1. Once again, strings were necessary for keeping things together. I will take the opportunity to present a fascinating picture from ancient Egypt: 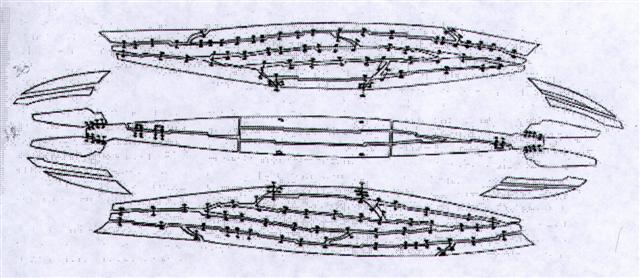 "... It is interesting to note … that the bottom planking and backing timbers of the Cheops ship consists of twelve timbers ... In antiquity the Egyptians were notorious for doing things differently from other peoples. This was certainly true for the techniques they used in shipbuilding. While many cultures built 'sewn' or 'lashed' ships with their planks held together with ligatures, only the Egyptians used transverse lashings that did not penetrate the hull. Furthermore, while the shipwrights of other nations were careful to create straight planking seams, the ancient Egyptian shipwrights intentionally 'joggled' their planking edges into jigsawlike patterns that prevented longitudinal sliding ..." (Shirley Wachsmann, Seagoing Ships & Seamanship in the Bronze Age Levant.) Egyptian ships were built with cedar timbers from Lebanon. But other early vessels were created from other material, e.g. from hides stitched together. 12 planks presumably corresponded to 12 months with 30 days in each, the basic Egyptian measure for the solar year. Then again, the Black Cloth of Polynesia can be interpreted to refer to the dark side of a cycle of light. It should be 'stitched together' with the multicoloured pieces of the front side of the cycle. At the equinoxes there must be strings which hold together the nondescript back side with the variegated patches of the front side. Such is the picture my imagination offers, relying on pieces of myth, e.g.: ... He turned round and round to the right as he fell from the sky back to the water. Still in his cradle, he floated on the sea. Then he bumped against something solid. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said a voice. The Raven saw nothing. He heard the same voice again, and then again, but still he saw nothing but water. Then he peered through the hole in his marten-skin blanket. Beside him was a grebe. 'Your illustrious grandfather asks you in', said the grebe and dived. Level with the waves beside him, the Raven discovered the top of a housepole made of stone. He untied himself from his cradle and climbed down the pole to the lowermost figure. Hala qaattsi ttakkin-gha, a voice said: 'Come inside, my grandson.' Behind the fire, at the rear of the house, was an old man white as a gull. 'I have something to lend you', said the old man. 'I have something to tell you as well. Dii hau dang iiji: I am you.' Slender bluegreen things with wings were moving between the screens at the back of the house. Waa'asing dang iiji, said the old man again: 'That also is you.' The old man gave the Raven two small sticks, like gambling sticks, one black, one multicoloured ... (Cfr Camp 4.) ... The Katawihi distinguish two rainbows: Mawali in the west, and Tini in the east. Tini and Mawali were twin brothers who brought about the flood that inundated the whole world and killed all living people, except two young girls whom they saved to be their companions. It is not advisable to look either of them straight in the eye: to look at Mawali is to become flabby, lazy, and unlucky at hunting and fishing; to look at Tini makes a man so clumsy that he cannot go any distance without stumbling and lacerating his feet against all obstacles in his path, or pick up a sharp instrument without cutting himself ... The Mura also believed that there were two rainbows, an 'upper' and a 'lower' ... Similarly, the Tucuna differentiated between the eastern and the western rainbows and believed them both to be subaquatic demons, the masters of fish and potter's clay respectively ... In South America the rainbow has a double meaning. On the one hand, as elsewhere, it announces the end of rain; on the other hand, it is considered to be responsible for diseases and various natural disasters [dis-aster]. In its first capacity the rainbow effects a disjunction between the sky and the earth which previously were joined through the medium of rain. In the second capacity it replaces the normal beneficient conjunction by an abnormal, maleficient one - the one it brings about itself between sky and earth by taking the place of water ... (Cfr The Tail Feathers.) ... M172. Arawak. 'How birds acquired their colored plumage'. Men and birds joined forces to destroy the huge watersnake, which dragged all living creatures down to his lair. But the attackers took fright and cried off, one after the other, offering as their excuse that they could only fight on dry land. Finally, the duckler (K.G.: a diver) was brave enough to dive into the water; he inflicted a fatal wound on the monster which was at the bottom, coiled round the roots of an enormous tree. Uttering terrible cries, the men succeeded in bringing the snake out of the water, where they killed it and removed its skin. The duckler claimed the skin as the price of its victory. The Indian chiefs said ironically, 'By all means! Just take it away!' 'With pleasure', replied the duckler as it signalled to the other birds. Together they swooped down and, each one taking a piece of the skin in its beak, flew off with it. The Indians were annoyed and angry and, from then on, became the enemies of birds. The birds retired to a quiet spot in order to share the skin. They agreed that each one should keep the part that was in its own beak. The skin was made up of marvelous colors - red, yellow, green, black, and white - and had markings such as no one had ever seen before. As soon as each bird was provided with the part to which it was entitled, the miracle happened: until that time all birds had had dingy plumage, but now suddenly they became white, yellow, and blue ... The parrots were covered in green and red, and the macaws with red, purple, and gilded feathers, such as had never before been seen. The duckler, to which all the credit was due, was left with the head, which was black. But it said it was good enough for an old bird ... (Cfr Camp 6.)
|
