The list of sugarcane (toa) varieties continues, and
there were 7 of them:
|
he toa |
|
1 |
he |
rangi koro vao. |
a Teke. a Oti. |
|
2 |
tua
mamari manu. |
|
3 |
tua manu
auau |
|
4 |
ruma. |
|
5 |
tuitui koviro. |
|
6 |
vitiviti. |
|
7 |
marikuru. |
Marikuru. 1. A white, clayey earth. 2. A tree (Sapindus
saponaria) of which very few specimens are left. Vanaga. Ash-wood T. Churchill.
... 'Canne à sucre en fleur' (blooming sugar cane) is the
explanation given by Bishop Jaussen (according to Barthel):
Die in den Metorogesängen oft vorkommende Benennung der Zeichen
65 bzw. 66 als toa wurde von Jaussen auf das Zuckerrohr
bezogen; eine Auffassung, die keine Stütze
in den Tafeltexten findet.
Berücksichtigt man aber, daß die Metorogesänge phonetisch nicht
immer ganz exakt niedergeschrieben wurden, so findet man eine
sinnvolle Lösung, wenn man zwischen tôa
und to'a
underscheidet: Das erste Wort bedeutet Zuckerrohr, das zweite
dagegen Feind, Mörder.³
³) Englert 1948, 503: 'caña
de azucar' bzw. 'enemigo; asesino'. Ferner: he to'a o te îka,
el que ha dado muerte a una persona'.

| he ki
hokoou a Teke.kia Oti.ka oho ki roto |
Then Teke said to Oti, 'Go to the sugarcane
plantation [ka oho ki roto ki te toa] and
carefully break off [ka hahati] pieces of
cane. Not one variety shall be left (i.e., shall be
omitted) when the pieces of sugarcane are taken
along.' |
| ki te
toa ka hahati tahi.te mee o to ea eta(-) |
| hi.koia
ko pupura ana
too.mai.he oho. |
|
Pura. To
turn white; glow, brilliance; he-pura te mata,
the eyes twinkle (said of someone who looks at
something with great interest). Purapura,
descendent; koau he purapura o Miru, I am a
descendent of the Miru tribe. Pupura, the
part of the sugarcane or of the ti plant
which is cut off and planted again: pupura tôa,
pupura ti. Vanaga. |
| a Teke.a
Oti.toraua titiro tokoa.he
ōo. ki |
Teke and Oti went with their assistants, entered
into the sugarcane plantation, and broke off pieces
everywhere.
Teke said the names [he nape i te ingoa]
of all the different varieties of sugarcane. |
| roto ki
te toa.he hahati tahi.he nape i te ingoa o |
| te toa.e
Teke. |
|
 |
|
E:70 |
|
etahi te piere te
amonga o te toa.he ki a Teke. |
There were a thousand loads [te amonga] of
sugarcane. Teke said to Oti [oti], 'Bring [ka
mau] (that) on board the canoe!'
The men picked up [he mau] the sugarcane,
came on board the canoe, and left it there.
The men returned (to the other things) [ki te
me'e] and took
these too. |
| kia oti
ka mau ki runga ki te miro.he mau te |
|
tangata.i te toā.he tuu
he hakarere i runga i te |
| miro.he
hoki mai te tangata.ki te mee |
| he too
tokou. |
| he ki
hokoou te ariki a Hotu kia Teke. |
Then King Hotu spoke to Teke, 'Take along the
four-legged animals (manu vae eha), the pigs
(? kekepu), the sea swallows (manu
tara), and the flies (takaure)!' King
Hotu continued to speak to Teke, 'The thing [he
mee] that you must not forget under any
circumstances are the flies! The flies are creatures
[he mee o rehu a takaure] that must not be
forgotten.
