According to Hamlet's Mill:
"The Mesopotamian cylinder seal shows in the upper part the 'God Boat'; in the lower part people are building a ziggurat, the proposition being that the boat is bringing the me from Eridu-Canopus, the measures of creation." Measures are numbers, and the Greek letters were numbers. Although the resemblance between the words me and mēm might be coincidental:
I.e., the measures of creation enabled Man to Create exact mathematical replicas. These measures were documented and the same constructs could be recreated again and again. The centralized agrarian culture had been born.
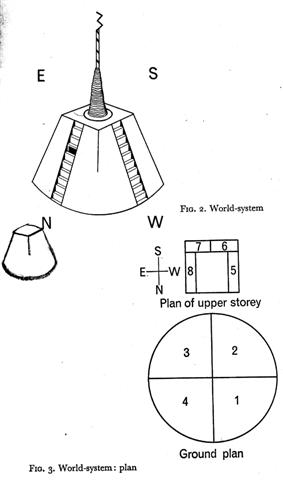
... and then, with stunning abruptness, at a crucial date that can be almost precisely fixed at 3200 BC (in the period of the archaeological stratum known as Uruk B), there appears in this little Sumerian mud garden - as though the flowers of its tiny cities were suddenly bursting into bloom - the whole cultural syndrome that has since constituted the germinal unit of all the high civilization of the world. And we cannot attribute this event to any achievement of the mentality of simple peasants. Nor was it the mechanical consequence of a simple piling up of material artifacts, economically determined. It was actually and clearly the highly conscious creation (this much can be asserted with complete assurance) of the mind and science of a new order of humanity, which had never before appeared in the history of mankind; namely, the professional, full-time, initiated, strictly regimented temple priest. The new inspiration of civilized life was based, first, on the discovery, through long and meticulous, carefully checked and rechecked observations, that there were, besides the sun and moon, five other visible or barely visible heavenly spheres (to wit, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) which moved in established courses, according to established laws, along the ways followed by the sun and moon, among the fixed stars; and then, second, on the almost insane, playful, yet potentially terrible notion that the laws governing the movements of the seven heavenly spheres should in some mystical way be the same as those governing the life and thought of men on earth. The whole city, not simply the temple area, was now conceived as an imitation on earth of the cosmic order, a sociological 'middle cosmos', or mesocosm, established by priestcraft between the macrocosm of the universe and the microcosm of the individual, making visible the one essential form of all. The king was the center, as a human representative of the power made celestially manifest either in the sun or the moon, according to the focus of the local cult; the walled city was organized architecturally in the design of a quartered circle (like the circles designed on the ceramic ware of the period just preceeding), centered around the pivotal sanctum of the palace or ziggurat (as the ceramic designs around the cross, rosette, or swastika); and there was a mathematically structured calendar to regulate the seasons of the city's life according to the passages of the sun and moon among the stars - as well as a highly developed system of liturgical arts, including music, the art rendering audible to human ears the world-ordering harmony of the celestial spheres. It was at this moment in human destiny that the art of writing first appeared in the world and that scriptorially documented history therefore begins. Also, the wheel appeared. And we have evidence of the development of the two numerical systems still normally employed throughout the civilized world, the decimal and the sexigesimal; the former was used mostly for business accounts in the offices of the temple compounds, where the grain was stored that had been collected as taxes, and the latter for the ritualistic measuring of space and time as well. Three hundred and sixty degrees, then as now, represented the circumference of a circle - the cycle of the horizon - while three hundred and sixty days, plus five, marked the measurement of the circle of the year, the cycle of time. The five intercalated days that bring the total to three hundred and sixty-five were taken to represent a sacred opening through which spiritual energy flowed into the round of the temporal universe from the pleroma of eternity, and they were designated, consequently, days of holy feast and festival. Comparably, the ziggurat, the pivotal point in the center of the sacred circle of space, where the earthly and heavenly powers joined, was also characterized by the number five; for the four sides of the tower, oriented to the points of the compass, came together at the summit, the fifth point, and it was there that the energy of heaven met the earth. The early Sumerian temple tower with the hieratically organized little city surrounding it, where everyone played his role according to the rules of a celestially inspired divine game, supplied the model of paradise that we find, centuries later, in the Hindu-Buddhist imagery of the world mountain, Sumeru, whose jeweled slopes, facing the four directions, peopled on the west by sacred serpents, on the south by gnomes, on the north by earth giants, and on the east by divine musicians, rose from the mid-point of the earth as the vertical axis of the egg-shaped universe, and bore on its quadrangular summit the palatial mansions of the deathless gods, whose towered city was known as Amaravati, 'The Town Immortal'. But it was the model also of the Greek Olympus, the Aztec temples of the sun, and Dante's holy mountain of Purgatory, bearing on its summit the Earthly Paradise. For the form and concept of the City of God conceived as a 'mesochosm' (an earthly imitation of the celestial order of the macrocosm) which emerged on the threshold of history circa 3200 BC, at precisely that geographical point where the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates reach the Persian Gulf, was disseminated eastward and westward along the ways already blazed by the earlier neolithic. The wonderful life-organizing assemblage of ideas and principles - including those of kingship, writing, mathematics, and calendrical astronomy - reached the Nile, circa 2800 BC; it spread to Crete on the one hand, and on the other, to the valley of the Indus, circa 2600 BC; to Shang China, circa 1600 BC; and, according to at least one high authority, Dr Robert Heine-Geldern, from China across the Pacific, during the prosperous seafaring period of the late Chou Dynasty, between the seventh and fourth centuries BC, to Peru and Middle America ...
