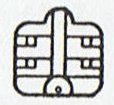
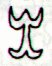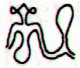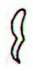506. Whereas the Mayas had internal
signs in their glyphs in order to express meanings
the rongorongo glyphs as a rule had their signs
outside with no signs inside:
... Only the outline of an object or
a 'person' should be drawn according
to the rongorongo rules of writing.
In this respect the rongorongo
system evidently stands in
opposition to the Mayan glyphs,
where the inside is very detailed.
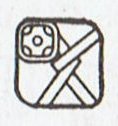
A few
random examples:
|
Mayan glyphs |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Rongorongo glyphs |
 |
 |
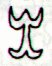 |
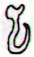 |
When this rule
was broken it was in order to
draw attention, for instance in
Cb5-14 and Cb5-16 which flanked
Acubens at the Full Moon:
|
CLOSE TO THE
SUN: |
|
Jan 31 |
Febr 1 (32) |
2 |
3 |
4 (*320) |
5 |
|
'Jan 4 |
5 (370 = 740 /
2) |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
 |
 |
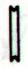 |
 |
 |
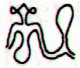 |
|
Cb5-13 (107) |
Cb5-14 (392 +
108) |
Cb5-15 (365 +
136) |
Cb5-16 |
Cb5-17 (503) |
Cb5-18 (584 -
80) |
|
CLOSE TO THE
FULL MOON: |
|
Aug 1
γ Pyxidis
(133.6) |
2 (214 = 32 +
182)
ζ
Hydrae (134.1),
ρ
Cancri (134.2),
ζ
Oct.
(134.3), ο
Cancri (134.6),
δ Pyxidis
(134.9) |
3
ACUBENS = α
Cancri,
TALITHA BOREALIS
= ι Ursae
Majoris
(135.0), σ
Cancri (135.2),
ρ Ursa Majoris
(135.6) |
4
ν Cancri
(136.0),
TALITHA
AUSTRALIS = κ
Ursae Majoris
(136.1), ω
Hydrae (136.8) |
5
9h (137.0)
σš Ursa Majoris
(137.0), κ
Cancri (137.3),
τ Cancri
(137.4),
ALSUHAIL (al
Wazn, of the
Weight) = λ
Velorum
(137.5), σ˛ Ursa
Majoris (137.6),
τ Ursa Majoris
(137.7), ξ
Cancri (137.8)
*96.0 = *137.4 -
*41.4 |
6 (584 → Venus)
κ Pyxidis
(138.0), ε
Pyxidis (138.5) |
|
'July 5 |
6 (*107) |
7 |
8 |
9 (190) |
10 |
|
133 |
134 |
135 |
136 |
137 |
138 |
The vertical line
inside the maitaki type
of glyph may have signified
'the old year was completed
and a new one was in front'.
Here it marked the Sun at
February 1 (32) with the Full
Moon in August 2 (214).
The Full Moon at
Rogo, in right ascension day
500, with a 'knee' (atiga)
in front (in Cb5-16),
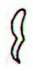
... Atiga.
Angle,
corner. Mgv.: hatiga, the
corner of a house; hatiga,
hatihatiga, the joints or
articulation of a limb. Mq.:
fatina, hatika,
joint, articulation, link. Ta.:
fatiraa, articulation ...
can be
compared with the Full Moon at
tagata in day 500, where
the 'broken Bird Man arm' in front may
have indicated a 'full stop':
... During his descent the
ancestor still possessed the
quality of a water spirit, and
his body, though preserving its
human appearance, owing to its
being that of a regenerated man,
was equipped with four flexible
limbs like serpents after the
pattern of the arms of the Great
Nummo. The ground was rapidly
approaching. The ancestor was
still standing, his arms in
front of him and the hammer and
anvil hanging across his limbs.
