184. There were 2 rainbows
some people in South America stated:
... The Katawihi distinguish two rainbows: Mawali in the west, and Tini in the east. Tini and Mawali were twin brothers who brought about the flood that inundated the whole world and killed all living people, except two young girls whom they saved to be their companions. It is not advisable to look either of them straight in the eye: to look at Mawali is to become flabby, lazy, and unlucky at hunting and fishing; to look at Tini makes a man so clumsy that he cannot go any distance without stumbling and lacerating his feet against all obstacles in his path, or pick up a sharp instrument without cutting himself ...
| Tini. To be at the zenith: ku-tini-á te raá; middle of a journey, of a period of time; te tini o te raá, the middle of the day. Vanaga. 1. A great number, innumerable, infinite, indefinite. Tinitini, million, billion. T Pau.: tinitini, innumerable. Mgv.: tini, a countless number, infinite. Mq.: tini, id. Ta.: tini, numerous. 2. Raa tini, noon; tini po, midnight; te tini te raa, zenith; topa tini, abortion. Churchill. |
| ... A man once said to his careless son: The world is as sharp as a knife. If you don't watch out, you'll fall right off. His son replied that the earth was wide and flat; no one could fall off. And as he kicked at the ground to show how solid and reliable it was, he ran a splinter into his foot and died soon after ... (Robert Bringhurst, A Story as Sharp as a Knife. The Classical Haida Mythtellers and Their World.) |
| Vari. 1. Menstruation, period (also: tiko). 2. To tack, to veer (nautical); ku-vari-mai-á te miro, the boat arrives, have veered [around Rano Kau]. Vanaga.
About, circumference, to turn in a circle; hakavari, pliant, to bend, square; varivari, about, to go around; vavari, a garland; varikapau, circumference, to surround, a compass, to admire; hiriga varikapau, to go in a ring; pa varikapau, to close in; varitakataka (vari-taka 3) to surround. Churchill.
Pau.: Vari, marsh, mire, dirt. Ta.: vari, dirt, mud. Rar.: vari, mud. Churchill. Mgv.: Vari, paste well diluted. Mq.: vaivai, to dilute, to thin. Ha.: waliwali, soft, pasty. Churchill. |
... The Mura also believed that there were two rainbows, an 'upper' and a 'lower' ... Similarly, the Tucuna differentiated between the eastern and the western rainbows and believed them both to be subaquatic demons, the masters of fish and potter's clay respectively ...
| LIBRA: |
| 16 |
Visakha |
α, β, γ and ι Librae |
Triumphal arch, potter's wheel |
Oct 31 (304) |
| forked, having branches (or the gift, rādhā) |
Zuben Elgenubi |
| Mea. 1. Tonsil, gill (of fish). 2. Red (probably because it is the colour of gills); light red, rose; also meamea. 3. To grow or to exist in abundance in a place or around a place: ku-mea-á te maîka, bananas grow in abundance (in this place); ku-mea-á te ka, there is plenty of fish (in a stretch of the coast or the sea); ku-mea-á te tai, the tide is low and the sea completely calm (good for fishing); mau mea, abundance. Vanaga.
1. Red; ata mea, the dawn. Meamea, red, ruddy, rubricund, scarlet, vermilion, yellow; ariga meamea, florid; kahu meamea purple; moni meamea, gold; hanuanua meamea, rainbow; pua ei meamea, to make yellow. Hakameamea, to redden, to make yellow. PS Ta.: mea, red. Sa.: memea, yellowish brown, sere. To.: memea, drab. Fu.: mea, blond, yellowish, red, chestnut. 2. A thing, an object, elements (mee); e mea, circumstance; mea ke, differently, excepted, save, but; ra mea, to belong; mea rakerake, assault; ko mea, such a one; a mea nei, this; a mea ka, during; a mea, then; no te mea, because, since, seeing that; na te mea, since; a mea era, that; ko mea tera, however, but. Hakamea, to prepare, to make ready. P Pau., Mgv., Mq., Ta.: mea, a thing. 3. In order that, for. Mgv.: mea, because, on account of, seeing that, since. Mq.: mea, for. 4. An individual; tagata mea, tagata mee, an individual. Mgv.: mea, an individual, such a one. Mq., Ta.: mea, such a one. 5. Necessary, urgent; e mea ka, must needs be, necessary; e mea, urgent. 6. Manners, customs. 7. Mgv.: ako-mea, a red fish. 8. Ta.: mea, to do. Mq.: mea, id. Sa.: mea, id. Mao.: mea, id. Churchill. 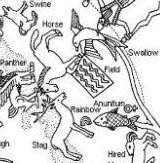
|
| December solstice |
| 8 |
South Dipper |
φ Sagittarii (?) |
Unicorn |
(284.0) |
Dec 30 (364) |
| 9 |
Ox / Herd Boy |
β Capricornii (Dabih) |
Buffalo |
(308.0) |
Jan 23 (388) |
| 10 |
Girl |
ε Aquarii (Albali) |
Bat |
(314.8) |
Jan 29 (394) |
| 11 |
Emptiness |
β Aquarii (Sadalsud) |
Rat |
(325.9) |
Feb 9 (405) |
| 12 |
Rooftop |
α Aquarii (Sadalmelik) |
Swallow |
(334.6) |
Feb 18 (414) |
| 13 |
House |
α Pegasi (Markab) |
Pig |
(349.5) |
Mar 5 (429) |
... On Easter Island it was the sooty tern, the sea swallow, manu tara, who arrived on wings with spring - like the bird sent out by Noah:
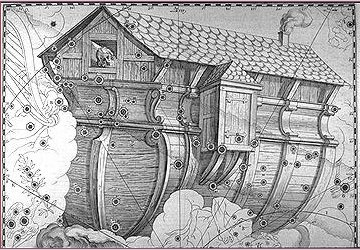
Swallows are swallowing insects (the souls of the unborn) and their return in spring should mean the return of the spirits to Mother Nature. ... Now birds and fishes are born under the sign of the Yin, but they belong to the Yang. This is why birds and fishes both lay eggs. Fishes swim in the waters, birds fly among the clouds. But in winter, the swallows and starlings go down into the sea and change into mussels ...

