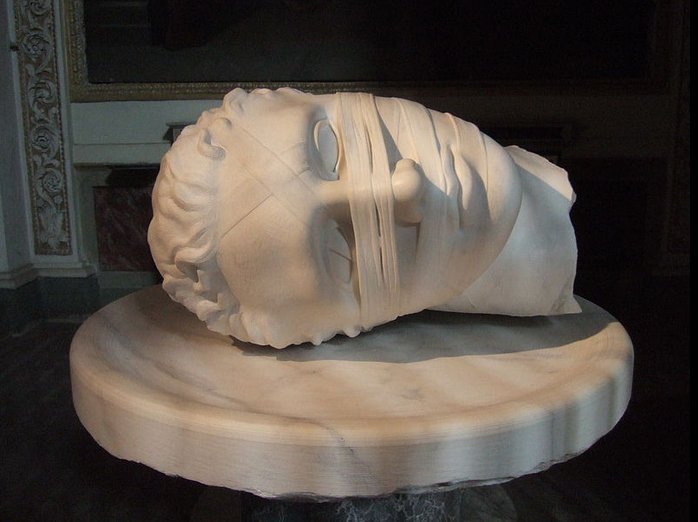
... Ure Honu was amazed and said, 'How beautiful you are! In the head of the new bananas is a skull, painted with yellow root and with a strip of barkcloth around it.'
The first star in Corona Borealis is κ (designed like a reversed Phoenician kaph).
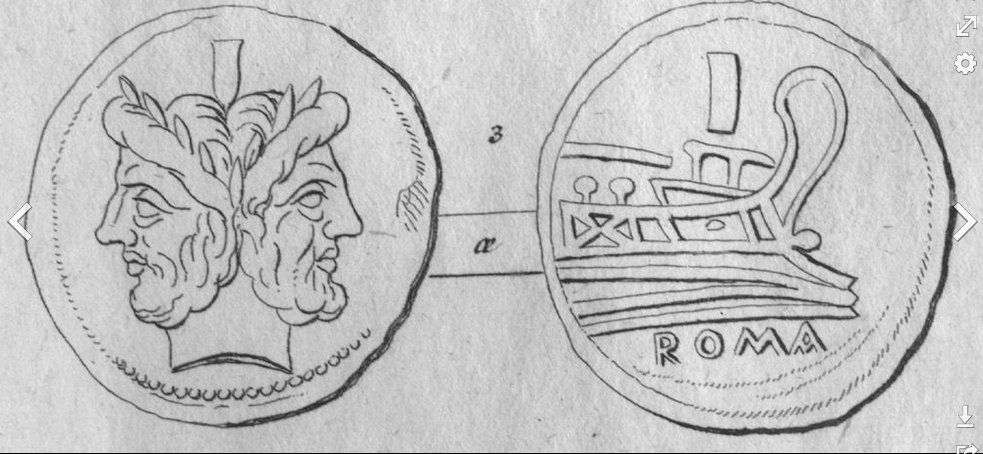
The 'head' of St John obviously should be contrasted with the Corona Borealis 'crown'. The headgear is the opposite of the head itself. With St John born in June 24 his 'tail' = 'headgear' should be at the opposite side of the year, cfr 'heads and tails': ... The evening of 23 June, St. John's Eve, is the eve of celebration before the Feast Day of Saint John the Baptist. The Gospel of Luke (Luke 1:36, 56-57) states that John was born about six months before Jesus; therefore, the feast of John the Baptist was fixed on 24 June, six months before Christmas Eve. "Coin flipping as a game was known to the Romans as navia aut caput ('ship or head'), as some coins had a ship on one side and the head of the emperor on the other." (Wikipedia)
Lewis Carroll has this to say in the matter: 'Who are you talking to?' said the King, coming up to Alice, and looking at the Cat's head with great curiosity. 'It's a friend of mine - a Cheshire-Cat,' said Alice: 'allow me to introduce it.' 'I don't like the look of it at all,' said the King: 'however, it may kiss my hand, if it likes.' 'I'd rather not,' the Cat remarked. 'Don't be impertinent,' said the King, 'and don't look at me like that!' He got behind Alice as he spoke. 'A cat may look at a king,' said Alice. 'I've read that in some book, but I don't remember where.' 'Well, it must be removed,' said the King very decidedly: and he called to the Queen, who was passing at the moment, 'My dear! I wish you would have this cat removed!' The Queen had only one way of settling all difficulties, great or small. 'Off with his head!' she said without even looking around ...
