Once again: "Nevertheless, by virtue of a series of spectacular coincidences, Cook made a near-perfect ritual exit on the night of 3 February. The timing itself was nearly perfect, since the Makahiki rituals would end 1 February (± 1 day), being the 14th day of the second Hawaiian month [Kau-lua].
This helps explain Mr. King's entry for 2 February in the published Voyage: 'Terreoboo [Kalaniopu'u] and his Chiefs, had, for some days past, been very inquisitive abouth the time of our departure' - to which his private journal adds, '& seem'd well pleas'd that it was soon'. Captain Cook, responding to Hawaiian importunities to leave behind his 'son', Mr. King, had even assured Kalaniopu'u and the high priest that he would come back again the following year. Long after they had killed him, the Hawaiians continued to believe this would happen. With the high priest's permission, the British just before leaving removed the fence and certain images of Hikiau temple for firewood. Debate raged in the nineteenth century about the role of this purported 'sacriledge' in Cook's death, without notice, however, that following Lono's sojourn the temple is normally cleared and rebuilt - indeed, the night the British left one of the temple houses was set on fire. Among the other ritual coincidences, perhaps the most remarkable was the death of poor old Willie Watman, seaman A. B., on the morning of 1 February. Watman was the first person among Cook's people to die at Kealakekua: on the ceremonial day, so far as can be calculated, that the King's living god Kahoali'i would swallow the eye of the first human sacrifice of the New Year. And it was the Hawaiian chief - or by one account, the King himself - who specifically requested that old Watman be buried at Hikiau temple. Messrs. Cook and King read the burial service, thus introducing Christianity to the Sandwich Islands, with the assistance however of the high priest Ka'oo'oo and the Lono 'brethren', who when the English had finished proceeded to make sacrifices and perform ceremonies at the grave for three days and nights. So in the early hours of 4 February, Cook sailed out of Kealakekua Bay, still alive and well. The King, too, had survived Lono's visit and incorporated its tangible benefits, such as iron adzes and daggers. In principle, the King would now make sacrifices to Kuu and reopen the agricultural shrines of Lono. The normal cosmic course would be resumed. Hence the ultimate ritual coincidence, which was meteorological: one of the fertilizing storms of winter, associated with the advent of Lono, wreaked havoc with the foremast of the Resolution, and the British were forced to return to Kealakekua for repairs on 11 February 1779 ... Mr. King remarks that there were not as many hundreds of people at their return to Kealakekua as there had been thousands when they first came in. A tabu was in effect, which was ascribed to the king's absence. By the best evidence, the British had interrupted the annual bonito-fishing rite, the transition from the Makahiki season to normal temple ceremonies. Cook was now hors cadre. And things fell apart ... Early on Sunday morning, 14 February [2-14] 1779, Captain Cook went ashore with a party of marines to take the Hawaiian king, Kalaniopu'u, hostage against the return of the Discovery's cutter, stolen the night before in a bold maneuver - of which, however, the amiable old ruler was innocent. At the decisive moment, Cook and Kalaniopu'u, the God and the King, will confront each other as cosmic adversaries. Permit me thus an anthropological reading of the historical texts. For in all the confused Tolstoian narratives of the affray - among which the judicious Beaglehole refuses to choose - the one recurrent certainty is a dramatic structure with the properties of a ritual transformation. During the passage inland to find the king, thence seaward with his royal hostage, Cook is metamorphosed from a being of veneration to an object of hostility. When he came ashore, the common people as usual dispersed before him and prostrated face to earth; but in the end he was himself precipitated face down in the water by a chief's weapon, an iron trade dagger, to be rushed upon by a mob exulting over him, and seeming to add to their own honors by the part they could claim in his death: 'snatching the daggers from each other', reads Mr. Burney's account, 'out of eagerness to have their share in killing him'. In the final ritual inversion, Cook's body would be offered in sacrifice by the Hawaiian King." (Sahlins)
The 'coincidences' are piling up like firewood. °February 14 (45) - i.e., 13 days after day 14 in the 2nd Hawaiian month - corresponded to All Hearts' Day:
"Albatross ... Usually taken to be alteration, by assoc. with L. albus, white, of †alcatras pelican, gannet, sea-mew, frigate bird ... Sp., Pg. alcatraz, var. of an irrigating water-wheel, corr. to Sp. alcaduz, arcaduz - Arab. alqādūs 'the pitcher', i.e. al-qādūs ... Gr. kádos jar, itself of Sem. origin (cf. Heb. kad bucket). The orig. ref. is held to have been to the pelican's large pouch, in which it was supposed to carry water ..." (The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology.)
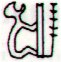
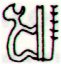
Up to now I have been unable to make sense of the extraordinary Gb2-16, but it could be a water-wheel (alcatraz) or some similar contraption, turning around without ever stopping:
This would fit 'well' with the previous figure, who probably is not eating but drinking (by throwing water into his mouth).
