517. In Roman
times the summer solstice was when the Full Moon was
at χ Carinae in Argo Navis:
|
May 16 (136) |
51 |
July 7 (188 = 204 - 16) |
5 |
July 13 (194) |
21 |
August 4 (216) |
65 |
October 9 (282) |
|
*56 |
*108 |
*114 |
*136 |
*202 |
|
Te Maro 1 (152) |
He Anakena 23 (204) |
He Anakena 29 (204) |
Hora Iti 20 (232) |
Tangaroa Uri 25 (298) |
|
|
Rangi Meamea |
Oromanga |
Papa O Pea |
|
|
29 |
|
CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
|
Jan 12 |
13 (378) |
14 |
15 |
|
'Dec 16 (350) |
17 |
18 |
19 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
erua marama |
tagata noho i to
mea |
kua vaha |
|
Vaha.
Hollow; opening;
space between the
fingers (vaha
rima); door
cracks (vaha
papare).
Vahavaha, to
fight, to wrangle,
to argue with
abusive words.
Vanaga.1. Space,
before T; vaha
takitua,
perineum. PS Mgv.:
vaha, a
space, an open
place. Mq.: vaha,
separated, not
joined. Ta.: vaha,
an opening. Sa.:
vasa, space,
interval. To.:
vaha, vahaa,
id. Fu.: vasa,
vāsaà, id.
Niuē: vahā.
2. Muscle, tendon;
vahavaha, id.
Vahahora (vaha
1 - hora 2),
spring. Vahatoga
(vaha 1 -
toga 1), autumn.
3. Ta.: vahavaha,
to disdain, to
dislike. Ha.:
wahawaha, to
hate, to dislike.
Churchill. |
|
Cb4-17 (392 + 88 =
480) |
Cb4-18 (30 + 59 =
89) |
Cb4-19 |
Cb4-20 (91) |
|
ε Sagittae (297.1),
σ Aquilae (Ant.)
(297.4),
SHAM (Arrow) = α
Sagittae
(297.8)
*256.0 = *297.4 -
*41.4 |
β Sagittae (298.0),
χ Aquilae (298.3), ψ
Aquilae (298.8) |
υ Aquilae (299.1),
TARAZED
(Star-striking
Falcon) = γ Aquilae
(299.3), δ Sagittae
(299.6), π Aquilae
(299.9) |
Sravana-23 (Ear or
Three Footprints)
TYL =
ε
Draconis
(300.0),
ζ
Sagittae (300.1),
ALTAIR (Flying
Eagle) =
α
Aquilae
(300.3),
ο
Aquilae (300.5),
BEZEK =
η
Aquilae
(Ant.)
(300.8) |
 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
He Anakena 29 |
30 |
31 (212 = 196 +16) |
Hora Iti 1 |
|
July 13
ANA-TAHUA-VAHINE-O-TOA-TE-MANAVA-7
(Pillar for
elocution)
υ
Gemini (114.0),
MARKAB PUPPIS =
κ
Puppis
(114.7),
ο
Gemini (114.8),
PROCYON =
α
Canis Minoris
(114.9) |
14 (80 + 115 = 195)
α Monocerotis
(115.4), σ Gemini
(115.7)
*74.0 = *115.4 -
*41.4 |
15 (196)
Mash-mashu-arkū-11
(Eastern One of the
Twins)
κ Gemini (116.1),
POLLUX = β Gemini
(116.2), π Gemini
(116.9) |
16
AZMIDISKE = ξ Puppis
(117.4)
*76.0 = *117.4 -
*41.4 |
|
'June 16 |
17 (168 = 195 - 27) |
18 |
19 |
|
"June 2 |
3 (154 = 195 - 41) |
4 |
5 |
|
MAY 10 |
11 |
12 (132 = 196 - 64) |
13 |
|
DAY 114 |
115 → MERCURY |
116 (= 4 * 29) |
117 |
|
CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
|
Jan 16 (381 =
365 + 16) |
17 |
18 |
|
'Dec 20 (354 =
12 * 29½) |
Solstice |
22 |
 |
 |
 |
|
te moa |
tagata - te
maro |
te tagata |
|
Cb4-21 (392 + 92
= 484) |
Cb4-22 |
Cb4-23 |
|
ι Sagittarii (301.2),
TEREBELLUM = ω
Sagittarii, ξ Aquilae (301.3), ALSHAIN (Falcon) = β Aquilae
(301.6), φ
Aquilae (301.8) |
ε Pavonis, θ
Sagittarii
(302.3), γ
Sagittae
(302.5), μ
Pavonis (302.7) |
τ Aquilae
(303.8) |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
Hora Iti
2 |
3 |
4 (216 = 200 +
16) |
|
July 17
φ Gemini (118.4)
*77.0 = *118.4 -
*41.4 |
18
DRUS (Hard) = χ
Carinae
(119.9) |
19 (200)
ω Cancri (120.2)
*79.0 = *120 -
*41 |
|
Drus → L.
