In
rongorongo
times
glyph
396
on
the
Mamari
tablet
could
have
been at
the
Back
of
the
Head
of Ku,
which
would
have corresponded
to
day
30
counted
from
0h.
396
- 30
=
366:
The knot (Al Risha) was at the dorsal side of Ku (given my interpretation of the nature of Cetus):
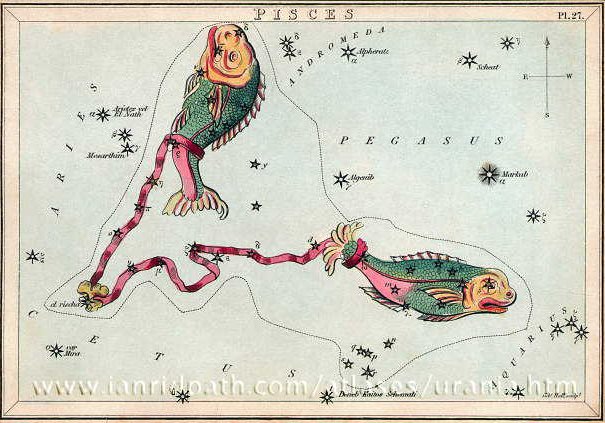

And at the time when Hyadum II was at 0h this would have been in All Heart's Day (FEBRUARY 14).
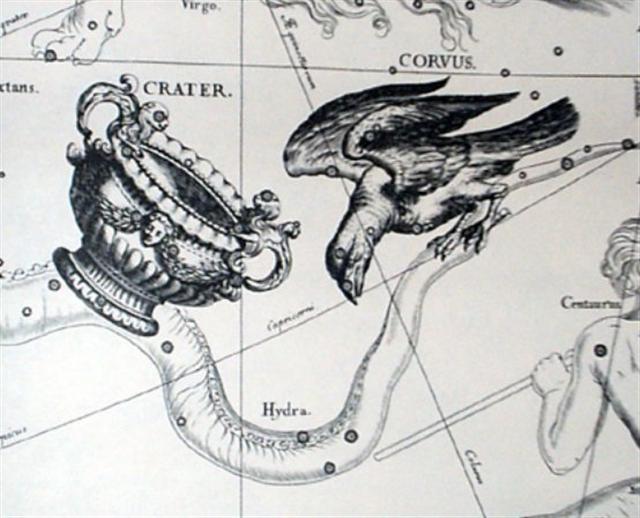
When Alkes (α Crateris) culminated at midnight in FEBRUARY 15 it could have been interpreted as a Sign of how now the long drought was over and how the hard shell of mother earth (te henua) would soften up from the spring rains.
... the bird, being sent with a cup for water, loitered at a fig-tree till the fruit became ripe, and then returned to the god with a water-snake in his claws and a lie in his mouth, alleging the snake to have been the cause of the delay. In punishment he was forever fixed in the sky with the Cup [Crater] and the Snake [Hydra]; and, we may infer, doomed to everlasting thirst by the guardianship of the Hydra over the Cup and its contents. From all this came other poetical names for our Corvus - Avis Ficarius, the Fig Bird; and Emansor, one who stays beyond his time; and a belief, in early folk-lore, that this alone among birds did not carry water to its young ...
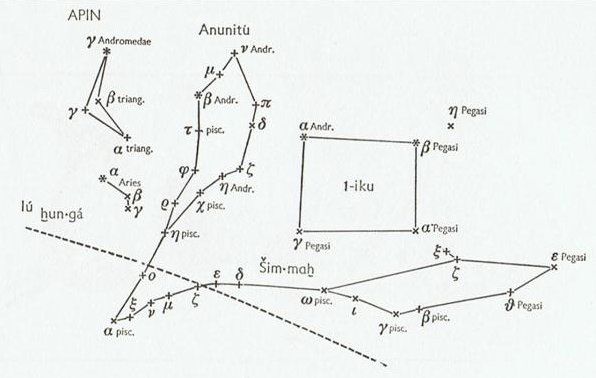
Although this process of returning to life may once upon a time have begun alreday at heliacal Anunitum (τ Piscium) in FEBRUARY 1 (day 396 + 1):
| JAN 31 (396) |
FEBRUARY 1 |
2 (33) |
3 |
4 |
5 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| *Ca14-18 |
*Ca14-19 |
*Ca14-20 |
*Ca14-21 (384) |
*Ca14-22 |
*Ca14-23 |
| te honu paka |
te henua |
honu kau |
te mata |
te honu |
kua heheu |
| 1h (15.2) |
Al Batn Al Hūt-26 / Revati-28 / 1-iku |
ν Phoenicis (17.4), κ Tucanae (17.6) |
no star listed (18) |
Adhil (19.3), θ Ceti (19.7) |
Ksora (20.1), ω Andromedae (20.6), γ Phoenicis (20.8) |
| β Phoenicis (15.1), υ Phoenicis, ι Tucanae (15.6), ζ Phoenicis, η Ceti (15.7) |
MIRACH, Keun Nan Mun (16.0), ANUNITUM (16.5), REVATI (16.9)
Regulus
|
| April 5 |
6 (96) |
7 |
464 = 366 + 98 |
9 |
10 (100) |
At the time of Hyadum II day 396 was the last day of JANUARY. In rongorongo times, 64 precessional days later, glyph 396 counted from 0h was at heliacal Hamal (α Arietis). 396 - 30 = 366. In order to get the rongorongo numbers right we have to count with a year measuring not 365 but 366 days.
