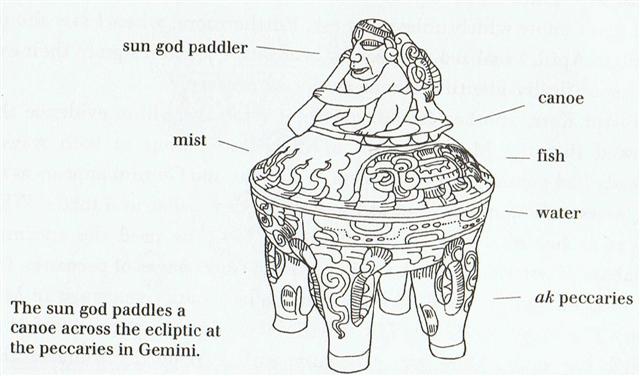
In early spring the waters of the shadow were flowing down from the flat solstice place high up. The mountain had forced the dark clouds upwards into the cold and they could no longer keep their raindrops. The clouds disintegrated, all their sinews came apart, and the sky became a clear blue.  But somewhere beyond the midsummer tree the water serpent had to return to his origin, to the place where new clouds would form. ... It was 4 August 1968, and it was the feast day of Saint Dominic, patron of Santo Domingo Pueblo, southwest of Santa Fe. At one end of the hot, dusty plaza, a Dominican priest watched nervously as several hundred dancers arranged in two long rows pounded the earth with their moccasined feet as a mighty, collective prayer for rain, accompanied by the powerful baritone singing of a chorus and the beat of drums. As my family and I viewed this, the largest and in some ways the most impressive Native American public ceremony, a tiny cloud over the Jémez Mountains to the northwest got larger and larger, eventually filling up the sky; at last the storm broke, and the sky was crisscrossed by lightning and the pueblo resounded with peals of rolling thunder ... The cycle was evidently the same as that of the Sun, who behaved as if nailed to the rim of the wheel of the year, thereby creating an ecliptic serpentine curve.  There had to be a force who carried the serpent up again, 
who could replace him at the apex of the mountain:  It should be the work of someone who had digested the water. I.e., it had to be accomplished by some living creature down on earth - but not necessarily by a human. Vegetation clearly consumed most of the rain water and certainly must somehow also release the humidity. The Babylonians had a pair of sisters named Furrow (in which the vai ora would flow) and Frond (growing upwards):  The G tablet is fluted, but not the Egg (Mamari) tablet. Once upon a time the pair Furrow and Frond were close together like sisters at a place where sweet water was far down and inaccessible:  ... Frond (Coma Berenices & western part of Virgo): The Frond is represented in the heavens by the figure of the goddess Erua holding her sacred branch of the Date-palm. Her constellation rises in the autumn months as the dates are ripening on the fronds. Furrow (Eastern half of Virgo): The Furrow is obviously the origin of our modern Virgo with her familiar ear of barley. The constellation rises in the autumn when the fields have been prepared and are ready to be sown with the coming season's barley seed ...
... There was no water in the village. The lakes and rivers were dry. Raven and Crow, two young girls who were having their first menstrual courses, were told to go and draw water from the ocean. Finding the journey too long, Raven decided just to urinate into her basket-bucket. She decieved no one and was severly scolded. Crow returned much later but with drinking water. As a punishment, Raven was condemned never to find water in the summer; only in winter would she find something to drink. For that reason the Raven never drinks during the hot months; she speaks with a raucous voice because of her dry throat ... The idea (etymon) of a furrow was also used in the name for the 4th Babylonian ecliptic station at Aldebaran:
This furrow in heaven would have been followed by a later furrow down on earth, a furrow waiting for the raindrops needed for the new generation of crops to grow. From Aldebaran to Spica there were 282 (October 9) - 148 (May 28) = 134 days (and 365 - 134 = 231 = 3 * 77).
The left version of Imix above appears to have a single non-sun (cloud) symbol at his tail, whereas the right Imix - rising in rain - appears to have a sun symbol. Gates says the left version is showing Imix rising from the 'great green' (sea water), whereas the right version shows him in torrents of rain with a double Imix crest sign high on his head. "Green color is used in the Dresden as a background in the pictures, in three ways: with red and yellow, solid ... next in running drops denoting rain, most commonly below a 'constellation band', or in the ? 'eclipse glyphs', and finally as a light solid color, with darker wavy green lines, over which the deity rows a boat, etc. The third case obviously denotes the sea, or other 'waters'." (Gates, a.a.)
|