dūrus = hard
(as oak). This
star was at the
root of the mast
of the Ship:
 |
|
'June 20 |
Solstice |
22 (173 = 200 -
27) |
|
"June 6 |
7 |
8 (159 = 200 -
41) |
|
MAY 14 |
15 |
16 (136 = 200 -
64) |
|
DAY 118 (= 4 *
29½) |
119 |
120 (= 4 * 30) |
|
Egyptian
sticks |
 |
Phoenician
taw |
 |
Greek chi |
Χ (χ) |
|
Greek tau |
Τ (τ) |
|
In Plato's
Timaeus,
it is
explained
that the two
bands that
form the
soul of the
world cross
each other
like the
letter Χ.

Roman XII =
12 → XIII =
13, with the
Nose in
between -
and later,
after the
Mouth, the
cycle would
begin anew
(I).
Chi or X is
often used
to
abbreviate
the name
Christ, as
in the
holiday
Christmas
(Xmas). When
fused within
a single
typespace
with the
Greek letter
Rho, it is
called the
labarum and
used to
represent
the person
of Jesus
Christ.
(Wikipedia)

... tau
is the 19th
letter of
the Greek
alphabet. In
the system
of Greek
numerals it
has a value
of 300 ...
Taw
is believed
to be
derived from
the Egyptian
hieroglyph
meaning
'mark' ...
Taw,
Tav
or Taf
is the
twenty-second
and last
letter in
many Semitic
abjads ...
In gematria
Tav
represents
the number
400, the
largest
single
number that
can be
represented
without
using the
Sophit forms
...
'From
Aleph to
Taf'
describes
something
from
beginning to
end; the
Hebrew
equivalent
of the
English
'From A to
Z' ...
Tav
is the last
letter of
the Hebrew
word emet,
which means
truth. The
midrash
explains
that emet
is made up
of the
first,
middle, and
last letters
of the
Hebrew
alphabet (Aleph,
Mem,
and Tav...).
Sheqer
(falsehood),
on the other
hand, is
made up of
the 19th,
20th, and
21st (and
penultimate)
letters.
Thus, truth
is
all-encompassing,
while
falsehood is
narrow and
deceiving.
In Jewish
mythology it
was the word
emet
that was
carved into
the head of
the Golem
which
ultimately
gave it
life. But
when the
letter
'aleph' was
erased from
the
Golem's
forehead,
what was
left was 'met'
- dead. And
so the
Golem
died ...
(Wikipedia)
 |
This was
where one half of the
year ended and another began, where the
male Sun (who up to now had risen
higher and higher)
'changed sex' and began
to gravitate downwards,
pregnate with a new
generation.
... Atea took a
third husband,
Fa'a-hotu, Make
Fruitful. Then occurred
a curious event. Whether
Atea had wearied
of bringing forth
offspring we are not
told, but certain it is
that Atea and her
husband Fa'a-hotu
exchanged sexes. Then
the eyes of Atea
glanced down at those of
his wife Hotu and
they begat Ru. It
was this Ru who
explored the whole earth
and divided it into
north, south, east, and
west ...
