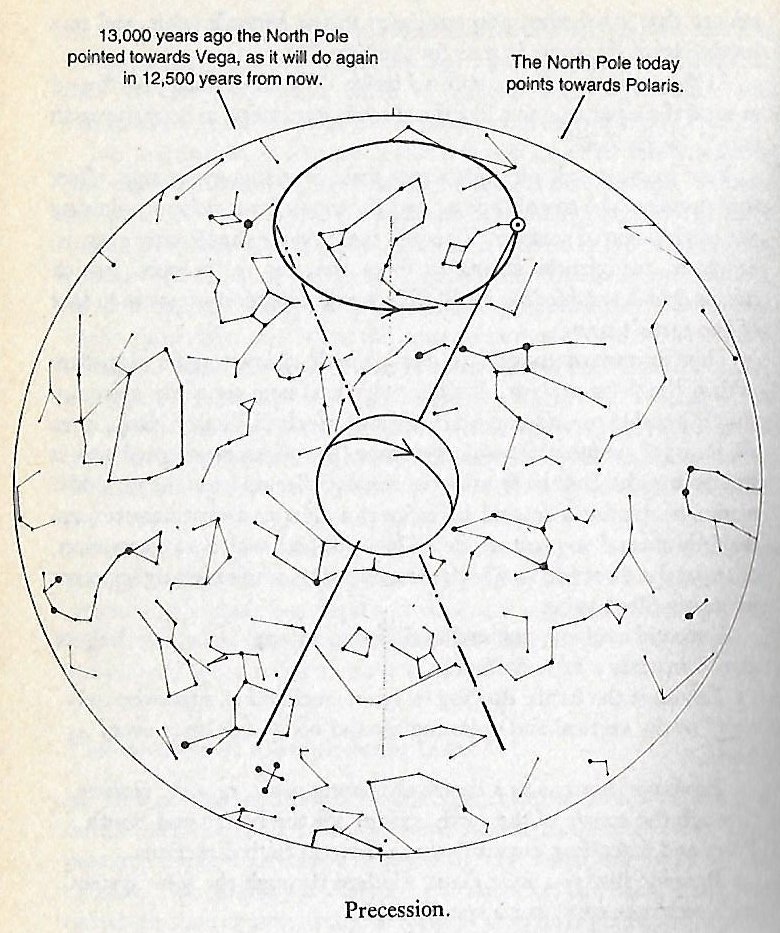
363. In order to see the constellations as they had been a quarter of 26000 years ago we should reorient the Chinese map,
and such a re-orientation will bring the Red (fire) Bird to be at right in spring and the Green (water) Serpent to be at left in autumn, with the White Tiger upside down at the top and the Blue Dragon at bottom.
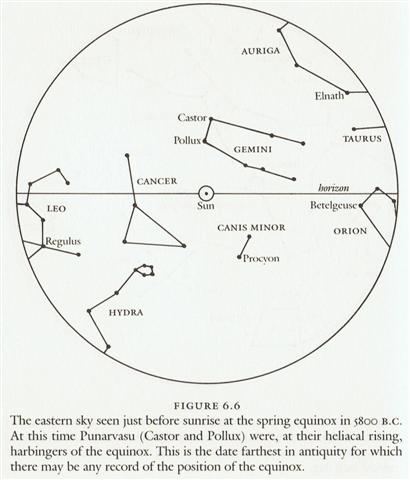
The Red Bird was beginning at Castor and Pollux, the Blue Dragon at Spica; the neck of the Green Serpent was at the South Dipper, and the tail of the White Tiger was at Andromeda. ... In Hindu legend there was a mother goddess called Aditi, who had seven offspring. She is called 'Mother of the Gods'. Aditi, whose name means 'free, unbounded, infinity' was assigned in the ancient lists of constellations as the regent of the asterism Punarvasu. Punarvasu is dual in form and means 'The Doublegood Pair'. The singular form of this noun is used to refer to the star Pollux. It is not difficult to surmise that the other member of the Doublegood Pair was Castor. Then the constellation Punarvasu is quite equivalent to our Gemini, the Twins. In far antiquity (5800 B.C.) the spring equinoctial point was predicted by the heliacal rising of the Twins (see fig. 6.6):
... Punarvasu is one of the twenty-seven (or twenty-eight) zodiacal constellations in the Indian system of Nakshatras. In each of the Nakshatras there is a 'yoga', a key star that marks a station taken by the moon in its monthly (twenty-seven- or twenty-eight-day course) through the stars. (The sidereal period of the moon, twenty-seven days and a fraction [14 * 27 = 378, synodic cycle of Saturn, and 14 * 28 = 392, number of glyphs on side a of the C tablet], should be distinguished from the synodic, or phase-shift period of 29.5 days, which is the ultimate antecedent of our month.) In ancient times the priest-astronomers (Brahmans) determined the recurrence of the solstices and equinoxes by the use of the gnomon. Later they developed the Nakshatra system of star reference to determine the recurrence of the seasons, much as the Greeks used the heliacal rising of some star for the same purpose ... The Square House for observing the ancient place of the winter solstice
... it is not too much to assume that the Egyptians observed, and taught people to observe, the sun on the horizon. This being so, the chances are that at first they would observe the stars on the horizon too, both stars rising and stars setting; this indeed is rendered more probable by the very careful way in which early astronomers defined the various conditions under which a star can rise or set, always, be it remembered, in relation to the sun ... Although the Egyptians knew nothing about telescopes, it would seem that they had the same problem before them which we solve by a special arrangement in the modern telescope - they wanted to keep the light pure, and to lead it into their sanctuary as we lead it to the eyepiece. To keep the light that passes into the eyepiece of a modern telescope pure, we have between the object-glass and the eyepiece a series of what are called diaphragms; that is, a series of rings right along the tube, the inner diameter of the rings being greatest close to the object-glass, and smallest close to the eyepiece; these diaphragms must so be made that all the light from the object-glass shall fall upon the eyepiece, without loss or reflection by the tube. These apertures in the pylons and separating walls of Egyptian temples exactly represent the diaphragms in the modern telescope ...