One of these rainbows obviously could have referred to the time when the Sea Beast opened his mouth wide at Menkar (α Ceti), to let his red gills become visible, and the other one should be at the opposite side of the year, at Libra. 304 (October 31) - 49 (February 18) = 255 (= 471 - 216 = 355 - 100).

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| ki te ariki - e ka hua ra tona rima |
koia kua iri i ruga o te rima - e o to vaha mea |
manu moe ra |
ki to mata |
e nuku mata |
hoea |
| → 16 |
Cb1-17 |
→ 4 * 29½ |
Cb1-19 |
Cb1-20 (412) |
→ 14 * 29½ |
| INVISIBLY CLOSE TO THE SUN NORTH OF THE EQUATOR: |
| KE KWAN (Cavalry Officer) = β Lupi (226.3), KE KWAN = κ Centauri (226.4), ZUBEN ELAKRIBI = δ Librae (226.8), π¹ Oct. (226.9) |
ω Bootis (227.2), NEKKAR = β Bootis (227.3), σ Librae (227.5), π² Oct. (227.7),
NADLAT = ψ Bootis (227.8), π Lupi (227.9) |
15h (228.3)
ZUBEN HAKRABIM = ν Librae (228.3), λ Lupi (228.9) |
ω Oct. (229.3), ι Librae (229.6), κ Lupi (229.7), ζ Lupi (229.8) |
Al Zubānā-14b
χ Bootis (230.3), PRINCEPS = δ Bootis (230.6), ZUBEN ELSCHEMALI = β Librae (230.8) |
μ Lupi, γ Tr. Austr. (231.3), ο Librae (231.8) |
| 2 (80 + 226) |
3 (*227 → 3.14 |
4 |
5 (*229) |
6 |
7 |
| ºOct 29 |
30 |
31 (304) |
ºNov 1 |
2 |
3 (*227 → π) |
| 'Oct 6 |
7 (280 = 307 - 27) |
8 |
9 (*202) |
10 |
11 |
| "Equinox |
23 (307 - 41) |
"Sept 24 |
25 (*188) |
26 |
27 (270) |
| AUG 30 (306 - 64) |
31 (60 + 183) |
SEPT 1 (244) |
2 (*165) |
3 |
4 |
| 222 |
223 |
224 |
225 |
226 |
→ 3.14 |
 |
| CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON ON EASTER ISLAND: |
| ρ Arietis (43.0), GORGONEA SECUNDA = π Persei (43.5), ACAMAR (End of the Stream) = θ Eridani (43.6), ε Arietis (43.7), λ Ceti (43.9) |
MENKAR = α Ceti (44.7) |
3h (45.7)
GORGONEA TERTIA = ρ Persei (45.1), ALGOL = β Persei (45.9) |
ι Persei (46.1), MISAM = κ Persei (46.2), GORGONEA QUARTA = ω Persei (46.7), BOTEIN (Pair of Bellies) = δ Arietis (46.9) |
ζ Arietis (47.7) |
ZIBAL (Young Ostriches) = ζ Eridani (48.0), κ Ceti (48.9) |
| May 3 (123) |
4 |
5-5 (125) |
6 (*46) |
7 |
8 (128 = 64 + 64) |
| ºApril 29 |
30 |
ºMay 1 (121) |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| 'April 6 |
7 |
4-8 |
9 |
10 (100) |
11 (*21 = *48 - 27) |
| "March 23 |
3-24 |
JULIAN EQUINOX |
(85 = 126 - 41) |
27 |
28 (*7 = *48 - 41) |
| 2-28 (59 = 123 - 64) |
MARCH 1 (60) |
3-2 (61 = 126 - 65) |
3 |
4 |
MARCH 5 (64) |
| 39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
|
The first day in MARCH, where at the time of rongorongo the 'nose' (open jaw, vaha mea) of the Great Fish (α Ceti) rose heliacally, came 16 + 1 days after Sheratan, and at the time of Bharani this place was 3-24, the day before the Julian equinox.