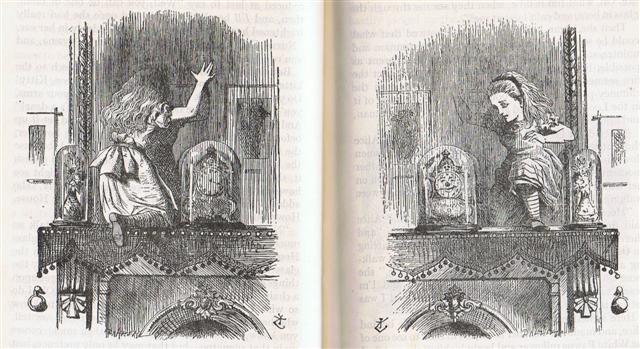
On side a
of the C tablet the sign
of crossing over has
been clearly stated, we
should remember:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
te
maitaki |
te
henua |
kua
haga te
mea ke |
manu
puoko i
tona ahi |
kua
heu te
huki |
|
Heu.
Offspring
of
parents
from two
different
tribes,
person
of
mixed
descent,
e.g.
father
Miru,
mother
Tupahotu.
Heuheu,
body
hair
(except
genitals
and
armpits).
Vanaga.
1.
Heheu;
ivi
heheu,
the
cachalot,
bone
needle;
hakaheu,
spade,
to
shovel,
to grub
up, to
scratch
the
ground,
to
labor;
rava
hakaheu,
laborious,
toilsome.
2.
Hakaheu,
affair.
Churchill.
M.
Heu,
to
separate,
to pull
asunder;
the
eaves of
a house;
heu,
a single
hair;
hau.
to hew;
heru,
to comb;
huru,
hair on
the
body;
down;
feathers;
maheu,
scattered;
maheuheu,
shrubs;
mahuru,
scrub;
heuea,
to be
separated.
Text
Centre.
Nonoma
ran, he
quickly
went to
Te
Hikinga
Heru
(a
ravine
in the
side of
the
crater
Rano
Kau)
and
looked
around.
There he
saw the
double
canoe
way out
near the
(offshore)
islets,
and the
two
(hulls
of the
canoe)
were
lashed
together. |
|
Ca5-12 |
Ca5-13
(472 / 4
= 118) |
Ca5-14
(78 +
41) |
Ca5-15
(360 /
3) |
Ca5-16
(11 *
11) |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL
MOON: |
|
Hora Iti
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 (216 =
200 +
16) |
5 |
|
July 16
AZMIDISKE
= ξ
Puppis
(117.4)
*76.0 =
*117.4 -
*41.4 |
17
φ Gemini
(118.4)
*77.0 =
*118.4 -
*41.4 |
18
DRUS = χ
Carinae
(119.9) |
19 (200)
ω Cancri
(120.2) |
20
8h
(121.7)
χ Gemini
(121.0),
NAOS = ζ
Puppis
(121.3) |

The Sun
was
placed
at the
Stern →
star as
in
starboard
for the
right
side of
the
ship,
the
place
for
women. X
was
formed
by the
timbers
which
had held
the Sail
(Ra)
in its
proper
place,
the
structure
of
which,
however,
the
collision
with the
Oak had
broken
to
pieces.
Drus →
L. dūrus
= hard
(as oak).
... The
seventh
tree is
the oak,
the tree
of Zeus,
Juppiter,
Hercules,
The
Dagda
(the
chief of
the
elder
Irish
gods),
Thor,
and all
the
other
Thundergods,
Jehovah
in so
far as
he was
'El',
and
Allah.
The
royalty
of the
oak-tree
needs no
enlarging
upon:
most
people
are
familiar
with the
argument
of Sir
James
Frazer's
Golden
Bough,
which
concerns
the
human
sacrifice
of the
oak-king
of Nemi
on
Midsummer
Day. The
fuel of
the
midsummer
fires is
always
oak, the
fire of
Vesta at
Rome was
fed with
oak, and
the
need-fire
is
always
kindled
in an
oak-log.