If you forget the flies [ana rehu te takaure i
a koe] the multitude [te piere] of
people will perish [he ngaro]. But when you
bring the flies on land [ana tomo ki runga ki te
kainga te takaure], then there will be a great
number of people (he piere tangata)!' |
| ka too
te manu vae eha.te kekepu. te manu |
| tara.te
takaure.(h)e ki hokoou te ariki a Hotu |
| kia
Teke. te mee mo tae rehu i a koe he taka(-) |
| ure.he
mee o rehu a te takaure. ana rehu te |
| takaure
i a koe.he ngaro te piere tangata. |
| ana tomo
ki runga ki te kainga te takaure ena |
| i a koe
ka aī te mee he piere
tangata. |
|
...From a religious point of
view, the high regard for flies, whose increase or
reduction causes a similar increase or reduction in
the size of the human population, is interesting,
even more so because swarms of flies are often a
real nuisance on Easter Island, something most
visitors have commented on in vivid language. The
explanation seems to be that there is a parallel
relationship between flies and human souls, in this
case, the souls of the unborn. There is a widespread
belief throughout Polynesia that insects are the
embodiment of numinous beings, such as gods or the
spirits of the dead, and this concept extends into
Southeast Asia, where insects are seen as the
embodiment of the soul ... |
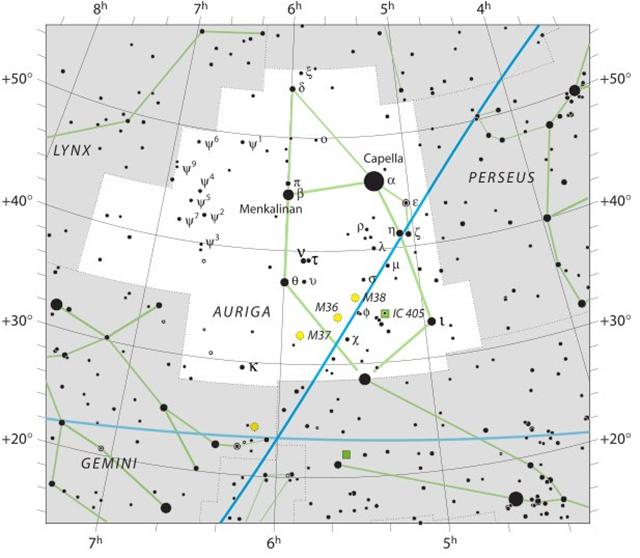
Supposing we should move ahead from Ga1-6,
|
MARCH 24
(83) |
25 (Julian equinox) |
26 (*5) |
27 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-3 |
Ga1-4 |
Ga1-5 |
Ga1-6 |
|
no star
listed (67) |
Rohini-4 (The Red One) /
Pidnu-sha-Shame-4 (Furrow of Heaven)
/
ANA-MURI-2 (Rear pillar - at the foot of which was
the place for tattooing)
ALDEBARAN
= α Tauri
(68.2),
THEEMIN = υ² Eridani
(68.5) |
no star
listed (69) |
no star
listed (70) |
|
May 27 |
28 (148) |
29 |
30 (*70) |
|
°May
23 |
24 (144) |
25 (*65) |
26 |
|
'April
30 |
'May 1
(121) |
2 (*42) |
3 |
|
16 (471 = 314 *
1½) |
"April 17 (107) |
18 (*28) |
19 |
|
DAY 67 -
64 = 3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
3 Hanga Roa
a tuki tukau |
4 Okahu
a uka ui hetuu |
5 Ra Tahai
a uo |
6 Ahu Akapu
a mata kurakura |
|
Ku hú á te huka-huka, ku herohero
á i roto i te ahi, burning wood shows red in the
fire.
Oka.
1. Lever, pole; to dig holes in the
ground with a sharpened stick, as was done in
ancient times to plant vegetables; used generally in
the meaning of making plantations. 2. The four
sideways poles supporting a hare paega.
Okaoka, to jab, to pierce, to prick repeatedly.
Vanaga. Digging stick, stake, joist; to prick, to
pierce, to stick a thing into, to drive into, to
slaughter, to assassinate; kona oka kai,
plantation; pahu oka, a drawer. Okaoka,
a fork, to prick, to dig. Okahia, to prick.
