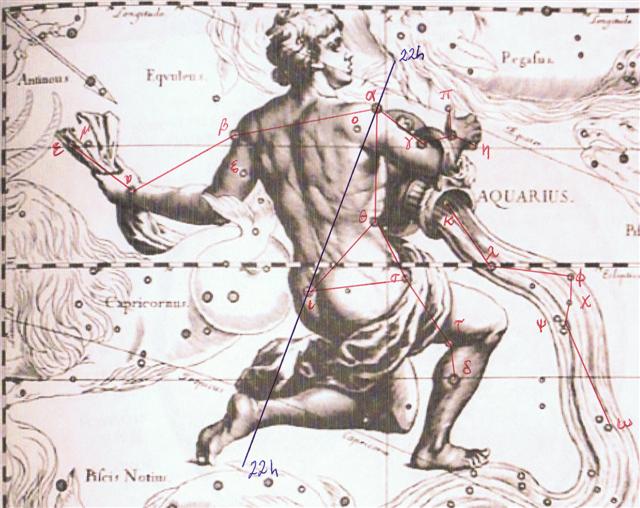
Since the time of the Bull the precession had carried Aquarius forward in the year with 64 days:
The thumb up star of Aquarius (π) had been carried from the solstice to February 23, the date which the Romans had defined as Terminalia, the day before the leap day: ... The leap day was introduced as part of the Julian reform. The day following the Terminalia (February 23) was doubled, forming the 'bis sextum - literally 'double sixth', since February 24 was 'the sixth day before the Kalends of March' using Roman inclusive counting (March 1 was the 'first day'). Although exceptions exist, the first day of the bis sextum (February 24) was usually regarded as the intercalated or 'bissextile' day since the third century. February 29 came to be regarded as the leap day when the Roman system of numbering days was replaced by sequential numbering in the late Middle Ages ... Evidently the Sun dates at the midnight culmination of Castor had always been arranged in good cosmic order in spite of precessional time running quickly ahead:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||