck (tuliulu), elbow (tulilima), knee (tulivae). They go inland at the land. The child nursed and tended grows up, is able to go and play. Each day he now goes off a bit further away, moving some distance away from the house, and then returns to their house. So it goes on and the child is fully grown and goes to play far away from the place where they live. He goes over to where some work is being done by a father and son. Likāvaka is the name of the father - a canoe-builder, while his son is Kiukava ...
In Sharp as a Knife we can read how Raven falls from the sky to the level of the sea and then climbs down all the way to the floor of the sea (papa), where he finds himself as an Old Man, as Nangkilstlas his own grandfather, resting there by his fire:
... In the morning of the world, there was nothing but water. The Loon was calling, and the old man who at that time bore the Raven's name, Nangkilstlas, asked her why. 'The gods are homeless', the Loon replied. 'I'll see to it', said the old man, without moving from the fire in his house on the floor of the sea. Then as the old man continued to lie by his fire, the Raven flew over the sea. The clouds broke. He flew upward, drove his beak into the sky and scrambled over the rim to the upper world. There he discovered a town, and in one of the houses a woman had just given birth. The Raven stole the skin and form of the newborn child. Then he began to cry for solid food, but he was offered only mother's milk. That night, he passed through the town stealing an eye from each inhabitant. Back in his foster parents' house, he roasted the eyes in the coals and ate them, laughing. Then he returned to his cradle, full and warm. He had not seen the old woman watching him from the corner - the one who never slept and who never moved because she was stone from the waist down. Next morning, amid the wailing that engulfed the town, she told what she had seen. The one-eyed people of the sky dressed in their dancing clothes, paddled the child out to mid-heaven in their canoe and pitched him over the side. He turned round and round to the right as he fell from the sky back to the water. Still in his cradle, he floated on the sea. Then he bumped against something solid. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said a voice. The Raven saw nothing. He heard the same voice again, and then again, but still he saw nothing but water. Then he peered through the hole in his marten-skin blanket. Beside him was a grebe. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said the grebe and dived. Level with the waves beside him, the Raven discovered the top of a housepole made of stone. He untied himself from his cradle and climbed down the pole to the lowermost figure. Hala qaattsi ttakkin-gha, a voice said: 'Come inside, my grandson.' Behind the fire, at the rear of the house, was an old man white as a gull. 'I have something to lend you', said the old man. 'I have something to tell you as well. Dii hau dang iiji: I am you.' Slender bluegreen things with wings were moving between the screens at the back of the house. Waa'asing dang iiji, said the old man again: 'That also is you.' The old man gave the Raven two small sticks, like gambling sticks, one black, one multicoloured. He gave him instructions to bite them apart in a certain way and told him to spit the pieces at one another on the surface of the sea. The Raven climbed back up the pole, where he promptly did things backwards, just to see if something interesting would occur, and the pieces bounced apart. It may well be some bits were lost. But when he gathered what he could and tried again - and this time followed the instructions he had been given - the pieces stuck and rumpled and grew to become the mainland and Haida Gwaii ... An echo of this phenomenon, how a 'living (is)land' could be created through the junction of 'a pair of 'gambling sticks' (similar to how the X and Y chromosomes will generate offspring at random) can be found in Manuscript E, where a pair of canoe-hulls were separated at the southwestern corner (toga) later to be reunited at the other side of Easter Island, where the next generation would be born. In between Easter Island had been (re)created. ... The canoes of Ava Rei Pua and of Hotu were seen near the (off-shore) islets. On the fifteenth day of the month of October (tangaroa uri) the canoe of Hotu and the canoe of Ava Rei Pua landed. On the fifteenth day of the month of October (tangaroa uri), Nonoma left the house during the night to urinate outside. At this point Ira called out to Nonoma, 'Look at the canoe!' Nonoma ran, he quickly went to Te Hikinga Heru (a ravine in the side of the crater Rano Kau) and looked around. There he saw the double canoe way out near the (offshore) islets, and the two (hulls of the canoe) were lashed together. He ran and returned to the front of the house. He arrived and called into the house: 'Hey you! This canoe has arrived during the night without our noticing it!' Ira asked Nonoma, 'Where is the canoe, which you say is lying out there (in the water)?' Nonoma's voice came back: 'It is out there (in the water) close to the (offshore) islets! There it lies, and the two (hulls) are lashed together.' The four of them (corrected for 'the six