Churchill. |
|
5 he nahoo
Naho'o |
1 ngeti uri |
2 ngeti tea |
3
he ngaatu
Taro gaatu apó |
moving on with one glyph for each type of taro - i.e. with a further 17 steps,
|
he taro |
|
1 |
he |
ngeti uri |
a Oti. |
|
1 |
ngeti tea |
|
1 |
ngaatu |
|
1 |
tavari |
|
1 |
riku |
|
1 |
ngaoho |
|
1 |
naunau. |
|
1 |
uku koko |
|
1 |
nehenehe |
|
1 |
poporo. |
|
1 |
kavakava atua |
|
1 |
kohe. |
|
1 |
nehenehe [sic!] |
|
1 |
pua |
|
1 |
harahara |
|
1 |
hua taru. |
|
1 |
makere |
|
1 |
hata. |
|
1 |
tuere heu. |
|
1 |
tureme |
then
the beginning of the 7 sugarcane (toa) variants -
belonging to both Teke and Oti - could have arrived at right ascension day number *70 + *18 = *88, viz.
at Betelgeuze.
|
APRIL 8 |
9 (*19) |
10 (100) |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-18 |
Ga1-19 |
Ga1-20 |
|
KHUFU
MINTAKA (Belt) =
δ
Orionis,
υ
Orionis (82.4),
χ
Aurigae (82.5),
ε
Columbae (82.6)
*41 = *82.4 - *41.4 |
KHAFRE
Al Hak'ah-3 (Brand) /
Mrigashīrsha-5 (Stag's Head) /
Turtle Head-20 (Monkey) /
Mas-tab-ba-tur-tur (Little
Twins)
ARNEB = α Leporis, Crab Nebula = M1
Tauri
(83.0,
φ¹
Orionis (83.1),
HEKA
= λ Orionis, Orion Nebula = M42
(83.2),
φ²
Orionis (83.6),
ALNILAM (String of Pearls) = ε Orionis
(83.7) |
MENKAURE
Three Stars-21 (Gibbon) /
Shur-narkabti-sha-shūtū-6 (Star in the
Bull towards the south)
/
ANA-IVA-9 (Pillar of exit)
HEAVENLY GATE = ζ Tauri,
ν
Columbae (84.0),
ω
Orionis (84.2),
ALNITAK (Girdle) = ζ Orionis,
PHAKT (Phaet) = α Columbae
(84.7) |
|
11 |
June 12 |
13 (*84) |
|
7 |
°June 8 |
9 (*80) |
|
15 (135) |
'May 16 (136) |
17 |
|
"May 1 (121) |
"May 2 |
3 (133) |
|
DAY 82 - 64
= 18 |
19 (= 115 - 84 - 12) |
20 |
|
18 Vai Tara Kai Uo
a ngao roaroa a ngao tokotokoa |
19
Hia Uka
a hakairiiri a hakaturuturu |
20
Hanga Ohiro
a pakipaki renga |
|
13
harahara |
14
hua taru |
15
makere |
|
...
The original Arabic name, Al Hak'ah,
a White Spot, was from the added faint
light of the smaller φ¹and
φ² in the
background, and has descended to us as
Heka and Hika ...
Uka.
Uka
hoa, female friend,
companion.
Ukauka: 1. Firewood. 2.
Leathery, tough. PS Mgv.:
ukauka,
hard to chew. Mq.:
ukakoki,
leathery. Ta.:
uaua,
id. Sa.:
u'a, tough, tenacious,
glutinous. To.:
uka,
sticky. Niuē;
uka, tough. Viti: kaukamea,
metal. Churchill.
... Teke said to
Oti, 'Go and take the hauhau
tree, the paper mulberry tree, rushes,
tavari plants, uku koko
grass, riku ferns, ngaoho
plants, the toromiro tree,
hiki kioe plants (Cyperus vegetus),
the sandalwood tree, harahara
plants, pua nakonako plants,
nehenehe ferns, hua taru
grass, poporo plants, bottle
gourds (ipu ngutu), kohe
plants, kavakava atua ferns,
fragrant tuere heu grass,
tureme grass (Diochelachne
sciurea), matie grass, and
the two kinds of cockroaches makere
and hata.'