At the time of Bharani the Demon star Algol was at the Julian equinox and at the time of Hyadum II the Mouth of the Sea Beast (Menkar) would have arrived in day 60 (MARCH 1). FEBRUARY 28 was day 31 + 28 = 59 corresponding to May 3 (123) - 64.
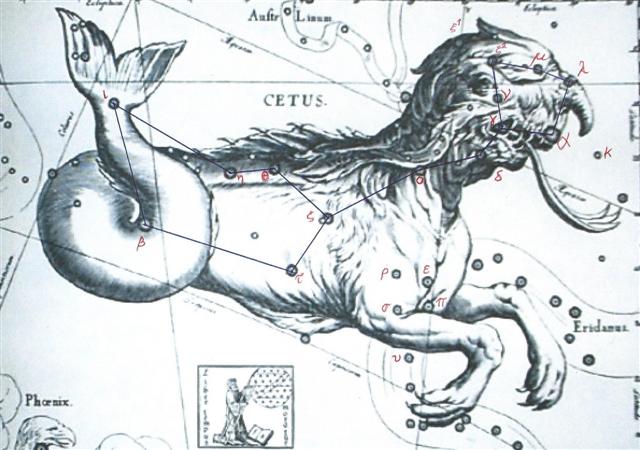
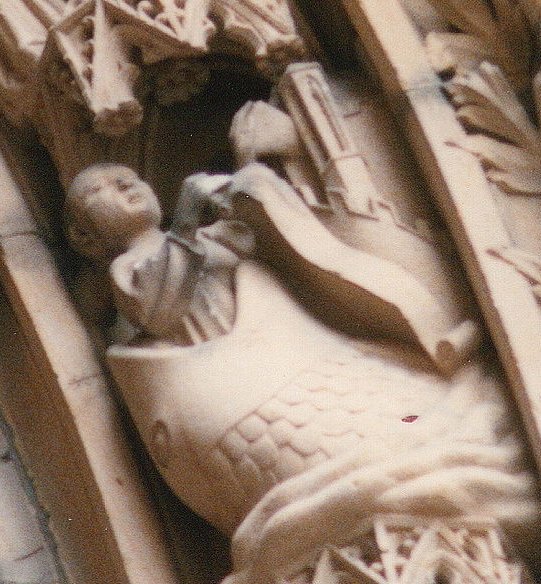
...Then the big Fish did swallow him, and he had done acts worthy of blame.
Had it not been that he (repented and) glorified Allah, He would certainly have remained inside the Fish till the Day of Resurrection. - Qur'an, chapter 37 (As-Saaffat), verse 139–144.
But We cast him forth on the naked shore in a state of sickness,
And We caused to grow, over him, a spreading plant of the gourd kind.
And We sent him (on a mission) to a hundred thousand (men) or more.
And they believed; so We permitted them to enjoy (their life) for a while. - Qur'an, chapter 37 (As-Saaffat), verse 145–148 ...

|
The languages in South America often have words quite similar to those in Polynesia, for instance Mawali ↔ ma-vari, Tini ↔ tini. ... The Gilbert Islanders are Polynesians, having emigrated, according to their traditions, from Upolu, Samoa, which they look upon as te buto (Maori pito), the Navel of the World. They never counted the nights of the Moon beyond the twentieth, so far as Grimble was able to ascertain, and in the vagueness of their lunar calendar bore no resemblance to their Micronesian neighbors of the Carolines ... One of the names for east, Makai-oa, was said to be the name of a far eastern land, not an island, which their navigators had visited in ancient times. Tradition called this great land 'the containing wall of the sea, beyond the eastern horizon, a continous land spreading over north, south, and middle, having a marvelous store of all sorts of food, high mountains and rivers'. It was also called Maia-wa (wa being 'space, distant'). This is a clear reference to ancient voyages to the American coast from which the Polynesians are thought to have introduced the sweet potato into the Pacific area. The similarity of Maia to Maya may be more than a coincidence ...... One of the parallels suggested by Heyerdahl is that between Polynesian pito 'navel'…and Quito, the very ancient Ecuadorian capital. In Hawaiian, the equator is defined as ke ala i ka piko a wakea 'the road to the navel (or birth-place) of Wakea (= Light)', where piko is the regular reflex of PPN *pito. Thus the possibility should exist to postulate kito, meaning 'navel', as a word of the pre-Incaic Andean language(s), to be used as a place-name later and therefore preserved today. The question remains open whether there could be - as in the Hawaiian example - any connection with the equator crossing the area. (The Incas' ancient capital, Kosco or Cuzco, meant 'navel' too.) ...
It would be rather natural for people living close to the equator to perceive a vernal equinox also in the west, at Libra.

|