The shock of his final impact on
the earth when he came to the
end of the rainbow, scattered in
a cloud of dust the animals,
vegetables and men disposed on
the steps. When calm was
restored, the smith was still on
the roof, standing erect facing
towards the north, his tools
still in the same position. But
in the shock of landing the
hammer and the anvil had broken
his arms and legs at the level
of elbows and knees, which he
did not have before. He thus
acquired the joints proper to
the new human form, which was to
spread over the earth and to
devote itself to toil
...
|
CLOSE TO THE SUN: |
|
Nov 13 |
14 |
15 |
16 (320) |
|
'Oct 17 (290) |
18 |
19 |
20 |
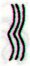 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Cb2-4 (420 = 740 - 320) |
Cb2-5 (392 + 29) |
Cb2-6 (30 = 108 - 78) |
Cb2-7 |
|
CLOSE TO THE FULL MOON: |
|
May 14
δ Persei (54.7) |
15 (500 = 365 + 135)
Al Thurayya-27 (Many Little
Ones) /
Krittikā-3 (Nurses of
Kārttikeya) /
TAU-ONO (Six Stones)
ATIKS =
ο
Persei,
RANA (Frog) =
δ
Eridani
(55.1),
CELAENO (16 Tauri), ELECTRA
(17), TAYGETA (19),
ν
Persei (55.3),
MAIA (20), ASTEROPE (21),
MEROPE (23)
(55.6) |
16 (136)
Hairy Head-18 (Cockerel) /
Temennu-3 (Foundation Stone)
ALCYONE
(56.1),
PLEIONE (28 Tauri), ATLAS
(27 Tauri)
(56.3) |
17
MENKHIB (Next to the
Pleiades =
ζ
Persei
(57.6)
PORRIMA (γ Virginis) |
|
'April 17 (80 + 27) |
18 (108 = 135 - 27) |
19 |
20 |
|
BISSEXTUM (54 - 55) |
56 (8 WEEKS) |
57 (= 137 - 64 - 16) |
|
... The leap day was
introduced as part of the
Julian reform. The day
following the Terminalia
(February 23) was doubled,
forming the 'bis sextum
- literally 'double sixth',
since February 24 was 'the
sixth day before the Kalends
of March' using Roman
inclusive counting (March 1
was the 'first day').
Although exceptions exist,
the first day of the bis
sextum (February 24) was
usually regarded as the
intercalated or 'bissextile'
day since the third century.
February 29 came to be
regarded as the leap day
when the Roman system of
numbering days was replaced
by sequential numbering in
the late Middle Ages ... |
The South
Pole star, Dramasa, was
at right ascension day
*320 in February 4 and
the 'broad daylight
band' going down on the
belly of Rogo in
Cb5-16 was crossed over
by a thin line going up.

|
Egyptian sticks |
 |
Phoenician
taw |
 |
Greek chi |
Χ (χ) |
|
Greek tau |
Τ (τ) |
|
In Plato's
Timaeus, it
is explained
that the two
bands that form
the soul of the
world cross each
other like the
letter Χ.

Roman XII = 12 →
XIII = 13, with
the Nose in
between - and
later, after the
Mouth, the cycle
would begin anew
(I).
Chi or X is
often used to
abbreviate the
name Christ, as
in the holiday
Christmas
(Xmas). When
fused within a
single typespace
with the Greek
letter Rho, it
is called the
labarum and used
to represent the
person of Jesus
Christ.
(Wikipedia)

... tau
is the 19th
letter of the
Greek alphabet.
In the system of
Greek numerals
it has a value
of 300 ...
Taw is
believed to be
derived from the
Egyptian
hieroglyph
meaning 'mark'
...
Taw,
Tav or
Taf is the
twenty-second
and last letter
in many Semitic
abjads ... In
gematria Tav
represents the
number 400, the
largest single
number that can
be represented
without using
the Sophit forms
...
'From Aleph
to Taf'
describes
something from
beginning to
end; the Hebrew
equivalent of
the English
'From A to Z'
...
Tav is
the last letter
of the Hebrew
word emet,
which means
truth. The
midrash explains
that emet
is made up of
the first,
middle, and last
letters of the
Hebrew alphabet
(Aleph,
Mem, and
Tav...).