... The division into quarters of
a 28-series can be applied to the main
phases of the moon during the visible
period as was as to a (reflex of the old
world?) sidereal month.
The separate subgroup (29
makere - 30 hata) consists of
the names of two types of cockroaches,
but in related eastern Polynesian
languages these names can also be
explained on a different level. MAO.
makere, among others, 'to die', and
whata, among others, 'to be laid
to rest on a platform', deserve special
attention.
The theme hinted at is one of
death and burial. In our scheme they
occur at just that time when the moon
'has died'! This lends further support
to the lunar thesis.
Barthel 2.
 |
|
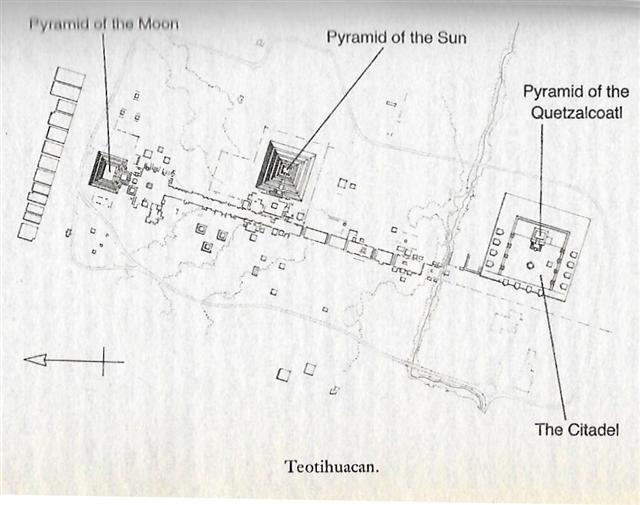
...
the real surprise revealed by Bauval's
astronomical calculations was this:
despite the fact that some aspects of
the Great Pyramid did relate
astronomically to the Pyramid Age, the
Giza monuments as a whole were so
arranged as to provide a picture of the
skies (which alter their appearance down
the ages as a result of the precession
of the equinoxes) not as they had looked
in the Fourth Dynasty around 2500 BC,
but as they had looked - and only
as they had looked - around the year
10,450 BC ...
.jpg) |
|
APRIL 11 |
12 |
13 |
14 (104) |
15 |
16 (*26) |
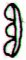 |
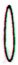 |
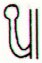 |
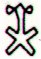 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-21 |
Ga1-22 |
Ga1-23 |
Ga1-24 |
Ga1-25 |
Ga1-26 |
|
ο Aurigae (85.8), γ Leporis (85.9)
YANG MUN (α Lupi)
|
μ
Columbae,
SAIPH
(Sword) =
κ
Orionis
(86.5),
τ
Aurigae,
ζ
Leporis (86.6) |
υ Aurigae (87.1), ν Aurigae (87.2),
WEZN (Weight) = β Columbae,
δ Leporis (87.7),
TZE (Son) = λ Columbae
(87.9) |
Ardra-6 (The Moist One) /
ANA-VARU-8 (Pillar to sit by)
χ¹
Orionis,
ξ
Aurigae (88.1),
BETELGEUZE
=
α
Orionis
(88.3),
ξ
Columbae (88.5),
σ
Columbae (88.7) |
η
Leporis (89.0),
PRAJA-PĀTI (Lord of Created Beings) =
δ
Aurigae,
MENKALINAN (Shoulder of the Rein-holder) = β
Aurigae, MAHASHIM (Wrist) = θ Aurigae,
and
γ
Columbae (89.3),
π
Aurigae (89.4),
η
Columbae (89.7)
*48.0 = *89.4 - *41.4 |
μ Orionis (90.3), χ² Orionis (90.5) |
|
June 14 (165) |
15 |
16 |
17 (168) |
18 |
19 |
|
°June 10 (161) |
11 |
12 |
13 (164) |
14 |
15 (*86) |
|
'May 18 (*58) |
19 |
20 (140) |
21 |
22 |
23 (*63) |
|
"May 4 (*54) |
5 |
6 |
7 (127) |
8 |
9 (*49) |
|
DAY 85 - 64 = 21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
|
21 Ko
Roto Kahi
a touo renga |
22 Ko
Papa Kahi
a roro (ko pa) |
23 Ko
Puna A Tuki
hauhau renga |
24 Ko Ehu
Ko Mahatua
a piki rangi a hakakihikihi mahina |
25 Ko Maunga Teate(t)a
a pua katiki |
26 Ko Te
Hakarava
a hakanohonoho |
|
16
hata |
17
tuere heu |
18
tureme |
|
|
|
|
Hata. 1. Table,
bureau. P Pau.: afata, a chest, box.
