One important question remains. How does the interrex (mock-king) correlate with the type of glyph which I have named hakaariki (to make a king)?
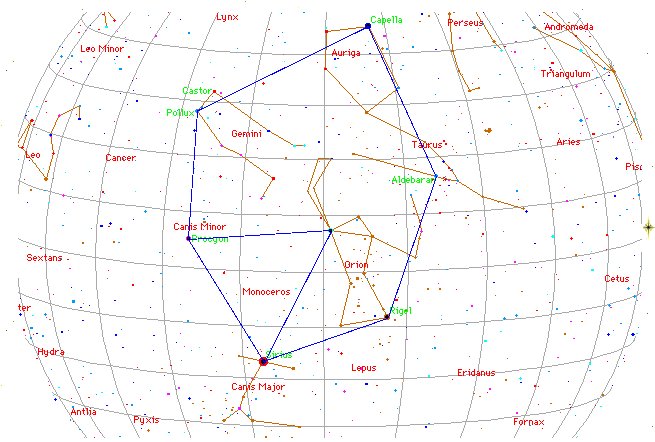
The G text carries only one example, although with the triplet looking ahead instead of straight at us - which I interpret to mean that at the time of the Bull there was a good future ahead for the king (and not a death at a solstice - the precession since then having moved the equinoxes towards the solstices).
Counted from the first glyph on side a of the G tablet the following kava type of glyph is number 378, which could allude (or refer) to the synodic cycle of Saturn.
From day 364 to day 378 there was a fortnight:
... dramatic conditions are imposed on the sovereignity at the time of the ruler's accession. Hocart observes that the Fijian chief is ritually reborn on this occasion; that is, as a domestic god. If so, someone must have killed him as a dangerous outsider. He is indeed killed by the indigenous people at the very moment of his consecration, by the offering of kava that conveys the land to his authority (lewaa). Grown from the leprous body of a sacrificed child of the native people, the kava the chief drinks poisons him ... Sacred product of the people's agriculture, the installation kava is brought forth in Lau by a representative of the native owners (mataqali Taqalevu), who proceeds to separate the main root in no ordinary way but by the violent thrusts of a sharp implement (probably, in the old time, a spear). Thus killed, the root (child of the land) is then passed to young men (warriors) of royal descent who, under the direction of a priest of the land, prepare and serve the ruler's cup ... the tuu yaqona or cupbearer on this occasion should be a vasu i taukei e loma ni koro, 'sisterīs son of the native owners in the center of the village' ... Traditionally, remark, the kava root was chewed to make the infusion: The sacrificed child of the people is cannibalized by the young chiefs. The water of the kava, however, has a different symbolic provenance. The classic Cakaudrove kava chant, performed at the Lau installation rites, refers to it as sacred rain water from the heavens ... This male and chiefly water (semen) in the womb of a kava bowl whose feet are called 'breasts' (sucu), and from the front of which, tied to the upper part of an inverted triangle, a sacred cord stretches out toward the chief ... The cord is decorated with small white cowries, not only a sign of chieftainship but by name, buli leka, a continuation of the metaphor of birth - buli, 'to form', refers in Fijian procreation theory to the conceptual acception of the male in the body of the woman. The sacrificed child of the people will thus give birth to the chief. But only after the chief, ferocious outside cannibal who consumes the cannibalized victim, has himself been sacrificed by it. For when the ruler drinks the sacred offering, he is in the state of intoxication Fijians call 'dead from' (mateni) or 'dead from kava' (mate ni yaqona), to recover from which is explicitly 'to live' (bula [hura]). This accounts for the second cup the chief is alone accorded, the cup of fresh water. The god is immediately revived, brought again to life - in a transformed state ...
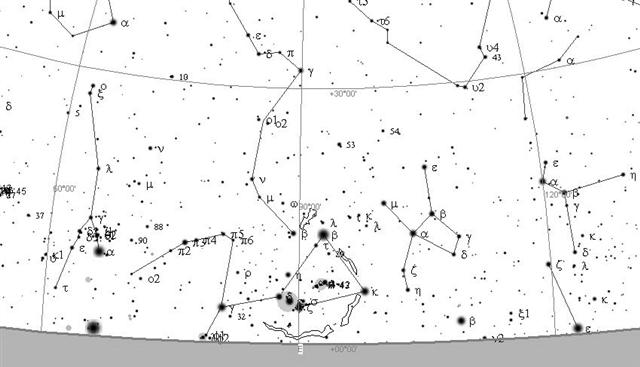
Although we are dealing with the cycle of the Sun it should be of interest to see what stars here rose heliacally at the time of the Bull:
In the C text, we remember, this place was evidently at the Full Moon and illustrated by Rogo:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






.jpg)