474. Winter and nighttime were like the black new moon, a time for sleeping. To wake up again meant opening the eyes (<) and this in turn suggested the 'break of dawn' (<): ... The Polynesians mingle the time-indications based on the position of the sun with others which are derived from the life of men and nature. We are told that the Hawaiian day was divided into three general parts, 1, breaking the shadows, 2, the plain, full day, 3, the decline of the day ... The lapse of night, however, was noted by five stations: 1, about sunset; 2, between sunset and midnight; 3, midnight; 4, between midnight and sunrise; 5, sunrise. A native Hawaiian [Malo] writes: - 'When the stars fade away and disappear, it is ao, daylight; when the sun rises, day has come, la [ra]; when the sun becomes warm, morning is past; when the sun is directly overhead it is awahea, noon; when the sun inclines to the west in the afternoon, the expression is wa ani ka la. After that come evening, ahi-ahi (ahi, fire), and then sunset, napoo ka la, and then comes po, the night, and the stars shine out ... In Tahiti the day has six divisions which are fairly accurately determined by the height of the sun. Names are given for midnight, midnight to daybreak, daybreak, sunrise, the time when the sun begins to be hot, when it reaches the meridian, evening before sunset, the time after sunset. For the Marquesas are given: - daybreak, twilight, dawn, ('the day or the red sky, the fleeing night'), broad day - bright day from full morning to about ten o'clock -, noon ('belly of the sun'), afternoon ('back part of the sun'), evening ('fire-fire', the same expression as in Hawaii, i.e. the time to light the fires on the mountains or the kitchen fire for supper) ... ... What happens after (or happened, or will happen sometime, for this myth is written in the future tense), is told in the Völuspa, but it is also amplified in Snorri's Gylfaginning (53), a tale of a strange encounter of King Gylfi with the Aesir themselves, disguised as men, who do not reveal their identity but are willing to answer questions: 'What happens when the whole world has burned up, the gods are dead, and all of mankind is gone? You have said earlier, that each human being would go on living in this or that world.' So it is, goes the answer, there are several worlds for the good and the bad. Then Gylfi asks: 'Shall any gods be alive, and shall there be something of earth and heaven?' And the answer is: 'The earth rises up from the sea again, and is green and beautiful and things grow without sowing. Vidar and Vali are alive, for neither the sea nor the flames of Surt have hurt them and they dwell on the Eddyfield, where once stood Asgard. There come also the sons of Thor, Modi and Magni, and bring along his hammer. There come also Balder and Hoder from the other world. All sit down and converse together. They rehearse their runes and talk of events of old days. Then they find in the grass the golden tablets that the Aesir once played with. Two children of men will also be found safe from the great flames of Surt. Their names, Lif and Lifthrasir, and they feed on the morning dew and from this human pair will come a great population which will fill the earth. And strange to say, the sun, before being devoured by Fenrir, will have borne a daughter, no less beautiful and going the same ways as her mother.' Then, all at once, concludes Snorri's tale wryly, a thunderous cracking was heard from all sides, and when the King looked again, he found himself on the open plain and the great hall had vanished ... This open plain should correspond to that part of the plane of the ecliptic (the Eddyfield) which was outside Mother Earth, I think:
... The Euripus, which has already come up in the Phaedo, was really a channel between Euboea and the mainland, in which the conflict of the tides reverses the current as much as seven times a day, with ensuing dangerous eddies - actually a case of standing waves rather than a true whirl. We meet the name again at a rather unexpected place, in the Roman circus or hippodrome, as we know from J. Laurentius Lydus (De Mensibus I.12), who states that the center of the circus was called Euripos; that in the middle of the stadium was a pyramid, belonging to the Sun; that by the Sun's pyramid were three altars, of Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, and below the pyramid, altars of Venus, Mercury, and the Moon, and that there were not more than seven circuits (kykloi) around the pyramid, because the planets were only seven. (See also F. M. Cornford's chapter on the origin of the Olympic games in J. Harrison's Themis (1962), p. 228; G. Higgins' Anacalypsis (1927), vol. 2., pp. 372ff.) This brings to mind (although not called Euripus, obviously, but 'the god's place of skulls') the Central American Ball Court which had a round hole in its center, termed by Tezozomoc 'the enigmatic significance of the ball court', and from this hole a lake spread out before Uitzilopochtli was born. See W. Krickeberg, 'Der mittelamerikanische Ballspielplatz und seine religiöse Symoblik', Paideuma 3 (1948), pp. 135ff., 155, 162. And here the unstable Euripus of the Ocean, which flows back to the beginnings of its mysterious source, dragged with irresistible force the unhappy sailors, thinking by now only of death, towards Chaos. This is said to be the maw of the abyss, that unknown depth in which, it is understood, the ebb and flow of the whole sea is absorbed and then thrown up again, which is the cause of the tides. This is reflection of what had been a popular idea of antiquity. But here comes a version of the same story in North America. It concerns the canoe adventures of two Cherokees at the mouth of Suck Creek. One of them was seized by a fish, and never seen again. The other was taken round and round to the very lowest center of the whirlpool, when another circle caught him and bore him outward. He told afterwards that when he reached the narrowest circle of the maelstroem the water seemed to open below and he could look down as through the roof beam of a house, and there on the bottom of the river he had seen a great company, who looked up and beckoned to him to join them, but as they put up their hands to seize him the swift current caught him and took him out of their reach. It is almost as if the Cherokees have retained a better memory, when they talk of foreign regions, inhabited by 'a great company' - which might equally well be the dead, or giants with their dogs - there, where in 'the narrowest circle of the maelstroem the water seemed to open below' ...
Therefore, when Epimenides slept inside his cave for 57 years it ought to have corresponded to a time inside (the orbit of) Mother Earth. ... The original story was by Diogenes Laertius, an Epicurean philosopher circa early half third century, in his book On the Lives, Opinions, and Sayings of Famous Philosophers. The story is in Chapter ten in his section on the Seven Sages, who were the precursors to the first philosophers. The sage was Epimenides. Apparently Epimenides went to sleep in a cave for fifty-seven years. But unfortunately, 'he became old in as many days as he had slept years'. Although according to the different sources that Diogenes relates, Epimenides lived to be one hundred and fifty-seven years, two hundred and ninety-nine years, or one hundred and fifty-four years. A similar story is told of the Seven Sleepers of Ephesus, Christian saints who fall asleep in a cave while avoiding Roman persecution, and awake more than a century later to find that Christianity has become the religion of the Empire ...
57 = 3 * 19 = 393 - 336 (Ca12-20):
