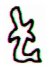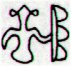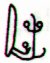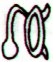|
TRANSLATIONS
Next page:
There are two kinds of tao in G, one - apparently - for the sun and one for the moon. I have once again looked at the tao glyphs in G and found them to be 7 + 7 + 4 = 18. I have deleted Gb4-20 from tao in the catalogue:
The suggested structure reveals that the simple tao glyphs come in pairs. Ga8-19 and Gb2-35 are related, it seems. Both have strange variants of hua poporo at right. Ga8-19 has 3 + 3 peculiar 'twigs' and Gb2-35 has 3 'branches' with 'berries' + 3 'branches' without. Ga8-19 has a sign of wilting, while Gb2-35 has a sign of growing. I imagine we can relate the two kinds of 'canoe' to the myth of Osiris. "The basic myth of dynastic Egypt was that of the death and resurrection of Osiris, the good king, 'fair of face', who was born to the earth-god Geb and sky-goddess Nut. He was born together with his sister-wife, the goddess Isis, during the sacred interval of those five supplementary days that fell between one Egyptian calendric year of 360 days and the next. He and his sister were the first to plant wheat and barley, to gather fruit from trees, and to cultivate the vine, and before their time the races of the world had been savage cannibals. But Osiris's evil brother, Set, whose sister-wife was the goddess Nephtys, was mortally jealous both of his virtue and of his fame, and so, stealthily taking the measure of his good brother's body, he caused a beautifully decorated sarcophagus to be fashioned and on a certain occasion in the palace, when all were drinking and making merry, had it brought into the room and jestingly promised to give it to the one whom it should fit exactly. All tried, but, like the glass slipper of Cinderella, it fitted but one; and when Osiris, the last, laid himself within it, immediately a company of seventy-two conspirators with whom Set had contrived his plot dashed forward, nailed the lid upon the sarcophagus, soldered it with molten lead, and flung it into the Nile, down which it floated to the sea. Isis, overwhelmed with grief, sheared off her locks, donned mourning, and searched in vain, up and down the Nile; but the coffin had been carried by the tide to the coast of Phoenicia, where, at Byblos, it was cast ashore. A tamarisk immediately grew up around it, enclosing the precious object in its trunk, and the aroma of this tree then was so glorious that the local king, and queen, Melqart and Astarte - who were, of course, a divine king and queen themselves, the local representatives, in fact, of the common mythology of Damuzi and Inanna, Tammuz and Ishtar, Adonis and Aphrodite, Osiris and Isis - discovering and admiring its beauty, had the tree felled and fashioned into a pillar of their palace. The bereaved and sorrowing Isis, meanwhile, wandering over the world in her quest - like Demeter in search of the lost Persephone - came to Byblos, where she learned of the wonderful tree. And, placing herself by a well of the city, in mourning, veiled and in humble guise - again like Demeter - she spoke to none until there approached the well the handmaidens of the queen, whom she greeted kindly. Braiding their hair, she breathed upon them such a wondrous perfume that when they returned and Astarte saw and smelt the braids she sent for the stranger, took her into the house, and made her the nurse of her child. The great goddess gave the infant her finger instead of breast to suck and at night, having placed him in a fire to burn away all that was mortal, flew in the form of a swallow around the pillar, mournfully chirping. But the child's mother, Queen Astarte, happening in upon this scene, shrieked when she spied her little son resting in the flames and thereby deprived him of the priceless boon. Whereupon Isis, revealing her true nature, begged for the pillar and, removing the sarcophagus, fell upon it with a cry of grief so loud that the queen's child died on the spot. Sorrowing, then, the two women placed Osiris's coffer on a boat, and when the goddess Isis was alone with it at sea, she opened the chest and, laying her face on the face of her brother, kissed him and wept. The myth goes on to tell of the blessed boat's arrival in the marshes of the Delta, and of how Set, one night hunting the boar by the light of the full moon, discovered the sarcophagus and tore the body into fourteen pieces, which he scattered abroad; so that, once again, the goddess had a difficult task before her. She was assisted, this time, however, by her little son Horus, who had the head of a hawk, by the son of her sister Nephtys, little Anubis, who had the head of a jackal, and by Nephtys herself, the sister-bride of their wicked brother Set. Anubis, the elder of the two boys, had been conceived one very dark, we are told, when Osiris mistook Nephtys for Isis; so that by some it is argued that the malice of Set must have been inspired not by the public virtue and good name of the noble culture hero, but by this domestic inadventure. The younger, but true son, Horus, on the other hand, had been more fortunately conceived - according to some, when Isis lay upon her dead brother in the boat, or, according to others, as she fluttered about the palace pillar in the form of a bird. The four bereaved and searching divinities, the two mothers and their two sons, were joined by a fifth, the moon-god Thoth (who appears sometimes in the form of an ibis-headed scribe, at other times in the form of a baboon), and together they found all of Osiris save his genital member, which had been swallowed by a fish. They tightly swathed the broken body in linen bandages, and when they performed over it the rites that thereafter were to be continued in Egypt in the ceremonial burial of kings, Isis fanned the corpse with her wings and Osiris revived, to become the rule of the dead. He now sits majestically in the underworld, in the Hall of the Two Truths, assisted by forty-two assessors, one from each of the principal districts of Egypt; and there he judges the souls of the dead. These confess before him, and when their hearts have been weighed in a balance against a feather, receive, according to their lives, the reward of virtue and the punishment of sin." (Campbell) Here is told about two 'canoes' (coffins):
Although Osiris is a moon god and not a sun god, the structure should be similar. Side a of G corresponds, I guess, to the return and side b to the exit. Osiris returns by landing in the marshes, the lowest point of the land, and he exits suddenly at the height of his glory, becoming invisible inside the coffin sealed by lead (Saturn's metal). There is only one tagata tao in G:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||