When
Gwion
writes
in the
Câd
Goddeu,
'Stout
Guardian
of the
door,
His name
in every
tongue',
he is
saying
that
doors
are
customarily
made of
oak as
the
strongest
and
toughest
wood and
that
'Duir',
the
Beth-Luis-Nion
name for
'Oak',
means
'door'
in many
European
languages
including
Old
Goidelic
dorus,
Latin
foris,
Greek
thura,
and
German
tür, all
derived
from the
Sanskrit
Dwr, and
that
Daleth,
the
Hebrew
letter
D, means
'Door' -
the 'l'
being
originally
an 'r'.
Midsummer
is the
flowering
season
of the
oak,
which is
the tree
of
endurance
and
triumph,
and like
the ash
is said
to
'court
the
lightning
flash'.
Its
roots
are
believed
to
extend
as deep
underground
as its
branches
rise in
the air
- Virgil
mentions
this -
which
makes it
emblematic
of a god
whose
law runs
both in
Heaven
and in
the
Underworld
... The
month,
which
takes
its name
from
Juppiter
the
oak-god,
begins
on June
10th and
ends of
July
7th.
Midway
comes
St.
John's
Day,
June
24th,
the day
on which
the
oak-king
was
sacrificially
burned
alive.
The
Celtic
year was
divided
into two
halves
with the
second
half
beginning
in July,
apparently
after a
seven-day
wake, or
funeral
feast,
in the
oak-king's
honour
...
...
Robur
Carolinum,
Charles'
Oak,
the
Quercia
of Italy
and the
Karlseiche
of
Germany,
was
formally
published
by
Halley
in 1679
in
commemoration
of the
Royal
Oak of
his
patron,
Charles
II, in
which
the king
had lain
hidden
for
twenty-four
hours
after
his
defeat
by
Cromwell
in the
battle
of
Worcester,
on the
3rd of
September
1651
...
Raa.
Sun;
day;
i te raá
nei,
today;
raá
îka,
good day
for
fishing.
Vanaga.
1. Sun.
2. Day.
3. Time.
4. Name
of
sub-tribe.
Fischer.
Te manu
i te raá
= comet.
Barthel.
'... The
substitution
of the
sun for
the
sail,
both of
which
are
called
ra
or
raa
in
Polynesia,
is a
remarkable
feature
in
Easter
Island
art ...
'
Heyerdahl
3.
1. The
sun;
raa
ea mai,
raa
puneki,
sunrise;
raa
tini,
raa
toa,
noon. P
Mgv.,
Ta.:
ra,
the sun.
Mq.:
a,
id. 2.
Day,
date;
a raa
nei a,
to-day,
now;
raa i
mua,
day
before.
P Mgv.,
Ta.:
ra,
a day.
Mq.:
a,
id.
Churchill.
'... The
chief
thus
makes
his
appearance
at
Lakeba
from the
sea, as
a
stranger
to the
land.
Disembarking
at the
capital
village
of
Tubou,
he is
led
first to
the
chiefly
house (vale
levu)
and next
day to
the
central
ceremonial
ground (raaraa)
of the
island
...'
(Islands
of
History)
Ta.:
toraaraa,
to raise
up.
Churchill
2.
LA,
s.
Haw.,
sun,
light,
day. N.
Zeal.,
ra,
sun,
day.
Marqu.,
a,
id.
Sam.,
la,
id.
Deriv.:
Haw.,
lae,
be
light,
clear,
shining;
lai,
shining
as the
surface
of the
sea,
calm,
still;
laelae
and
lailai,
intens.
Sam.,
lelei,
something
very
good;
lala,
to
shine;
lalangi,
to
broil.
Fiji.,
rai,
to see,
appear;
rai-rai,
a seer,
a
prophet.
Teor.,
la,
sun. Aru
Islands,
lara,
id.;
rarie,
bright,
shining.
Amblaw.,
laei,
sun,
day.
Irish,
la,
lae,
day.
Laghmani
(Cabul),
la'e,
day.
Sanskr.,
laj,
lanj,
to
appear,
shine;
râj,
to
shine.
Ved., to
govern;
s.
a king.