could possibly have begun in day 429 (March 5) - 184 / 2 = 337, although already the Roof Top (337 - 15 = 322) indicated the sky and the pillar between Regulus and Sadalmelik:
... The king, wearing now a short, stiff archaic mantle, walks in a grave and stately manner to the sanctuary of the wolf-god Upwaut, the 'Opener of the Way', where he anoints the sacred standard and, preceded by this, marches to the palace chapel, into which he disappears. A period of time elapses during which the pharaoh is no longer manifest. When he reappears he is clothed as in the Narmer palette, wearing the kilt with Hathor belt and bull's tail attatched. In his right hand he holds the flail scepter and in his left, instead of the usual crook of the Good Shepherd, an object resembling a small scroll, called the Will, the House Document, or Secret of the Two Partners, which he exhibits in triumph, proclaiming to all in attendance that it was given him by his dead father Osiris, in the presence of the earth-god Geb. 'I have run', he cries, 'holding the Secret of the Two Partners, the Will that my father has given me before Geb. I have passed through the land and touched the four sides of it. I traverse it as I desire.'
On Hawaii they observed the return of the Pleiades and then there were 33 days to the winter solstice. 337 + 33 = 370 days agrees with the sum of glyphs on the C tablet, where (392 + 348) / 2 = 370. ... The correspondence between the winter solstice and the kali'i rite of the Makahiki is arrived at as follows: ideally, the second ceremony of 'breaking the coconut', when the priests assemble at the temple to spot the rising of the Pleiades, coincides with the full moon (Hua tapu) of the twelfth lunar month (Welehu). In the latter eighteenth century, the Pleiades appear at sunset on 18 November. Ten days later (28 November), the Lono effigy sets off on its circuit, which lasts twenty-three days, thus bringing the god back for the climactic battle with the king on 21 December, the solstice (= Hawaiian 16 Makali'i). The correspondence is 'ideal' and only rarely achieved, since it depends on the coincidence of the full moon and the crepuscular rising of the Pleiades ... But instead of sacrificing a pig the Hawaiians offered an eye which could have been intended as a harmony with the disappearance of Lono (Rogo): ... in the ceremonial course of the coming year, the king is symbolically transposed toward the Lono pole of Hawaiian divinity ... It need only be noticed that the renewal of kingship at the climax of the Makahiki coincides with the rebirth of nature. For in the ideal ritual calendar, the kali'i battle follows the autumnal appearance of the Pleiades, by thirty-three days - thus precisely, in the late eighteenth century, 21 December, the winter solstice. The king returns to power with the sun. Whereas, over the next two days, Lono plays the part of the sacrifice. The Makahiki effigy is dismantled and hidden away in a rite watched over by the king's 'living god', Kahoali'i or 'The-Companion-of-the-King', the one who is also known as 'Death-is-Near' (Koke-na-make). Close kinsman of the king as his ceremonial double, Kahoali'i swallows the eye of the victim in ceremonies of human sacrifice ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


.jpg)