4 * 10(0) = 40(0) = 20 * 20 = 360 + 40 = 365 + 35 = 350 + 50 = 260 + 140 = 320 + 80 = 390 + 10 (there is a hole in the north): ... I became curious about this star ... called Nuutuittuq [= 'never moves'] ... So, on the lee side of our uquutaq (a snow windbreak) I positioned a harpoon pointing directly at this particular star to see if it would move. In the morning I checked it and discovered that the Tukturjuit (Ursa Major) had changed their position completely but the harpoon still pointed at this star ... I had discovered the stationary star ...
... the strange hologram of archaic cosmology must have existed as a conceived plan, achieved at least in certain minds, even as late as the Sumerian period when writing was still a jealously guarded monopoly of the scribal class. Such a mind may have belonged to a keeper of records, but not of the living world, still less of the living thought. Most of the plan was never recorded. Bits of it reach us in unusual, hesitant form, barely indicated, as in the wisdom and sketches of Griaule's teacher, OgotemmÍli, the blind centenarian sage. In the magic drawings of Lascaux, or in American Indian tales, one perceives a mysterious understanding between men and other living creatures which bespeaks of relationships beyond our imagination, infinitely remote from our analytical capacity. 'From now on', said Father Sun, grieving over Phaeton, his fallen child, 'you shall be Mink'. What meaning can this have for us? For such an understanding between men and men, and other living creatures too, we would need the kind of help King Arthur had at hand: 'Gwryr Interpreter of Tongues, it is meet that thou escort us on this quest. All tongues hast thou, and then canst speak all languages of men, with some of the birds and beasts.' This ability was also attributed to Merlin and Gwyon, those masters of cosmological wisdom whose names resound through the legends of the Middle Ages. In general, all fabulous communication was conceived as having such a range, not merely the Aesopian fable with is flat, all-too-wordly wisdom.
Much of this book has been peopled with the inhabitants of a Star Menagerie of profoundly meaningful animal characters. The forms of animal life have varied from the Fishes who turned into hairy Twins to the remarkable succession of doglike creatures occurring around the world from Ireland to YucatŠn. All of these animals have been of great significance, and each was invested with key functions in cosmological myth. It would be possible, for example, to prepare a most informative edition of the Romance of Reynard Fox illustrated entirely with reproductions from Egyptian and Mesopotamian ritual documents. For it is likely that these documents represent the last form of international initiatic language, intended to be misunderstood alike by suspicious authorities and the ignorant crowd. In any case, the language forms an excellent defense against the kind of misuse which Plato speaks about with surprising earnestness in Phaedrus (274D-275B). At the point in question, Thot/Hermes is feeling very proud of himself for having invented letters, and he claims that the alphabet will make the Egyptians wiser and improve their memory. Plato has the god Thamus, 'king of all Egypt', speak to him: 'Most ingenious Thoth', said the god and king Thamus, 'one man has the ability to beget arts, but the ability to judge of their usefulness or harmfulness to their users belongs to another; and now you, who are the father of letters, have been led by your affection to ascribe to them a power the opposite of that which they really possess. For this invention will produce forgetfulness in the minds of those who learn to use it, because they will not practise their memory. Their trust in writing, produced by external characters which are no part of themselves, will discourage the use of their own memory within them. You have invented an elixir not of memory, but of reminding; and you offer your pupils the appearance of wisdom, not true wisdom, for they will read many things without instruction and will therefore seem to know many things, when they are for the most part ignorant and hard to get along with, since they are not wise, but only appear wise.' Now that Plato's apprehensions have become fact, there is nothing left of the ancient knowledge except the relics, fragments and allusions that have survived the steep attrition of the ages ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.jpg)