If, as
Benfey
intimates,
the
Sanskrit
verb
bhrâj,
to
shine,
to beam,
is
'probably
abhi-râj',
an
already
Vedic
contraction,
then the
Polynesian
root-word
al
and
lae
will
reappear
in
several
of the
West
Aryan
dialects.
Lat.,
flagrare,
flamma,
flamen.
Greek,
φλεγω,
φλοξ.
A.-Sax.,
blac,
blæcan,
&c.
Probably
the
universal
Polynesian
lani,
langi,
rangi,
ra'i,
lanits
(Malg.)
designating
the
upper
air,
sky,
heaven,
and an
epithet
of
chiefs,
refers
itself
to the
same
original
la,
lai,
lanj,
referred
to
above,
to which
also be
referred:
Welsh,
glan,
clean
pure,
bright,
holy.
Sax.
clæne,
clean,
pure.
Swed.,
ren,
clean.
pure;
grann
(?),
fine,
elegant.
It may
be noted
in
connection
with
this
word,
either
as a
coincidence
or as an
instance
of
ancient
connection,
that in
the old
Chaldean
the name
of the
sun and
of the
Supreme
Deity
was
Ra,
and that
in Egypt
the sun
was also
named
Ra.
LA²,
s. Haw.,
Sam.,
Tong.,
ra.
N.
Zeal.,
the sail
of a
canoe;
abbreviated
from, or
itself
an older
form of,
the
Fiji.
laca,
a sail,
also the
mats
from
which
the
sails
were
made.
Sunda.,
Mal.,
layar,
sail.
Malg.,
laï,
sail,
tent,
flag.
Sanskr.,
lâta
(Pictet),
a cloth;
latâ
(Benfey),
a
creeper,
a plant;
lak-taka,
a rag.
As mats
and
clothing
in
primitive
times
were
made of
bark or
flexible
plants,
the
connection
between
the
Sanskrit
latâ
and
Polynesian
laca,
la,
becomes
intelligible.
Armen.,
lôtig,
a
mantle.
Lat.,
lodix,
a
blanket.
Irish,
lothar,
clothing.
(Fornander)
 |
The Egyptian
X could
have
been the same idea
expressed as a
star
configuration,
where the right armpit
of Orion (at
Betelgeuze) was
connected with
Naos in Argo
Navis (similar
to the change
from male to
female of
Fa'a-hotu,
Make Fruitful)
and where the
opposite line up
from
α
Columbae reached
to Procyon in
Canis Minor
(similar to the
change from
female to male
of
Atea):
.jpg)
 |
 |
|
hura |
Ca5-14
|
| Hura. 1. To fish with a small funnel-shaped net tied to the end of a pole. This fishing is done from the shore; fishing with the same net, but swimming, is called tukutuku. 2. To be active, to get moving when working: ka hura, ka aga! come on, get moving! to work! 3. Tagata gutu hura, a flatterer, a flirt, a funny person, a witty person. Hurahura, to dance, to
swing. Vanaga. 1. Sling. In his brilliant study of the distribution of the sling in the Pacific tracts, Captain Friederici makes this note (Beiträge zur Völker- und Sprachenkunde von Deutsch-Neuguinea, page 115b): 'Such, though somewhat modified, is the case in Rapanui, Easter Island. The testimony of all the reporters who have had dealings with these people is unanimous that stones of two to three pounds weight, frequently sharp chunks of obsidian, were thrown by the hand; no one mentions the use of slings. Yet Roussel includes this weapon in his vocabulary and calls it hura. In my opinion this word can be derived only from the Mangareva verb kohura, to throw a stone or a lance. So far as we know Rapanui has received its population in part by way of Mangareva.' To this note should be added the citation of kirikiri ueue as exhibiting this particular use of ueue in which the general sense is the transitive shake. 2. Fife, whistle, drum, trumpet, to play; hurahura, whistle. P Mq.: hurahura, dance, divertissement, to skip. Ta.: hura, to leap for joy. Pau.: hura-viru, well disposed. Churchill. H. Hula, a swelling, a protuberance under the arm or on the thigh. Churchill 2. |

|













.jpg)