Mgv.: avata, a box, case, trunk,
coffin. Mq.: fata, hata, a
piece of wood with several branches serving
as a rack, space, to ramify, to branch;
fataá, hataá, stage, step, shelf.
Ta.: fata, scaffold, altar. 2.
Hakahata, to disjoint; hakahatahata,
to loosen, to stretch. P Pau.: vata,
an interval, interstice. Mgv.: kohata,
the space between two boards, to be badly
joined; akakohata, to leave a space
between two bodies badly joined; hakahata,
to be large, broad, wide, spacious, far off.
Mq.: hatahata, fatafata,
having chinks, not tightly closed,
disjointed. Ta.: fatafata, open. 3.
Hatahata, calm, loose, prolix, vast.
Mgv.: hatahara, broad, wide,
spacious, at one's ease. Ta.: fatafata,
free from care. Mq.: hatahata, empty,
open. 4. Hatahata, tube, pipe,
funnel. Churchill. Sa.: fata, a
raised house in which to store yams, a
shelf, a handbarrow, a bier, a litter, an
altar, to carry on a litter; fatāmanu,
a scaffold. To.: fata,
a loft, a bier, a handbarrow, to carry on a
bier; fataki,
a platform. Fu.: fata,
a barrow, a loft; fatataki,
two sticks or canes attached to each other
at each side of a house post to serve as a
shelf. Niuē: fata,
a cage, a handbarrow, a shelf, a stage,
(sometimes) the upper story of a house.
Uvea: fata,
a barrow, a bier. Fotuna: fata,
a stage. Ta.: fata,
an altar, a scaffold, a piece of wood put up
to hang baskets of food on; afata,
a chest, a box, a coop, a raft, a scaffold.
Pau.: fata,
a heap; afata,
a box, a chest. Ma.: whata,
a platform or raised storehouse for food, an
altar, to elevate, to support. Moriori:
whata,
a raft. Mq.: fata,
hata,
hataá,
shelves. Rapanui: hata,
a table. Ha.: haka,
a ladder, an artificial henroost;
alahaka, a
ladder. Mg.: ata,
a shelf; atamoa,
a ladder; atarau,
an altar. Mgv.: avata,
a coffer, a box. Vi.: vata,
a loft, a shelf; tāvata,
a bier. The Samoan fata
is a pair of light timbers pointed at the
ends and tied across the center posts of the
house, one in front, the other behind the
line of posts; rolls of mats and bales of
sennit may be laid across these timbers;
baskets or reserved victuals may be hung on
the ends. The litter and the barrow are two
light poles with small slats lashed across
at intervals. The Marquesan fata
is a stout stem of a sapling with the stumps
of several branches, a hat tree in shape,
though found among a barehead folk. These
illustrations are sufficient to show what is
the common element in all these
fata
identifications, light cross-pieces spaced
at intervals. With this for a primal
signifaction it is easy to see how a ladder,
a raft, a henroost, an altar come under the
same stem for designation. Perhaps Samoan
fatafata
the breast obtains the name by reason of the
ribs; it would be convincing were it not
that the plumpness of most Samoans leaves
the ribs a matter of anatomical inference.