In Manuscript E we also find the myth of the separated head: ... At the time of the loading of the emigrant canoe, Hotu Matua ordered his assistant Teke to take a (stone) figure (moai) named 'Oto Uta' on board the canoe, along with the people (aniva) who were emigrating. However, the figure was left behind 'out in the bay' (E:73). After the arrival in the new land, after disembarkation in the bay of Anakena, and after the return of the explorers to the homeland, our source continues with the following account [E:87-90]. On the thirtieth day of the month of October ('Tangaroa Uri'), Hotu asked about the stone figure (moai maea) named Oto Uta. Hotu said to Teke, 'Where is the figure Ota Uta (corrected in the manuscript for Hina Riru)? Teke thought about the question and then said to Hotu, 'It was left out in the bay.' Hotu said to Pure O, to Pure Ki, and to Pure Vanangananga: 'You fellows (kope), sail to the friend (hoou), to Oto Uta. Bring him here, he who is resting out in the bay. Move him carefully (? nee), you fellows, so that the king, that Oto Uta is not damaged!' Pure O, Pure Ki, and Pure Vanangananga took the canoe, put it into the water, and sailed to Hiva. The canoe of Pure O left on the fifth day of the month of November ('Ruti'). After the canoe of Pure O had sailed and had anchored out in the bay, in Hanga Moria One, Pure saw the figure, which had been lying there all this time, and said to his younger brothers (ngaio taina), 'Let's go my friends (hoa), let us break the neck of this mean one (or, ugly one, rakerake). Why should we return to that fragment of earth (te pito o te kainga, i.e., Easter Island)? Let us stay in our (home)land!' After the canoe of Pure O had departed, King Hotu contacted his guardian spirits (atua akuaku), namely, first, Kuihi and, second, Kuaha ... ... Pure O picked up a large round stone (pureva) and hit the top of the figure. Because of the stone, the neck of Oto Uta was broken.Then the wind started blowing, the billow rose, the waves broke, the rain started falling, the flame (i.e., lightning) shone brightly, and the thunder rolled. As soon as the wind started blowing, the waves broke, the rain fell, and thunder rolled, King Hotu knew that Pure O had done harm to Oto Uta. Hotu spoke: 'These fellows have done a mean thing to King Oto Uta!' After the neck of Oto Uta had been broken, Kuihi and Kuaha arrived. They picked up the neck of King Oto Uta, took it, and brought it with them. They arrived out in the bay, in Hanga Rau. (There) Kuihi and Kuaha left (the fragment). After the neck of Oto Uta had been brought on land, out in the bay of Hanga Rau, the wind, the rain, the waves, and the thunder subsided. Kuihi and Kuaha arrived and told the king the following: 'King Oto Uta is out in the bay of Hanga Rau'. Hotu said to his servant (tuura) Moa Kehu, 'Go down to king Oto Uta and take him up out of the bay of Hanga Rau!' Moa Kehu arose, went down, picked up (the fragment), and carried (it) on his shoulders to the house. There he left it for King Hotu. King Hotu sat down and wept over King Oto Uta. This is Hotu's lament (tanginga): ka hati toou ngao e oto uta e te ariki e / mo tau papa rangaranga o haho i te tai / mo tuu huehue rangaranga o haho i te tai / mo tau hahave rere ai ka pae / mo tae ngu rere ai ka pae / mo te ika aringa riva nei he aku renga ai ka pae Broken is your neck, oh Oto Uta, oh king! / Floating (?) like a raft (?) out at sea. / To be erected for the drifting huehue (fish) out at sea. / Able (?) to put an end to the flight of the flying fish hahave; / Able (?) to put and end to the flight of the flying fish ngu; / Put an end to this fish, a dorado, with the good face! (E:87-90). (The Eighth Island) The first ariki motogi was Ko Oto Uta, a name which could refer to the opposite side of the year compared to that of Noah (the season when the Flood arrived), viz. the season when Land once again rose up from the waves.
