From Rogo at 0h to the end of the days when only cold food was served (as I am suggesting) there were 13 days:
And from Sirrah to Polaris there were twice 13 = 26 days:
Probably the resemblence between the pair Gb7-24--25 and the pair Ga1-3--4 was primarily intended to draw attention to the fact that the Gregorian calendar had shifted the northern spring equinox to be at a place 4 days earlier in the year. ... So the shift in the date of the equinox that occurred between the 4th and the 16th centuries was annulled with the Gregorian calendar, but nothing was done for the first four centuries of the Julian calendar. The days of 29 February of the years AD 100, AD 200, AD 300, and the day created by the irregular application of leap years between the assassination of Caesar and the decree of Augustus re-arranging the calendar in AD 8, remained in effect. This moved the equinox four days earlier than in Caesar's time ... ... These '4 unneccessary leap days' (prior to the Council of Nicaea) were approximately equal in number to the precessional distance in time between the epoch of the Pope and the time of rongorongo. The Gregorian calendar could therefore be easily understood by the Easter Islanders. The Pope had created a 'crooked calendar' but since his time the precession had fixed it ... *68 (Aldebaran) - *27 (Sheratan) = *41. Number 41 signified ( →) Bharani (*41.4), which star evidently had ruled the stations during the first half of the year:... I once upon a time discovered the key role played by Bharani from studying the manazil structure of the Arabs. This was my perception of the 1st half of the year (before Spica and Heze arrived at the beginning of the 2nd half):
After the 'crooked canoe' of Gregory XIII had been corrected by Tae-tagaloa (Not-Tagaroa → Tane); Tae. 1. Negation used in conditional and temporal clauses: ana ta'e hoa te ûa, ina he vai, when it does not rain, there is no water. Also used with some verbal forms such as: o te aha koe i-ta'e-oho mai-ai? why didn't you come? Otherwise its use is limited to adjectives or verbal adjectives: tagata ta'e hupehupe, person who is not weak, hard worker; nohoga ta'e oti, endless existence, eternity. 2. Interjection expressing admiration, always used with he: ta'e he tagata! what a man! Ta'e he aga! what a great job! Ta'e he tagata koe mo keukeu i te henua! what a good farmer you are! Vanaga. 1. Prepositive negative: without, not, none. PS To.: tae, prepositive negative. 2. To remain; tae atu ki, as far as, until. Taehaga (tae 1), to shake the head in sign of negation, reluctant, to disdain, to be displeased. 3. Pau.: tae, to arrive. Mgv.: tae, id. Ta.: tae, id. Ma.: tae, id. 4. Pau.: taetae, elephantiasis in scroto. Ta.: taetae, ill, illness. Churchill. ... Take the lower part of a gourd or hula drum, rounded as a wheel (globe), on which several lines are to be marked and burned in, as described hereafter. These lines are called na alanui o na hoku hookele, the highways of the navigation stars, which stars are also called na hoku ai-aina, the stars which rule the land. Stars lying outside these three lines are called na hoku a ka lewa, foreign, strange, or outside stars. The first line is drawn from Hoku-paa, the fixed or North Star, to the most southerly star of Newe, the Southern Cross. (This hour circle coincides with the meridian on an evening in June, when it would divide the visible sky into halves.) The portion (of the sky) to the right or east of this line (the observer is evidently assumed to be facing north) is called ke ala ula a Kane, the dawning or bright road of Kane, and that to the left or west is called ke alanui maawe ula a Kanaloa, the much-traveled highway of Kanaloa. (Kane and Kanaloa were important gods in the Polynesian pantheon, Kane being associated with light, Kanaloa with darkness.) Then three lines are drawn east and west, one across the northern section indicates the northern limit of the Sun (corresponding with the Tropic of Cancer) about the 15th and 16th days of the month Kaulua (i.e., the 21st or 22nd of June) and is called ke alanui polohiwa a Kane, the black-shining road of Kane. The line across the southern section indicates the southern limit of the Sun about the 15th or 16th days of the month Hilinama (December 22) and is called ke alanui polohiwa a Kanaloa, the black-shining road of Kanaloa. The line exactly around the middle of the sphere is called ke alanui a ke ku'uku'u, the road of the spider, and also ke alanui i ka Piko a Wakea, the way to the navel of Wakea (the Sky-father). Between these lines are the fixed stars of the various lands, na hokupaa a ka aina. (These are the stars which hang suspended in the zeniths of the Polynesian islands most of which lie within the tropics.) On the sides are the stars by which one navigates ... presumably a name for the sun personifying the precession - the measure once again became 41. So the last variant of the stolen purple yams was at Bharani:
The Hindu structure had Bharani 14 days after the First Point of Aries:
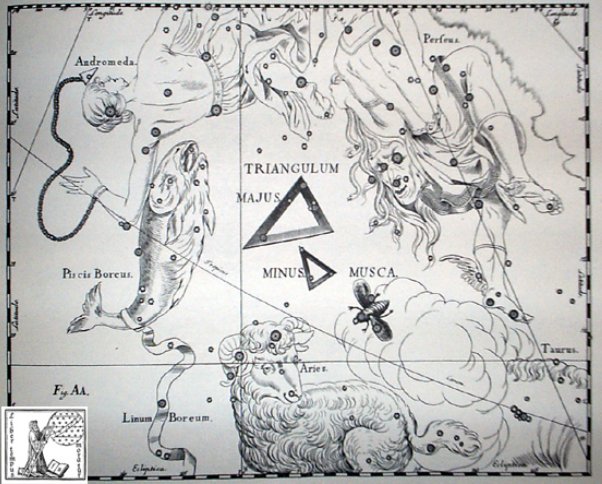
The 3 stars of Musca Borealis came 4 weeks after the 3 days when only cold food could be served:
In the Golden Age of the Bull the star 35 Arietis (at the Head of the Fly) would have risen heliacally in FEBRUARY 24: ... The leap day was introduced as part of the Julian reform. The day following the Terminalia (February 23) was doubled, forming the 'bis sextum - literally 'double sixth', since February 24 was 'the sixth day before the Kalends of March' using Roman inclusive counting (March 1 was the 'first day'). Although exceptions exist, the first day of the bis sextum (February 24) was usually regarded as the intercalated or 'bissextile' day since the third century. February 29 came to be regarded as the leap day when the Roman system of numbering days was replaced by sequential numbering in the late Middle Ages ... This fact suggests the 3 days of the Northern Fly (there was also a Southern Fly) were 'without fire'. And the hipu (gourd) signs in a sense confirm it: ... needfire ceremonies usually take place near the summer solstice (the Feast of St. John) ... but they occur in several other seasons as well. The summer date of the rite and its accompanying festival have to do, among other things, with fertility, as can can clearly be seen in a variant from the valley of the Moselle preserved for us by Jakob Grimm. Each household in the village was constrained to contribute a shock of straw to the nearby high place, Stromberg, where the males went at evening while the females went to a spring lower down on the slope. A huge wheel was wrapped with this straw. An axle run through the wheel served as the handles for those who were to guide it on its downward plunge. The mayor of a nearby town kindled the straw, for which office he was rewarded with a basketful of cherries. All the men kindled torches and some followed the burning orb as it was released downhill to shouts of joy. The women at the spring echoed these shouts as the wheel rushed by them. Often the fire went out of its own accord before it reached the river, but should the waters of the river extinguish it, an abundant vintage was forecast for that year ... Hipu. Calabash, shell, cup, jug, goblet, pot, plate, vase, bowl, any such receptacle; hipu hiva, melon, bottle; hipu takatore, vessel; hipu unuvai, drinking glass. P Mgv.: ipu, calabash, gourd for carrying liquids. Mq.: ipu, all sorts of small vases, shell, bowl, receptacle, coconut shell. Ta.: ipu, calabash, cup, receptacle. Churchill.
Maúga. 1. Last; aga maúga o te Ariki o Hotu Matu'a, King Hotu Matua's last work. 2. Hill, mountain. Mouga, moúga. Last; vânaga moúga o te Ariki O Hotu Matu'a, the last words of King Hotu Matu'a. Vanaga. Mauga kore, impalpable. Mouga. 1. Enough, that's all, at last. 2. Mountain, ridge of hills; mouga iti, hillock; tua mouga, mountain top; hiriga mouga; hillside, declivity, slope. P Pau.: mahuga, mountain. Mgv.: mou, maga, mountain. Mq.: mouna, mouka, peak or crest of a mountain. Ta.: maua, moua, mountain. 3. Extinction, end, interruption, solution; te mouga o te hiriga, end of a voyage; pagaha mouga kore, without consolation. 4. To get. Churchill. Puo. (Also pu'a); pu'o nua, one who covers himself with a nua (blanket), that is to say, a human being. Vanaga. 1. To dress, to clothe, to dress the hair; puoa, clothed; puoa tahaga, always dressed. 2. To daub, to besmear (cf. pua 2); puo ei oone, to daub with dirt, to smear. 3. Ata puo, to hill up a plant. Churchill. Puoko. 1. Head; tagata puoko hiohio, hard-headed, opinionated person. 2. Skull (also: pakahera puoko). Vanaga. Head, skull, crown of a hat; puoko garuru, headache; kiri puoko, scalp. T. Mgv.: upoko, head (men or animals). Mq.: upoko, upoó, head. Ta.: upoó, human head. (Sa.: ulupo'o, skull. To.: uluboko, id. Niuē: ulupoko, id.) Churchill. ... And here is the account of a maiden, the daughter of a lord named Blood Gatherer. And this is when a maiden heard of it, the daughter of a lord. Blood Gatherer is the name of her father, and Blood Moon is the name of the maiden. And when he heard the account of the fruit of the tree, her father retold it. And she was amazed at the account: I'm not acquainted with that tree they talk about. It's fruit is truly sweet! they say, I hear, she said. Next, she went all alone and arrived where the tree stood.
It stood at the Place of Ball Game Sacrifice.
What? Well! What's the fruit of this tree? Shouldn't this tree bear something sweet? They shouldn't die, they shouldn't be wasted. Should I pick one? said the maiden. And then the bone spoke; it was there in the fork of the tree: Why do you want a mere bone, a round thing in the branches of a tree? said the head of One Hunaphu when it spoke to the maiden. You don't want it, she was told. I do want it, said the maiden. Very well. Stretch out your right hand here, so I can see it, said the bone. Yes, said the maiden. She stretched out her right hand, up there in front of the bone. And then the bone spit out its saliva, which landed squarely in the hand of the maiden. And then she looked in her hand, she inspected it right away, but the bone's saliva wasn't in her hand. It is just a sign I have given you, my saliva, my spittle. This, my head, has nothing on it - just bone, nothing of meat. It's just the same with the head of a great lord: it's just the flesh that makes his face look good. And when he dies, people get frightened by his bones. After that, his son is like his saliva, his spittle, in his being, whether it be the son of a lord or the son of a craftsman, an orator. The father does not disappear, but goes on being fulfilled. Neither dimmed nor destroyed is the face of a lord, a warrior, craftsman, an orator. Rather, he will leave his daughters and sons. So it is that I have done likewise through you. Now go up there on the face of the earth; you will not die. Keep the word. So be it, said the head of One and Seven Hunaphu - they were of one mind when they did it ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||