Churchill 2.
Vao.
Mgv.: vao, uninhabited land. Ta.:
? [obliterated text] ... of the valleys.
Mq.: vao, bottom of a valley. Sa.:
vao, the bush. Ma.: wao, the
forest. Churchill. |

... The
earliest depiction that has been linked to
the constellation of Orion is a prehistoric
(Aurignacian) mammoth ivory carving found in
a cave in the Ach valley in Germany in 1979.
Archaeologists have estimated it to have
been fashioned approximately 32,000 to
38,000 years ago ... The artist cut,
smoothed and carved one side (A)
and finely notched the other side (B)
and the edges. Side A contains the
half-relief of an anthropoidal figure,
either human or a human-feline hybrid, known
as the 'adorant' because its arms are raised
as if in an act of worship.
|
Egyptian jubilation |
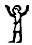 |
Phoenician
he |
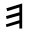 |
Greek
epsilon |
Ε
(ε) |
|
Wikipedia points at the Egyptian
gesture with arms held high as a
Sign of jubilation, which may
have been the origin (via
Phoenician he) of
epsilon.

 |
On side B together with the four
edges is a series of notches that are
clearly set in an intentional pattern. The
edges contain a total of 39 notches in
groups of 6, 13, 7 and 13. A further 49
notches on side B are arranged in
four vertical lines of 13, 10, 12 and 13
respectively plus a further notch that could
be in either of the middle two lines ... The
grouping of the notches on the plate
suggests a time-related sequence. The total
number of notches (88) not only coincides
with the number of days in 3 lunations
(88.5) but also approximately with the
number of days when the star Betelgeuse (α
Ori) disappeared from view each year between
its heliacal set (about 14 days before the
spring equinox around 33,000 BP) and its
heliacal rise (approximately 19 days before
the summer solstice).
Conversely, the nine-month period when Orion
was visible in the sky approximately matched
the duration of human pregnancy, and the
timing of the heliacal rise in early summer
would have facilitated a ‘rule of thumb’
whereby, by timing conception close to the
reappearance of the constellation, it could
be ensured that a birth would take place
after the severe winter half-year, but
leaving enough time for sufficient nutrition
of the baby before the beginning of the next
winter. There is a resemblance between the
anthropoid on side A and the constellation
Orion. None of these factors is convincing
when taken in isolation, because of the high
probability that apparently significant
structural and numerical coincidences might
have arisen fortuitously. However, taken
together they suggest that the anthropoid
represented an asterism equivalent to
today’s constellation of Orion, and that the
ivory plate as a whole related to a system
of time reckoning linked to the moon and to
human pregnancy. If so, then ethnographic
comparisons would suggest that the
Geißenklösterle culture related their
‘anthropoid’ asterism to perceived cycles of
cosmic power and fertility ...
 |
|
APRIL 17 (107) |
18 |
19 |
20 (*30) |
21 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ga1-27 |
Ga1-28 |
Ga1-29 |
Ga1-30 |
Ga2-1 |
|
CLOSE
TO THE
SUN: |
|
6h (91.3)
ν
Orionis (91.4),
θ
Columbae (91.5),
π
Columbae (91.6)
*50.0 = *91.4 - *41.4 |
ξ Orionis (92.5) |
Al Han'ah-4 (Brand) /
Maru-sha-pu-u-mash-mashu-7 (Front of the
Mouth of the Twins)
TEJAT PRIOR
=
η
Gemini
(93.4),
γ
Monocerotis (93.5),
κ
Aurigae (93.6),
κ
Columbae (93.8)
*52.0 = *93.4 - *41.4 |
FURUD = ζ Canis Majoris
(94.9) |
Well-22 (Tapir) /
Arkū-sha-pu-u-mash-mashu-8
(Back of the Mouth of the Twins)
δ
Columbae (95.2),
TEJAT POSTERIOR =
μ
Gemini,
MIRZAM (The Roarer) = β Canis Majoris
(95.4),
CANOPUS
(Canopy) =
α
Carinae
(95.6),
ε
Monocerotis (95.7),
ψ1
Aurigae (95.9)
*54.0 = *95.4 - *41.4 |
|
June 20 |
SOLSTICE |
22 (*93) |
23 (174) |
ST
JOHN'S DAY |
|
°June 16 |
17 (168) |
18 |
19 |
20 (*91) |
|
'May 24 (144) |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 (*68) |
|
"May 10 (130) |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 (*54) |
|
DAY 91 - 64 = 27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
|
27 Ko
Hanga Nui
a te Papa tata ika |
28 Ko
Tonga Riki
a henga eha tunu kioe. hakaputiti ai ka
hakapunenenene.henua mo opoopo o tau
kioe. |
29 Ko
Te Rano A Raraku
|
30
Oparingi
|
31
Oparingi
a uuri |
|
...