Sheqer
(falsehood), on
the other hand,
is made up of
the 19th, 20th,
and 21st (and
penultimate)
letters.
Thus, truth is
all-encompassing,
while falsehood
is narrow and
deceiving. In
Jewish mythology
it was the word
emet that
was carved into
the head of the
Golem
which ultimately
gave it life.
But when the
letter 'aleph'
was erased from
the Golem's
forehead, what
was left was 'met'
- dead. And so
the Golem
died ...
(Wikipedia)

|
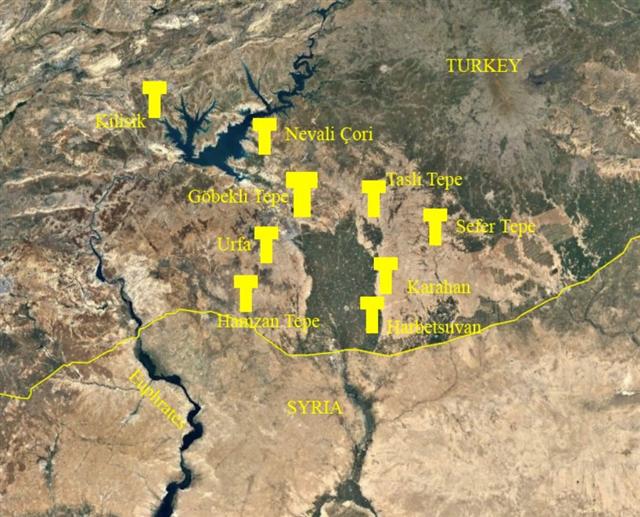
In the so
far most ancient
megalithic structures
discovered, viz. those
surrounding Göbekli Tepe
(ca 8000 BC), there
are prominent T-formed
monuments:

|
Tau.Year
(ta'u),
he-hoa ite
ta'u, to
confess to a
crime committed
long ago, by
publishing it in
the form of a
kohau motu mo
rogorogo (rongorongo
tablet). Vanaga.
1.To hang (tau),
to perch (said
of chickens on
tree branches at
night); rock on
the coast,
taller than
others so that
something can be
deposited on it
without fear of
seeing it washed
away by the
waves;
hakarere i ruga
i te tau, to
place something
on such a rock;
tau kupega,
rope from
which is hung
the oval net
used in ature
fishing. 2.
Pretty, lovely;
ka-tau!
how pretty!
Vanaga. 1. Year,
season, epoch,
age. P Pau.:
tau, a
season, period.
Mgv.: tau,
a year, the
season of
breadfruit. Mq.:
tau,
year. Ta.:
tau, season,
time. 2. Fit,
worthy,
deserving,
opportune;
tae tau,
impolite,
ill-bred,
unseemly; pei
ra tau,
system. PS Mgv.:
tau, fit,
suitable,
proper. Sa.:
tau, right,
proper. To.:
tau,
becoming, fit,
proper,
agreeable. Fu.:
tau, fit,
proper. 3. To
perch. P Pau.:
tau, a
perch for a
bird. Mgv.:
tau, to
mount on a
person's back.
Mq.: tau,
to perch, to
rest on. Ta.:
tau, to
perch, to alight
on. 4. To hang;
hakatau,
necklace;
hakatautau,
to append. P
Pau.:
fakatautau,
to hang up. Mq.:
tautau,
id. Ta.:
faatautau,
id. 5. Anchor;
kona tau,
anchorage, port.
P Mq.: katau,
anchor. Ta.:
tau, id. 6.
To fight;
hakatau,
challenge, to
defy, to incite;
hakatautau,
to rival. P Ma.:
whakatatau,
to quarrel.
Churchill. Pau.:
fakatau,
indolent. Ta.:
faatau,
id.
Fakatautau,
to delay, to
defer. Ta.:
haatautau,
id. Churchill.
The Malay word
for 'year' is
taun or
tahun. In
all Polynesian
dialects the
primary sense is
'a season', 'a
period of time'.