... On February 9 the Chorti Ah K'in, 'diviners', begin the agricultural year. Both the 260-day cycle and the solar year are used in setting dates for religious and agricultural ceremonies, especially when those rituals fall at the same time in both calendars. The ceremony begins when the diviners go to a sacred spring where they choose five stones with the proper shape and color. These stones will mark the five positions of the sacred cosmogram created by the ritual. When the stones are brought back to the ceremonial house, two diviners start the ritual by placing the stones on a table in a careful pattern that reproduces the schematic of the universe. At the same time, helpers under the table replace last year's diagram with the new one. They believe that by placing the cosmic diagram under the base of God at the center of the world they demonstrate that God dominates the universe. The priests place the stones in a very particular order. First the stone that corresponds to the sun in the eastern, sunrise position of summer solstice is set down; then the stone corresponding to the western, sunset position of the same solstice. This is followed by stones representing the western, sunset position of the winter solstice, then its eastern, sunrise position. Together these four stones form a square. They sit at the four corners of the square just as we saw in the Creation story from the Classic period and in the Popol Vuh. Finally, the center stone is placed to form the ancient five-point sign modern researchers called the quincunx ...
Looking in the C text we will find sweet water (vai) at the corresponding place:
Evidently the central stone in the quincunx could have corresponded to the central mata in the vai type of glyph. At the top (roof) of a mountain clouds would be forced to release their sweet drops of rain, which then would flow down to the plain.
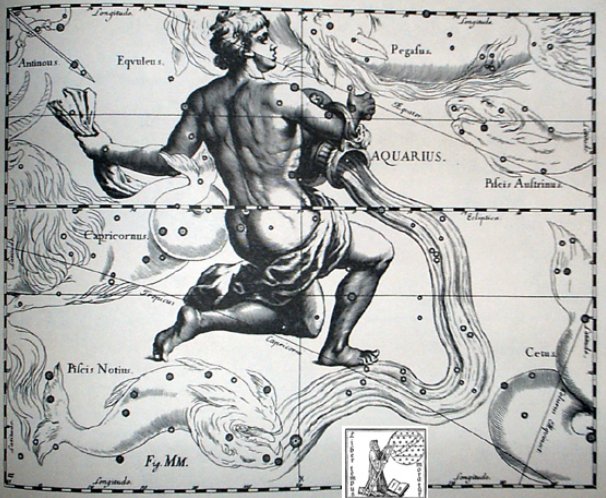
February 18 (414) - 64 = 350 (DECEMBER 16) = 80 + 270. At the opposite side of the sky and close to the Full Moon was the little king (urinating into a bucket, kad):
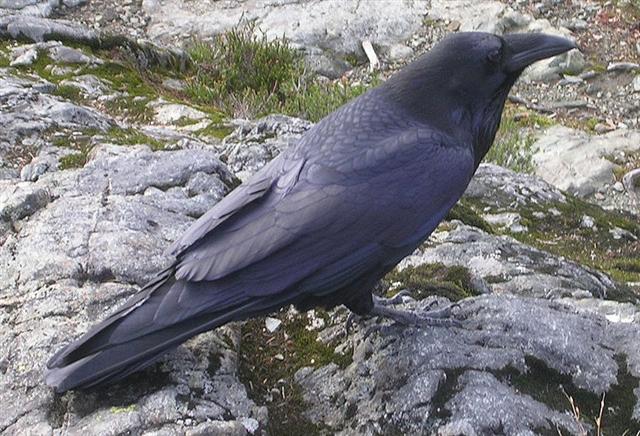
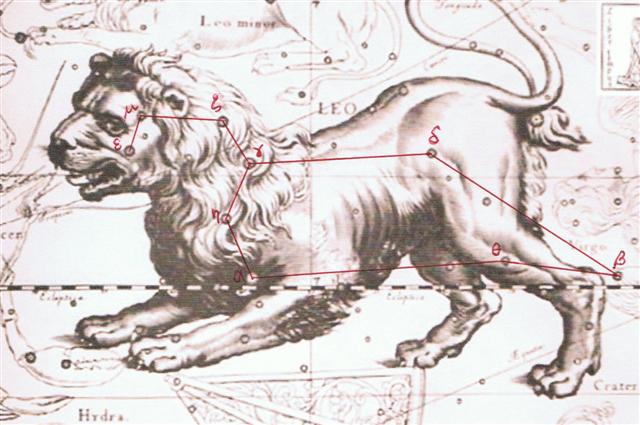
... There was no water in the village. The lakes and rivers were dry. Raven and Crow, two young girls who were having their first menstrual courses, were told to go and draw water from the ocean. Finding the journey too long, Raven decided just to urinate into her basket-bucket. She decieved no one and was severly scolded. Crow returned much later but with drinking water. As a punishment, Raven was condemned never to find water in the summer; only in winter would she find something to drink. For that reason the Raven never drinks during the hot months; she speaks with a raucous voice because of her dry throat ... ... the bird [Raven], being sent with a cup for water, loitered at a fig-tree till the fruit became ripe, and then returned to the god with a water-snake in his claws and a lie in his mouth, alleging the snake to have been the cause of the delay. In punishment he was forever fixed in the sky with the Cup and the Snake; and, we may infer, doomed to everlasting thirst by the guardianship of the Hydra over the Cup and its contents. From all this came other poetical names for our Corvus - Avis Ficarius, the Fig Bird; and Emansor, one who stays beyond his time; and a belief, in early folk-lore, that this alone among birds did not carry water to its young ...
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||