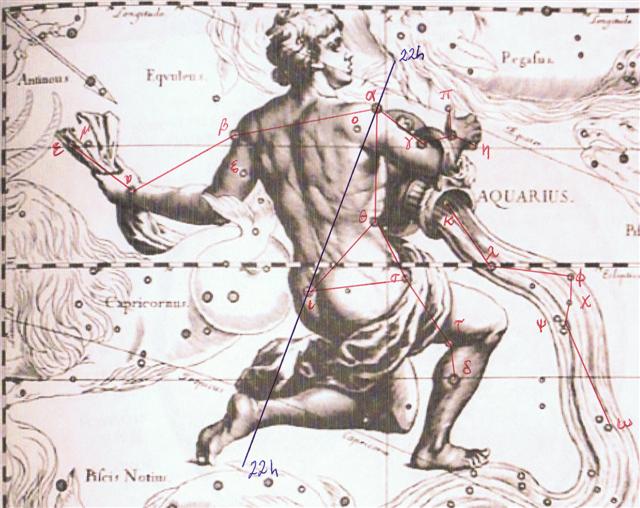
According to Manuscript E it was not Sirius which was Te Pou ... The actual props, pillars or posts which separated the sky and earth are called toko in New Zealand, to'o in the Marquesas Islands and pou in Tahiti. In Rapanui tuu and pou are known, with pou meaning column, pillar or post of either stone or wood. Sometimes the word is applied to a natural rock formation with postlike qualities which serves as an orientation point. The star Sirius is called Te Pou in Rapanui and functions in the same way ... but Regulus at the heart of Leo according to Hevelius: ... They took their provisions with them, carrying them on their shoulders, went on, and reached Te Pou. They made camp and slept in Te Pou on the tenth day of the month of July ('Anakena') ... (E:22)
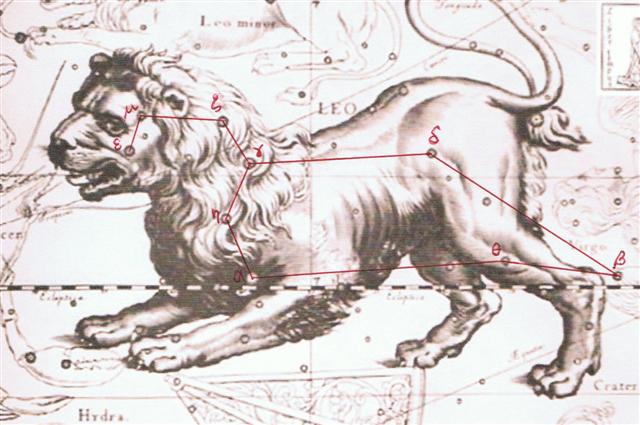
Why, then, is there no sign of koti here? Presumably because this place was not at the end of a dark season. Leo seems to have corresponded to Jupiter (Jus Piter, Father Light) and should therefor be on the outside of the path of Mother Earth around the Sun. It was presumably the opposite of a koti place, and it seems to be here that Epimenides - the tanist, the shadow, the dark player at the opposite side of Leo - went down into a cave to get cool water and to begin his sleep (kua moe) for 57 right ascension days:
... The original story was by Diogenes Laertius, an Epicurean philosopher circa early half third century, in his book On the Lives, Opinions, and Sayings of Famous Philosophers. The story is in Chapter ten in his section on the Seven Sages, who were the precursors to the first philosophers. The sage was Epimenides. Apparently Epimenides went to sleep in a cave for fifty-seven years. But unfortunately, 'he became old in as many days as he had slept years'. Although according to the different sources that Diogenes relates, Epimenides lived to be one hundred and fifty-seven years, two hundred and ninety-nine years, or one hundred and fifty-four years. A similar story is told of the Seven Sleepers of Ephesus, Christian saints who fall asleep in a cave while avoiding Roman persecution, and awake more than a century later to find that Christianity has become the religion of the Empire ... The kai gesture at the kua moe glyph (cfr also the strange gesture in front of the mouth of Epimenides) could mean he was very thirsty because he was at the opposite side of the waters of spring. Cupping his hand, dipping it into the source of fresh water and then throwing the water into his mouth was the ancient method of drinking.
... the bird, being sent with a cup for water, loitered at a fig-tree till the fruit became ripe, and then returned to the god with a water-snake in his claws and a lie in his mouth, alleging the snake to have been the cause of the delay. In punishment he was forever fixed in the sky with the Cup and the Snake; and, we may infer, doomed to everlasting thirst by the guardianship of the Hydra over the Cup and its contents. From all this came other poetical names for our Corvus - Avis Ficarius, the Fig Bird; and Emansor, one who stays beyond his time; and a belief, in early folk-lore, that this alone among birds did not carry water to its young ... ... There was no water in the village. The lakes and rivers were dry. Raven and Crow, two young girls who were having their first menstrual courses, were told to go and draw water from the ocean. Finding the journey too long, Raven decided just to urinate into her basket-bucket. She decieved no one and was severly scolded. Crow returned much later but with drinking water. As a punishment, Raven was condemned never to find water in the summer; only in winter would she find something to drink. For that reason the Raven never drinks during the hot months; she speaks with a raucous voice because of her dry throat ...