In the Samoan
group tau
or tausanga,
besides the
primary sense of
season, has the
definite meaning
of 'a period of
six months', and
conventionally
that of 'a
year', as on the
island of Tonga.
Here the word
has the further
sense of 'the
produce of the
year', and
derivatively 'a
year'. In the
Society group it
simply means
'season'. In the
Hawaiian group,
when not applied
to the summer
season, the word
keeps its
original sense
of 'an
indefinite
period of time',
'a life-time, an
age', and is
never applied to
the year: its
duration may be
more or less
than a year,
according to
circumstances.
So far our
authority
(Fornander, I,
124; cp. 119).
It seems however
to be
questionable
whether the
original sense
is not the
concrete
'produce of the
seasons', rather
than the
abstract 'period
of time'. It is
significant that
on the Society
Islands the
bread-fruit
season is called
te tau,
and the names of
the other two
seasons, te
tau miti rahi
and te tau
poai, are
formed by adding
to this name.
Nilsson. |
|
Kau,
v. Haw., to
hang up,
suspend, to tie
or gird on, to
put or place a
thing, to fall
upon, to put on,
as a burden, to
set or fix, as
boundaries of a
land, or a
decree, to
promulgate, as a
law; in a neuter
sense, to light
down, as a bird,
as a spiritual
influence;
adj. a
setting of the
sun, a resting,
a roost for
fowls; kau-a,
to hesitate, be
in doubt,
suspense, to beg
off; kau-o,
to draw, as a
load; morally,
to endure, to
incline to, to
pray for some
special
blessing;
kau-oha, a
dying charge,
bequest,
covenant,
commission,
command;
kau-kai, to
wait for an
event, to
expect;
kau-kau, to
take counsel, to
resolve, to
chide, to
reprove, to
explain, make
clear; kau-la,
a rope, cord,
tendon, a
prophet, a seer;
kau-la-i,
to hang up, put
up in the sun;
kau-lana,
fame, report,
renown;
ma-kau, be
ready, prepared;
akau, the
right hand
(dexter), to be
right, to the
north, north. In
the Southern
dialects we
find: Tong.,
tau, to
hang, overhang,
impend, extend
to, fit, be
suitable;
ma-tau, the
right hand;
ta-tau,
equal, like
(balanced);
tau-la, a
cable;
tau-ranga,
an anchoring
place. Sam.,
tau, to rest
on, light on,
fall on;
faa-ta-tau,
to compare;
tau, what is
proper and
right;
tau-au, to
tend towards,
either decline
or increase;
tau-me,
stretch up the
hand and not
reach, to desire
and not obtain;
tau-i,
reward, payment,
revenge;
tau-la, an
anchor, to
anchor, the
priest of a god;
tau-la-i,
to hang up to; tau-langa,
a sacred
offering, an
anchorage;
tau-lalo,
let the hands
drop in
fighting, be
conquered;
tau-tau, to
hang, hang up;
ma-tau,
right-hand side,
an axe;
faa-tau,
equally, alike;
v. to buy,
barter, sell;
faa-tau-oa,
a merchant.
Marqu., tau,
to carry on the
back; tau-tau,
suspended, hung
up; ta-tau,
to count,
reckon; tau-a,
a rope, a
priest; a-tau,
ka-tau,
an anchor. N.
Zeal., tau,
besided previous
meanings, to
meet; ma-tau,
expert,
dexterous,
shrewd. Tah.,
tau, to hang
upon, an anchor;
tau-ai,
to hang up,
spread out, as
clothes to dry;
tau-i,
price, cost, to
exchange, buy;
tau-ra,
cord, a troop,
crowd, be
inspired, a
prophet;
tau-e, a
swing, see-saw;
tau-piri,
tail for a kite;
tau-mata,
a visor, a mask;
tau-mi, a
breastplate,
plastron;
a-tau, right
hand, to the
right. Fiji.,
tau, to
fall, as of
rain, to fall
upon; tau-ca,
to place or put
down a thing;
tau-nga, a
swinging shelf.
Malg.,
mang-hatau,
mana-tao,
to place, put.
(Fornander) |
|