It is hard to avoid connecting the beheaded St John with the beheaded Ko Oto Uta. And then we should remember Rahu ... In Hindu tradition, Rahu is a cut-off head of an asura, that swallows the sun or the moon causing eclipses. He is depicted in art as a serpent with no body riding a chariot drawn by eight black horses ... According to legend, during the Samudra manthan, the asura Rahu drank some of the divine nectar. Sun and moon realized it and they alerted Mohini (the female avatar of Vishnu). Before the nectar could pass his throat, Mohini cut off his head. The head, however, remained immortal. It is believed that this immortal head occasionally swallows the sun or the moon, causing eclipses. Then, the sun or moon passes through the opening at the neck, ending the eclipse ... Rahu is a legendary master of deception who signifies cheaters, pleasure seekers, operators in foreign lands, drug dealers, poison dealers, insincere & immoral acts, etc. It is the significator of an irreligious person, an outcast, harsh speech, logical fallacy, falsehoods, uncleanliness, abdominal ulcers, bones, and transmigration ... Rahu was a mean one and this was also the opinion of Pure O regarding the stone statue (moai) of the first ariki motogi 'out in the bay' in Hiva, the 'old homeland'. The glyph at heliacal Canopus could indicate this was the proper place for Ko Oto Uta, where he 'swallowed up the sea':
Furthermore, if we read Oto as O-to, then we can guess the creators of Manuscript E may have alluded to to-ga. as the place from where the journey went higher up (uta).
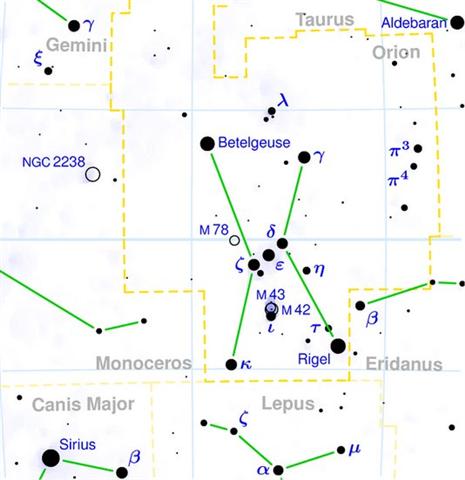
Manuscript E underlines the unhappy position of the stone image of Ko Oto Uta as remaining out in the bay. That is, it would be hard to see it. We remember Heka where the head of Orion ought to be, but where only the 'white spot' (Al Hak'ah) was visible. ... Al Maisān, the title of γ Geminorum, by some error of Firuzabadi was applied to this star [λ Orionis] as Meissa, and is now common for it. Al Sufi called it Al Tahāyī; but Al Ferghani and Al Tizini knew it as Rās al Jauzah, the Head of the Jauzah, which it marks. The original Arabic name, Al Hak'ah, a White Spot, was from the added faint light of the smaller φ╣and φ▓ in the background, and has descended to us as Heka and Hika. These three stars were another of the Athāfiyy [tripods used for cooking] of the Arabs; and everywhere in early astrology were thought, like all similar groups, to be of unfortunate influence in human affairs. They constituted the Euphratean lunar station Mas-tab-ba-tur-tur, the Little Twins, a title also found for γ and η Geminorum; and individually were important stars among the Babylonians, rising to them with the sun at the summer solstice, and, with α and γ, were known as Kakkab Sar, the Constellation of the King ... ... λ and the two stars phi furnish an easy refutation of the popular error as to the apparent magnitude of the moon's disc, Colas writing of this in the Celestial Handbook of 1892: In looking at this triangle nobody would think that the moon could be inserted in it; but as the distance from λ to φ╣ is 27', and the distance from φ╣ to φ▓ is 33', it is a positive fact; the moon's mean apparent diameter being 31' 7''. This illusion, prevalent in all ages, has attracted the attention of many great men; Ptolemy, Roger Bacon, Kepler, and others having treated of it. The lunar disc, seen by the naked eye of an uninstructed observer, appears, as it is frequently expressed 'about the size of a dinner-plate', but should be seen as only equal to a peppercorn ... From the rare total eclipse events it can be concluded that the face of the Sun is approximately of the same size as that of the Full Moon. The White Spot can therefore cover also the eye of the Sun ...
 The relevant page numbers of the Manuscript are E:73 and then E:87-90. These numbers could allude to ║June 2 (*73) respectively to ║June 16-19 (*87-*90):
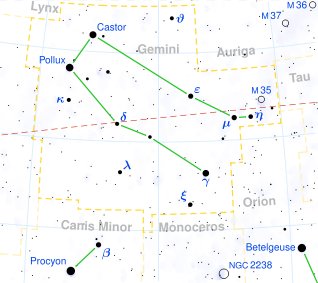
The 'stone' (star) head of Orion was not where it once had been and this must be explained. The missing head could have been removed in order to be at Gemini, where the new land rose up. The leading star of this region (Al Han'ah) was Alhena (the right foot of Pollux), rising 10 days after the left foot of Castor:
... Tejat prior is from Al Tahāyi, an anatomical term of Arabia, by which it was known in early days; a name also applied to stars in the head of Orion.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||