of them') went out and picked up leaves (on branches) to give signals. They picked them up, went and arrived at Te Hikinga and saw the canoe. Raparenga got up, picked up the leaves, took them in his hands, and waved, waved, waved, waved ... When Hotu's canoe had reached Taharoa, the vaginal fluid (of Hotu's pregnant wife) appeared. They sailed towards Hanga Hoonu, where the mucus (kovare seems to refer to the amniotic sac in this case) appeared. They sailed on and came to Rangi Meamea, where the amniotic fluid ran out and the contractions began. They anchored the canoe in the front part of the bay, in Hanga Rau. The canoe of Ava Rei Pua also arrived and anchoraged. After Hotu's canoe had anchoraged, the child of Vakai and Hotu appeared. It was Tuu Maheke, son of Hotu, a boy. After the canoe of Ava Rei Pua had also arrived and anchoraged, the child of Ava Rei Pua was born. It was a girl named Ava Rei Pua Poki ... (E:81) ... Then summoning her little boy, she bade him gather the breadfruit and bananas, and, reserving the largest and best for the gods, roasted the remainder in the hot coals, telling him that in the future this should be his food. With the first mouthful, health returned to the body of the child, and from that time he grew in strength and stature until he attained to the fullness of perfect manhood. He became a mighty warrior in those days, and was known throughout all the island, so that when he died, his name, Mokuola, was given to the islet in the bay of Hilo [Hiro] where his bones were buried; by which name it is called even to the present time ... A newborn needs milk from his mother and we can therefore understand why the central element in front in Ca10-24, as well as 'on board' in the glyph 363 days later (i.e. 3 days earlier), was depicted like the outline of a breast:
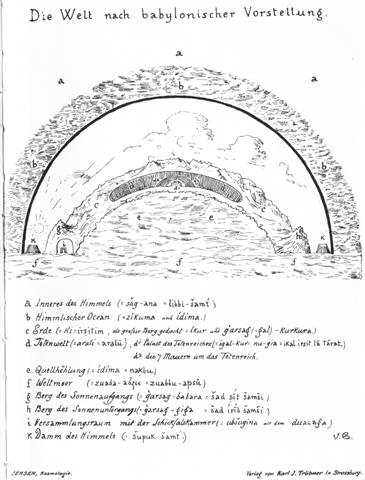
An element of hazard (gambling) was present at the equinoxes according to the ancient Babylonians: ... In ancient Babylonia they imagined the earth was bulging upwards because down below under the earth, in the darkness, there was a huge freshwater reservoir (apsū). The form of the earth was therefore like an overturned boat: 'Da ferner sofort nachgewiesen werden wird, dass sich der apsū unter der Erde ihrer ganzen Ausdehnung nach befindet und ein Höhlung unter der Erde nur verursacht werden kann durch eine Wölbung der Erde, werden wir nicht umhinkönnen, diese Vorstellung von dem apsū wieder gespiegelt zu sehen in dem Bericht des Diodor, dem gemäss die Erde von den Chaldäern in der Gestalt eines umgestülpten Bootes vorgestellt wurde.' (Jensen)
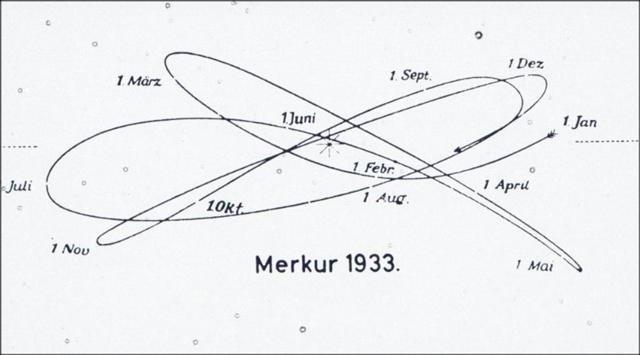
... At the letter i there is 'der Versammlungsraum mit der Schicksalskammer' (assembly hall with a room for deciding the outcome) ... ... Before the beginning of a new 'year' (= halfyear) it is not yet determined what will come. According to the Babylonian view there was a chamber of hazard where the sky roof meets earth: ... Als solch ein Ort (resp. ein Gemach) im Osten des apsū [water below the earth] und im Osten der Erde an der Grenze zwischen dem sichtbaren und unsichtbaren Reiche hat der Duazag eine ganz besondere Bedeutung im Glauben der Babylonier. Er ist ... 'der Ort der Geschicke', der ki nam-tar-tar-ini = aar imātum. Ein Solcher konnte nur im Osten liegen. Denn die Sonne geht im Osten auf. Die Ostsonne ist Marduk. Darum bringt auch Marduk die Geschicke aus der Behausung seines Vaters Ía, dem Urwasser, hervor ... Von diesem [Nebukadnezar's II grosser Inschrift] heisst es ... 'Duazag, der Ort der Geschicke im Ubugina [Versammlungsraum], das (dem?) Gemach der Geschicke, in dem im Zakmuku [= F(e)ast for Marduk at the beginning of the year to determine (make fast) the future (of the year/halfyear) for which the gods went to Marduk's tempel Ĭsagila in Babylon: '... zu dem sich die übrigen Götter und vor Allem Barsip(pa)'s Hauptgott Nabū in feierlichem Zuge zu Schiff ... begaben ...'] zu Jahresanfang am 8-ten (und?) am 11-ten Tage [rather: from the 8th up to and including the 11th day of the God-King] der (Gott-)König .... sich niederlässt und die Götter über Himmel und Erde .... das Schicksal der Zukunft .... bestimmen ....' ... Ganz ähnlich is der Name 'Gott von Duazag' des Gottes Nabū ... zu erklären. Er bezeichnet ihn als den Gott des Wachtstums, welches als aus dem Osten stammend betrachtet wird, weil die Sonne, die das Wachstum bringt, im Osten aufgeht. Dass aber Nabū als Ost-Gott aufgefasst wurde, hängt damit zusammen, dass sein Stern, der Mercur, nur im Osten oder Westen sichtbar ist ...
... Wir begreifen, warum der Tirītu durch 'Monat (des) Duazaga' bezeichnet wird. Denn in diesem findet die Aussaat des Korns (insbesondere ... des Weizens und der Gerste) statt, der Duazag aber hat zu diesen ... als Ort des Gottes, der das Wachstum des Weizens befördert, eine ganz bestimmte Beziehung ¹. ¹ Beachte aber, dass der erste Monat des Jahres nach dem Schicksalsgemach (= Ubugina) bezeichnet wird ... , der siebente aber d.i. der erste der zweiten Jahreshälfte nach dem im Ubugina befindlichen Duazaga. Sollte darum die Deutung des Namens Tirītu als 'Anfang' doch vorzuziehen sein? (Peter Jensen, Die Kosmologie der Babylonier.)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||