And the humpback outline of the sitting figure could mean this strange person corresponded to the old man at the bottom of the sea (Nangkilstlas). If Epimenides lived to be 157 years, then the last 57 of them may have been spent down in a cave as an old man. ... In the morning of the world, there was nothing but water. The Loon was calling, and the old man who at that time bore the Raven's name, Nangkilstlas, asked her why. 'The gods are homeless', the Loon replied. 'I'll see to it', said the old man, without moving from the fire in his house on the floor of the sea. Then as the old man continued to lie by his fire, the Raven flew over the sea. The clouds broke. He flew upward, drove his beak into the sky and scrambled over the rim to the upper world. There he discovered a town, and in one of the houses a woman had just given birth. The Raven stole the skin and form of the newborn child. Then he began to cry for solid food, but he was offered only mother's milk. That night, he passed through the town stealing an eye from each inhabitant. Back in his foster parents' house, he roasted the eyes in the coals and ate them, laughing. Then he returned to his cradle, full and warm. He had not seen the old woman watching him from the corner - the one who never slept and who never moved because she was stone from the waist down. Next morning, amid the wailing that engulfed the town, she told what she had seen. The one-eyed people of the sky dressed in their dancing clothes, paddled the child out to mid-heaven in their canoe and pitched him over the side. He turned round and round to the right as he fell from the sky back to the water. Still in his cradle, he floated on the sea. Then he bumped against something solid. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said a voice. The Raven saw nothing. He heard the same voice again, and then again, but still he saw nothing but water. Then he peered through the hole in his marten-skin blanket. Beside him was a grebe. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said the grebe and dived. Level with the waves beside him, the Raven discovered the top of a housepole made of stone. He untied himself from his cradle and climbed down the pole to the lowermost figure. Hala qaattsi ttakkin-gha, a voice said: 'Come inside, my grandson.' Behind the fire, at the rear of the house, was an old man white as a gull. 'I have something to lend you', said the old man. 'I have something to tell you as well. Dii hau dang iiji: I am you.' Slender bluegreen things with wings were moving between the screens at the back of the house. Waa'asing dang iiji, said the old man again: 'That also is you.' The old man gave the Raven two small sticks, like gambling sticks, one black, one multicoloured. He gave him instructions to bite them apart in a certain way and told him to spit the pieces at one another on the surface of the sea. The Raven climbed back up the pole, where he promptly did things backwards, just to see if something interesting would occur, and the pieces bounced apart. It may well be some bits were lost. But when he gathered what he could and tried again - and this time followed the instructions he had been given - the pieces stuck and rumpled and grew to become the mainland and Haida Gwaii ... Around (22h - 18h) / 24h * 26000 = 4333 years earlier, in the era of the great pyramids of Egypt, Sadalmelik would have been at the northern autumn equinox and Regulus at the northern spring equinox.
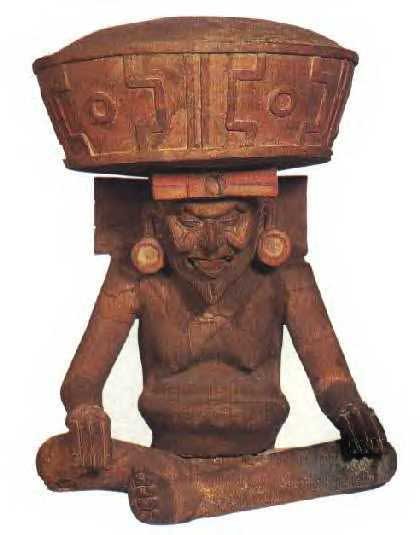
... Xiuhtecuhtli, the fire god, as Huehueteotl, 'the old god at the centre'. One of the oldest deities of ancient America, this clay figure from the Veracruz culture shows him seated with a brazier on his head. Xiuhtecuhtli was lord of the present 'Sun', or era, his ceremonies being particularly important at the end of every fifty-two-year cycle when all fires were put out and a fresh one was kindled on a prisoner's breast in order to keep time moving ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||