|
TRANSLATIONS
We will now move on to tao in the glyph dictionary:
Paukumi (closet, cupboard) makes us see a possible connection between pahu (coffin) and pau (finished). Kumi means 'long'. Pahure (to sweep everything away) sounds like making it ready for the newcomer. Like in the Mayan routines when the cycle has finished: ... Behold what was done when the years were bound - when was reached the time when they were to draw the new fire, when now its count was accomplished. First they put out fires everywhere in the country round. And the statues, hewn in either wood or stone, kept in each man's home and regarded as gods, were all cast into the water. Also (were) these (cast away) - the pestles and the (three) hearth stones (upon which the cooking pots rested); and everywhere there was much sweeping - there was sweeping very clear. Rubbish was thrown out; none lay in any of the houses ... The long hollow tree drum (pahu) marked the end of years in Mayan calendars:
... The period of 360 days was known in Yucatec by two terms, tun and haab, the latter being widely spread in the various Maya languages as a term for 'year'. The first glyph for the 360-day period (T548) was read as tun by Seler and may represent a drum ...
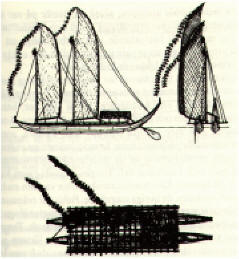
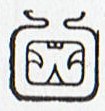
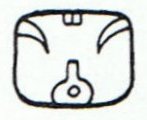
The tun glyph was identified as a wooden drum by Brinton (1895, p. 92), and Marshal H. Saville immediately accepted it. Figure 49 [excerpt above] shows the Aztec drum representation relied on by Brinton to demonstrate his point. It was not then known that an ancestral Mayan word for drum was *tun: Yucatec tunkul 'divine drum' (?); Quiche tun 'hollow log drum'; Chorti tun 'hollow log drum' (Wisdom 1940, pp. 175-176). The glyph is nearly the same as that for the month Pax (T549), except that the top part of the latter is split or divided by two curving lines. Brinton, without referring to the Pax glyph, identified the tun glyph as the drum called in Yucatec pax che (pax 'musical instrument'; che < *te 'wooden). Yucatec pax means 'broken, disappeared', and Quiche paxih means, among other things, 'split, divide, break, separate'. It would seem that the dividing lines on the Pax glyph may have been used as a semantic/phonetic determinative indicating that the drum should be read pax, not tun (cf. de Gruyter 1946, p. 27). Thus, one may expect that this glyph was used elsewhere meaning 'to break' and possibly for 'medicine' (Yuc. pax, Tzel., Tzo. pox) ... The meaning of the drum may have been to announce the 'breaking' of the old cycle. It is a time of death.
... Across the bows connecting each double canoe was a floor, covering the chambers containing idols, drums, trumpet shells, and other treasures for the gods and people of Ra'itea; and upon the floor were placed in a row sacrifices from abroad, which consisted of human victims brought for that purpose and just slain, and great fishes newly caught from fishing grounds of the neighboring islands. They were placed upon the floor, parallel with the canoe, alternatively a man and a cavalli fish, a man and a shark, a man and a turtle, and finally a man closed in the line. Behind this grim spectacle stood two or three priests in sacerdotal attire, which consisted of a plain loin girdle, a shoulder cape reaching down to the waist and tipped with fringe, wide or narrow according to their grades, and a circular cap fitting closely to the head - all made of finely braided purau bark bleached white. Seated at the paddles were the navigators and warrior chiefs in gay girdles and capes of tapa and helmets of various shapes, and wise men in plain girdles, capes, and turbans of brown or white tapa. As this terribly earnest procession arrived, the canoes were quietly drawn up along the shore, and the guests were met at the receiving marae by an imposing procession of the dignitaries and warriors of the land grandly attired, and also unarmed, headed by the king, the two primates, Paoa-uri and Paoa-tea, and the priests of the realm, who greeted them in low, solemn tones. Then everybody alike set to work silently disposing of the sacrifices just arrived, combined with others of the same mixed kind prepared by the inhabitants of the land. They strung them through the heads with sennit, and act called tu'i-aha, and then suspended them upon the boughs of the trees of the seaside and inwards, the fish diversifying the ghastly spectacle of the human bodies, a decoration called ra'a nu'u a 'Oro-mata-'oa (sacredness of the host of Warrior-of-long-face) ... |