Metoro said there was a 'turtle' (honu) with a dry shell (paka) in JANUARY 31.
| Paka 1. Dry; to become dry (of things); pakapaka, to dry out. Te paka is also the name of the moss-covered areas, between the small lakes of volcano Rano Kau, through which one can pass without getting one's feet wet. 2. To go, to depart; he-paka-mai, to come; he-oho, he-paka, they go away. 3. To become calm (of the sea): ku-paka-á te tai. Pakahera, skull, shell, cranium; pakahera puoko tagata, human skull; pakahera pikea, shell of crab or crayfish. Gutu pakapaka, scabbed lips. Hau paka, fibres of the hauhau tree, which were first soaked in water, then dried to produce a strong thread. Moa gao verapaka, chicken with bald neck. Ariki Paka, certain collateral descendents of Hotu Matu'a, who exercised religious functions. Vanaga.
1. Crust, scab, scurf; paka rerere, cancer; pakapaka, crust, scabby. 2. Calm, still. 3. Intensive; vera paka, scorching hot; marego paka, bald; nunu paka, thin. 4. To arrive, to come. 5. To be eager. 6. To absorb. 7. Shin T. Pakahera, calabash, shell, jug. Pakahia, to clot, curdle, coagulate. Pakapaka, dry, arid, scorching hot, cooked too much, a desert, to fade away, to roast, a cake, active; toto pakapaka, coagulated blood; hakapakapaka, to dry, to broil, to toast. Pakahera pikea, shell of crab or crayfish. Churchill. |
| Kau 1. To move one's feet (walking or swimming); ana oho koe, ana kau i te va'e, ka rava a me'e mo kai, if you go and move your feet, you'll get something to eat; kakau (or also kaukau), move yourself swimming. 2. To spread (of plants): ku-kau-áte kumara, the sweet potatoes have spread, have grown a lot. 3. To swarm, to mill around (of people): ku-kau-á te gagata i mu'a i tou hare, there's a crowd of people milling about in front of your house. 4. To flood (of water after the rain): ku-kau-á te vai haho, the water has flooded out (of a container such as a taheta). 5. To increase, to multiply: ku-kau-á te moa, the chickens have multiplied. 6. Wide, large: Rano Kau, 'Wide Crater' (name of the volcano in the southwest corner of the island). 7. Expression of admiration: kau-ké-ké! how big! hare kau-kéké! what a big house! tagata hakari kau-kéké! what a stout man! Vanaga.
To bathe, to swim; hakakau, to make to swim. P Pau., Mgv., Mq.: kau, to swim. Ta.: áu, id. Kauhaga, swimming. Churchill.
The stem kau does not appear independently in any language of Polynesian proper. For tree and for timber we have the composite lakau in various stages of transformation. But kau will also be found as an initial component of various tree names. It is in Viti that we first find it in free existence. In Melanesia this form is rare. It occurs as kau in Efaté, Sesake, Epi, Nguna, and perhaps may be preserved in Aneityum; as gau in Marina; as au in Motu and somewhere in the Solomon islands. The triplicity of the Efaté forms [kasu, kas, kau] suggests a possible transition. Kasu and kas are easy to be correlated, kasu and kau less easy. They might be linked by the assumption of a parent form kahu, from which each might derive. This would appear in modern Samoan as kau; but I have found it the rule that even the mildest aspirate in Proto-Samoan becoming extinct in modern Samoan is yet retained as aspiration in Nuclear Polynesia and as th in Viti, none of which mutations is found on this record. Churchill 2 |

|