The Pythagoreans make Phaeton
fall into Eridanus, burning part of its
water, and glowing still at the time
when the Argonauts passed by. Ovid
stated that since the fall the Nile
hides its sources. Rigveda 9.73.3 says
that the Great Varuna has hidden the
ocean. The Mahabharata tells in its own
style why the 'heavenly Ganga' had to be
brought down. At the end of the Golden
Age (Krita Yuga) a class of
Asura who had fought against the
'gods' hid themselves in the ocean where
the gods could not reach them, and
planned to overthrow the government. So
the gods implored Agastya
(Canopus, alpha Carinae = Eridu) for
help. The great Rishi did as he was
bidden, drank up the water of the ocean,
and thus laid bare the enemies, who were
then slain by the gods. But now, there
was no ocean anymore! Implored by the
gods to fill the sea again, the Holy One
replied: 'That water in sooth hath been
digested by me. Some other expedient,
therefore, must be thought of by you, if
ye desire to make endeavour to fill the
ocean ...
 |
And at the end of the sugarcane variants would
then be the
end of the first glyph line on
the G tablet, at the Marikuru type of
sugarcane, i.e. after 29 Te Rano a Raraku
and at 30 Oparingi.
Marikuru. 1. A white, clayey earth. 2. A tree (Sapindus
saponaria) of which very few specimens are left. Vanaga. Ash-wood T. Churchill.
Rigi.
A very detailed myth comes
from the island of Nauru. In the
beginning there was nothing but the sea, and
above soared the Old-Spider. One day the
Old-Spider found a giant clam, took it up, and
tried to find if this object had any opening,
but could find none. She tapped on it, and as it
sounded hollow, she decided it was empty. By
repeating a charm, she opened the two shells and
slipped inside. She could see nothing, because
the sun and the moon did not then exist; and
then, she could not stand up because there was
not enough room in the shellfish. Constantly
hunting about she at last found a snail. To
endow it with power she placed it under her arm,
lay down and slept for three days. Then she let
it free, and still hunting about she found
another snail bigger than the first one, and
treated it in the same way. Then she said to the
first snail: 'Can you open this room a little,
so that we can sit down?' The snail said it
could, and opened the shell a little. Old-Spider
then took the snail, placed it in the west of
the shell, and made it into the moon. Then there
was a little light, which allowed Old-Spider to
see a big worm. At her request he opened the
shell a little wider, and from the body of the
worm flowed a salted sweat which collected in
the lower half-shell and became the sea. Then he
raised the upper half-shell very high, and it
became the sky. Rigi, the worm, exhausted
by this great effort, then died. Old-Spider then
made the sun from the second snail, and placed
it beside the lower half-shell, which became the
earth. Larousse. Ta.: iki, iini,
to pour, to spill. Sa.: ligi, liligi,
id. Ma.: ringi, riringi, id.
Ta.: ninii,
id. Pau.: riringi,
id. Churchill.

|








.jpg)








